https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18661257/article/details/47622677
所谓的离散化,大家可以简单的理解为,将一组很大的数据,浓缩为一组很小的数据,用这组数据来代替原数据的作用,
比如给你1000个数,数的范围为(1,1e18)我们这里就可以用离散化,由于只有1000个数,我们可以用一个数组的下标代表提供的每一数,如果需要这个数据了,由于是下标,可以直接通过下标获得,如此就是离散化。
https://blog.csdn.net/xiangaccepted/article/details/73276826
离散化是什么:一些数字,他们的范围很大(0-1e9),但是个数不算多(1-1e5),并且这些数本身的数字大小不重要,重要的是这些数字之间的相对大小(比如说某个数字是这些数字中的第几小,而与这个数字本身大小没有关系,要的是相对大小)(6 8 9 4 离散化后即为 2 3 4 1)(要理解相对大小的意思)(6在这4个数字中排第二小,那么就把6离散化成2,与数字6本身没有关系, 8,9,4亦是如此)
离散化思想:因为数字太大,导致没有办法开那么大的数组,又因为数字个数并不多,这时候就可以对它们进行离散化,离散化是改变了数字的相对大小,例如,有500000个数字,他们的范围是0-1e9的,这样就满足离散化的条件。
就比如说,你可以开一个5e5的数组,但是你不能开一个1e9的数组。只改变这些数字的相对大小
第一种离散化
(包含重复元素,并且相同元素离散化后也要相同,推荐使用)
https://leetcode.com/problems/the-skyline-problem/discuss/61230/java-segment-tree-solution-47-ms
https://leetcode.com/articles/rectangle-area-ii/
https://leetcode.com/articles/falling-squares/
http://www.matrix67.com/blog/archives/108
对于“什么是离散化”,搜索帖子你会发现有各种说法,比如“排序后处理”、“对坐标的近似处理”等等。哪个是对的呢?哪个都对。关键在于,这需要一些例子和不少的讲解才能完全解释清楚。
离散化是程序设计中一个非常常用的技巧,它可以有效的降低时间复杂度。其基本思想就是在众多可能的情况中“只考虑我需要用的值”。下面我将用三个例子说明,如何运用离散化改进一个低效的,甚至根本不可能实现的算法。
《算法艺术与信息学竞赛》中的计算几何部分,黄亮举了一个经典的例子,我认为很适合用来介绍离散化思想。这个问题是UVA10173(http://acm.uva.es/p/v101/10173.html),题目意思很简单,给定平面上n个点的坐标,求能够覆盖所有这些点的最小矩形面积。这个问题难就难在,这个矩形可以倾斜放置(边不必平行于坐标轴)。

这里的倾斜放置很不好处理,因为我们不知道这个矩形最终会倾斜多少度。假设我们知道这个矩形的倾角是α,那么答案就很简单了:矩形面积最小时四条边一定都挨着某个点。也就是说,四条边的斜率已经都知道了的话,只需要让这些边从外面不断逼近这个点集直到碰到了某个点。你不必知道这个具体应该怎么实现,只需要理解这可以通过某种方法计算出来,毕竟我们的重点在下面的过程。
我们的算法很显然了:枚举矩形的倾角,对于每一个倾角,我们都能计算出最小的矩形面积,最后取一个最小值。
这个算法是否是正确的呢?我们不能说它是否正确,因为它根本不可能实现。矩形的倾角是一个实数,它有无数种可能,你永远不可能枚举每一种情况。我们说,矩形的倾角是一个“连续的”变量,它是我们无法枚举这个倾角的根本原因。我们需要一种方法,把这个“连续的”变量变成一个一个的值,变成一个“离散的”变量。这个过程也就是所谓的离散化。
所谓的离散化,大家可以简单的理解为,将一组很大的数据,浓缩为一组很小的数据,用这组数据来代替原数据的作用,
比如给你1000个数,数的范围为(1,1e18)我们这里就可以用离散化,由于只有1000个数,我们可以用一个数组的下标代表提供的每一数,如果需要这个数据了,由于是下标,可以直接通过下标获得,如此就是离散化。
https://blog.csdn.net/xiangaccepted/article/details/73276826
离散化是什么:一些数字,他们的范围很大(0-1e9),但是个数不算多(1-1e5),并且这些数本身的数字大小不重要,重要的是这些数字之间的相对大小(比如说某个数字是这些数字中的第几小,而与这个数字本身大小没有关系,要的是相对大小)(6 8 9 4 离散化后即为 2 3 4 1)(要理解相对大小的意思)(6在这4个数字中排第二小,那么就把6离散化成2,与数字6本身没有关系, 8,9,4亦是如此)
离散化思想:因为数字太大,导致没有办法开那么大的数组,又因为数字个数并不多,这时候就可以对它们进行离散化,离散化是改变了数字的相对大小,例如,有500000个数字,他们的范围是0-1e9的,这样就满足离散化的条件。
就比如说,你可以开一个5e5的数组,但是你不能开一个1e9的数组。只改变这些数字的相对大小
第一种离散化
(包含重复元素,并且相同元素离散化后也要相同,推荐使用)
const int maxn=1e5+10;
int a[maxn], t[maxn], b[maxn];
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
scanf("%d",a[i]),t[i]=a[i];
sort(t+1,t+n+1);
m=unique(t+1,t+1+n)-t-1;//求出的m为不重复的元素的个数
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
b[i]=lower_bound(t+1,t+1+m,a[i])-t;
https://leetcode.com/problems/the-skyline-problem/discuss/61230/java-segment-tree-solution-47-ms
https://leetcode.com/articles/rectangle-area-ii/

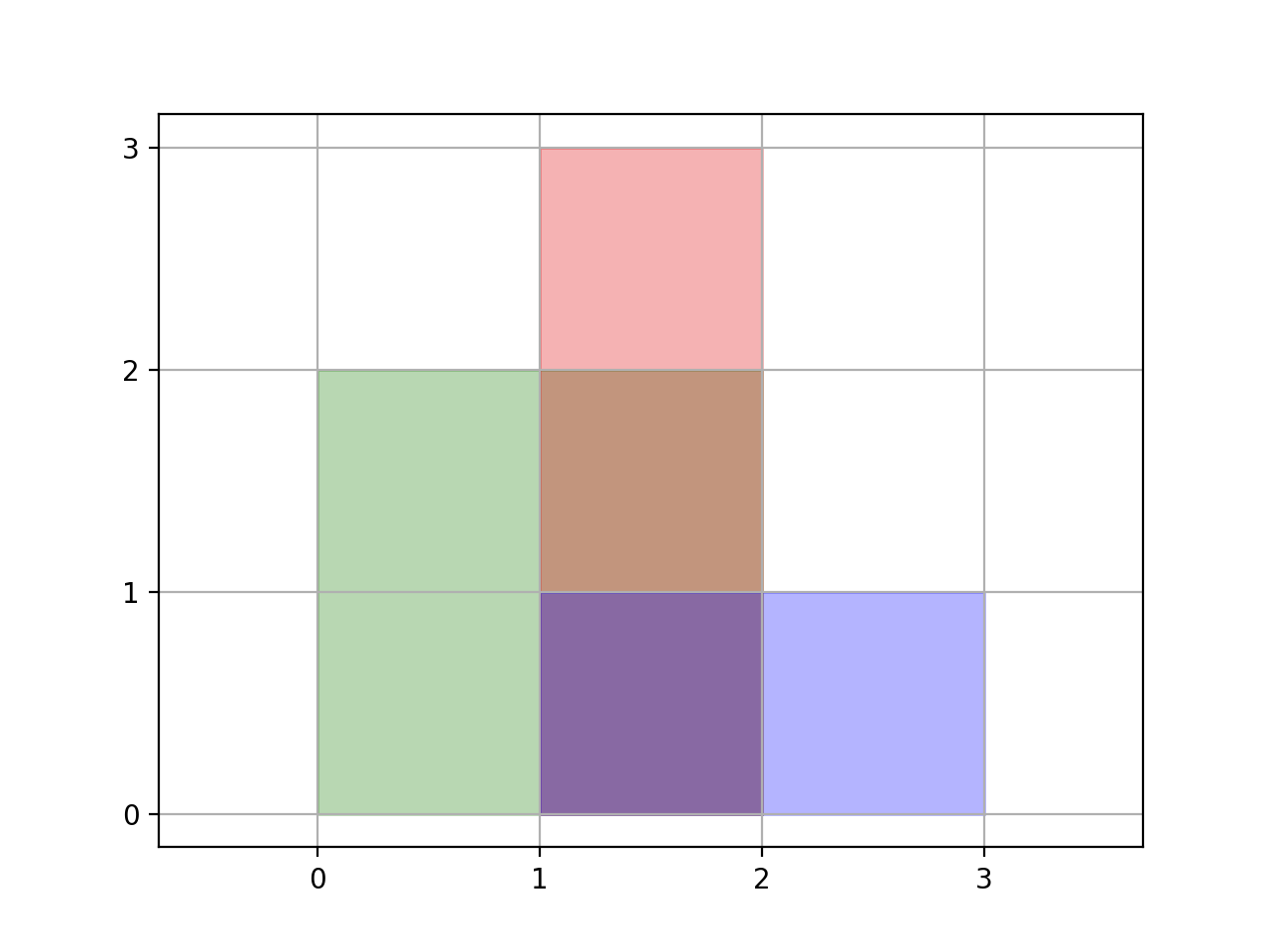
Suppose instead of
rectangles = [[0,0,2,2],[1,0,2,3],[1,0,3,1]], we had [[0,0,200,200],[100,0,200,300],[100,0,300,100]]. The answer would just be 100 times bigger.
What about if
rectangles = [[0,0,2,2],[1,0,2,3],[1,0,30002,1]] ? Only the blue region would have area 30000 instead of 1.
Our idea is this: we'll take all the
x and y coordinates, and re-map them to 0, 1, 2, ... etc. For example, if rectangles = [[0,0,200,200],[100,0,200,300],[100,0,300,100]], we could re-map it to [[0,0,2,2],[1,0,2,3],[1,0,3,1]]. Then, we can solve the problem with brute force. However, each region may actually represent some larger area, so we'll need to adjust for that at the end.
Re-map each
x coordinate to 0, 1, 2, .... Independently, re-map all y coordinates too.
We then have a problem that can be solved by brute force: for each rectangle with re-mapped coordinates
(rx1, ry1, rx2, ry2), we can fill the grid grid[x][y] = True for rx1 <= x < rx2 and ry1 <= y < ry2.
Afterwards, each
grid[rx][ry] represents the area (imapx(rx+1) - imapx(rx)) * (imapy(ry+1) - imapy(ry)), where if x got remapped to rx, then imapx(rx) = x ("inverse-map-x of remapped-x equals x"), and similarly for imapy.https://leetcode.com/articles/falling-squares/
Intuitively, there are two operations:
update, which updates our notion of the board (number line) after dropping a square; and query, which finds the largest height in the current board on some interval. We will work on implementing these operations.
Coordinate Compression
In the below approaches, since there are only up to
2 * len(positions) critical points, namely the left and right edges of each square, we can use a technique called coordinate compression to map these critical points to adjacent integers, as shown in the code snippets below.Set<Integer> coords = new HashSet(); for (int[] pos: positions) { coords.add(pos[0]); coords.add(pos[0] + pos[1] - 1); } List<Integer> sortedCoords = new ArrayList(coords); Collections.sort(sortedCoords); Map<Integer, Integer> index = new HashMap(); int t = 0; for (int coord: sortedCoords) index.put(coord, t++);
http://www.matrix67.com/blog/archives/108
对于“什么是离散化”,搜索帖子你会发现有各种说法,比如“排序后处理”、“对坐标的近似处理”等等。哪个是对的呢?哪个都对。关键在于,这需要一些例子和不少的讲解才能完全解释清楚。
离散化是程序设计中一个非常常用的技巧,它可以有效的降低时间复杂度。其基本思想就是在众多可能的情况中“只考虑我需要用的值”。下面我将用三个例子说明,如何运用离散化改进一个低效的,甚至根本不可能实现的算法。
《算法艺术与信息学竞赛》中的计算几何部分,黄亮举了一个经典的例子,我认为很适合用来介绍离散化思想。这个问题是UVA10173(http://acm.uva.es/p/v101/10173.html),题目意思很简单,给定平面上n个点的坐标,求能够覆盖所有这些点的最小矩形面积。这个问题难就难在,这个矩形可以倾斜放置(边不必平行于坐标轴)。
这里的倾斜放置很不好处理,因为我们不知道这个矩形最终会倾斜多少度。假设我们知道这个矩形的倾角是α,那么答案就很简单了:矩形面积最小时四条边一定都挨着某个点。也就是说,四条边的斜率已经都知道了的话,只需要让这些边从外面不断逼近这个点集直到碰到了某个点。你不必知道这个具体应该怎么实现,只需要理解这可以通过某种方法计算出来,毕竟我们的重点在下面的过程。
我们的算法很显然了:枚举矩形的倾角,对于每一个倾角,我们都能计算出最小的矩形面积,最后取一个最小值。
这个算法是否是正确的呢?我们不能说它是否正确,因为它根本不可能实现。矩形的倾角是一个实数,它有无数种可能,你永远不可能枚举每一种情况。我们说,矩形的倾角是一个“连续的”变量,它是我们无法枚举这个倾角的根本原因。我们需要一种方法,把这个“连续的”变量变成一个一个的值,变成一个“离散的”变量。这个过程也就是所谓的离散化。
我们可以证明,最小面积的矩形不但要求四条边上都有一个点,而且还要求至少一条边上有两个或两个以上的点。试想,如果每条边上都只有一个点,则我们总可以把这个矩形旋转一点使得这个矩形变“松”,从而有余地得到更小的矩形。于是我们发现,矩形的某条边的斜率必然与某两点的连线相同。如果我们计算出了所有过两点的直线的倾角,那么α的取值只有可能是这些倾角或它减去90度后的角(直线按“”方向倾斜时)这么C(n,2)种。我们说,这个“倾角”已经被我们 “离散化”了。虽然这个算法仍然有优化的余地,但此时我们已经达到了本文开头所说的目的。
对于某些坐标虽然已经是整数(已经是离散的了)但范围极大的问题,我们也可以用离散化的思想缩小这个规模。最近搞模拟赛Vijos似乎火了一把,我就拿两道Vijos的题开刀。
VOJ1056(http://www.vijos.cn/Problem_Show.asp?id=1056) 永远是离散化的经典问题。大意是给定平面上的n个矩形(坐标为整数,矩形与矩形之间可能有重叠的部分),求其覆盖的总面积。平常的想法就是开一个与二维坐标规模相当的二维Boolean数组模拟矩形的“覆盖”(把矩形所在的位置填上True)。可惜这个想法在这里有些问题,因为这个题目中坐标范围相当大(坐标范围为-10^8到10^8之间的整数)。但我们发现,矩形的数量n<=100远远小于坐标范围。每个矩形会在横纵坐标上各“使用”两个值, 100个矩形的坐标也不过用了-10^8到10^8之间的200个值。也就是说,实际有用的值其实只有这么几个。这些值将作为新的坐标值重新划分整个平面,省去中间的若干坐标值没有影响。我们可以将坐标范围“离散化”到1到200之间的数,于是一个200*200的二维数组就足够了。实现方法正如本文开头所说的“排序后处理”。对横坐标(或纵坐标)进行一次排序并映射为1到2n的整数,同时记录新坐标的每两个相邻坐标之间在离散化前实际的距离是多少。这道题同样有优化的余地。
最后简单讲一下计算几何以外的一个运用实例(实质仍然是坐标的离散)。才考的VOJ1238(http://www.vijos.cn/Problem_Show.asp?id=1238)中,标程开了一个与时间范围一样大的数组来储存时间段的位置。这种方法在空间上来看十分危险。一旦时间取值范围再大一点,盲目的空间开销将导致Memory Limit Exceeded。我们完全可以采用离散化避免这种情况。我们对所有给出的时间坐标进行一次排序,然后同样用时间段的开始点和结束点来计算每个时刻的游戏数,只是一次性加的经验值数将乘以排序后这两个相邻时间点的实际差。这样,一个1..n的数组就足够了。
VOJ1056(http://www.vijos.cn/Problem_Show.asp?id=1056) 永远是离散化的经典问题。大意是给定平面上的n个矩形(坐标为整数,矩形与矩形之间可能有重叠的部分),求其覆盖的总面积。平常的想法就是开一个与二维坐标规模相当的二维Boolean数组模拟矩形的“覆盖”(把矩形所在的位置填上True)。可惜这个想法在这里有些问题,因为这个题目中坐标范围相当大(坐标范围为-10^8到10^8之间的整数)。但我们发现,矩形的数量n<=100远远小于坐标范围。每个矩形会在横纵坐标上各“使用”两个值, 100个矩形的坐标也不过用了-10^8到10^8之间的200个值。也就是说,实际有用的值其实只有这么几个。这些值将作为新的坐标值重新划分整个平面,省去中间的若干坐标值没有影响。我们可以将坐标范围“离散化”到1到200之间的数,于是一个200*200的二维数组就足够了。实现方法正如本文开头所说的“排序后处理”。对横坐标(或纵坐标)进行一次排序并映射为1到2n的整数,同时记录新坐标的每两个相邻坐标之间在离散化前实际的距离是多少。这道题同样有优化的余地。
最后简单讲一下计算几何以外的一个运用实例(实质仍然是坐标的离散)。才考的VOJ1238(http://www.vijos.cn/Problem_Show.asp?id=1238)中,标程开了一个与时间范围一样大的数组来储存时间段的位置。这种方法在空间上来看十分危险。一旦时间取值范围再大一点,盲目的空间开销将导致Memory Limit Exceeded。我们完全可以采用离散化避免这种情况。我们对所有给出的时间坐标进行一次排序,然后同样用时间段的开始点和结束点来计算每个时刻的游戏数,只是一次性加的经验值数将乘以排序后这两个相邻时间点的实际差。这样,一个1..n的数组就足够了。
离散化的应用相当广泛,以后你会看到还有很多其它的用途。
2007.04.05补充:
VOJ1056那个例子看来还是有人不明白。
我发一张示意图,注意左边的10*7的数组是如何等价地转化为右边两个4*4的数组的

VOJ1056那个例子看来还是有人不明白。
我发一张示意图,注意左边的10*7的数组是如何等价地转化为右边两个4*4的数组的