https://leetcode.com/problems/subarrays-with-k-different-integers/
https://leetcode.com/problems/subarrays-with-k-different-integers/discuss/235235/C%2B%2BJava-with-picture-prefixed-sliding-window
X. https://leetcode.com/problems/subarrays-with-k-different-integers/discuss/234482/JavaC%2B%2BPython-Sliding-Window-with-Video
the total number of subarrays ending at
对于每一个位置 i,求出 lower[i] 表示达到正好 K 个不同数字的最小下标,和 upper[i] 表示达到正好 K - 1 个不同数字的最小下标。累计每个位置的 upper[i] - lower[i] 就是答案。
具体求的过程可以用双指针(滑动窗口)来求解。对于求 lower[i] 来说,如果 i > j,则显然有 lower[i] >= lower[j]。对于求 upper[i] 同理。
X.
https://leetcode.com/articles/subarrays-with-k-different-integers/
http://www.noteanddata.com/leetcode-992-Subarrays-with-K-Different-Integers-java-solution-note.html
Given an array
A of positive integers, call a (contiguous, not necessarily distinct) subarray of A good if the number of different integers in that subarray is exactly K.
(For example,
[1,2,3,1,2] has 3 different integers: 1, 2, and 3.)
Return the number of good subarrays of
A.
Example 1:
Input: A = [1,2,1,2,3], K = 2 Output: 7 Explanation: Subarrays formed with exactly 2 different integers: [1,2], [2,1], [1,2], [2,3], [1,2,1], [2,1,2], [1,2,1,2].
Example 2:
Input: A = [1,2,1,3,4], K = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: Subarrays formed with exactly 3 different integers: [1,2,1,3], [2,1,3], [1,3,4].
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 200001 <= A[i] <= A.length1 <= K <= A.length
还有一种更有趣的方法[1],没有显式地维护两个滑动窗口。我觉得这种方法的核心思路其实是这样的:
- 对于每一个数组元素
A[i],记sMin为使得A[sMin...i]中包含K个不同元素的最小index,sMax为使得A[sMax...i]中包含K个不同元素的最大index - 那么显然
A[sMin...i]和A[sMax...i]包含的元素是一样的(虽然可能个数不同) - 考虑从
A[i]转移到A[i+1]的情况:- 如果
A[i+1]是窗口中已经出现过的元素,则sMin不变,sMax可能会减小 - 如果
A[i+1]是窗口中没有出现过的元素,则sMin = sMax + 1,sMax >= sMin
- 如果
- 所以维护
sMax对应的小窗口就够了。
以及,有一个可以大幅度提速的优化。题目里给了数组元素的范围(
<=N),因此可以用数组代替map。int subarraysWithKDistinct(vector<int>& A, int K) { int sMin = 0, sMax = 0; unordered_map<int, int> window; int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) { // sMin不变,只修改sMax if (window.size() < K || window.find(A[i]) != window.end()) { window[A[i]]++; while (window.size() == K && window[A[sMax]] > 1) { window[A[sMax]]--; sMax++; } } // sMin和sMax都改变 else { window[A[i]]++; sMin = sMax + 1; while (window.size() >= K) { if (window.size() == K && window[A[sMax]] == 1) break; window[A[sMax]]--; if (window[A[sMax]] == 0) window.erase(A[sMax]); sMax++; } } if (window.size() == K) ans += sMax - sMin + 1; } return ans; }
If the problem talks about continuous subarrays or substrings, the sliding window technique may help solve it in a linear time. Such problems are tricky, though the solution is simple once you get it. No wonder I am seeing such problems in almost every interview!
Here, we will take a look at Subarrays with K Different Integers (LeetCode Hard), which appeared on LeetCode weekly contest #123. You can also master the sliding windows technique with these additional problems:
- Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
- Longest Substring with At Most Two Distinct Characters
- Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters
Intuition
If the subarray
[j, i] contains K unique numbers, and first prefix numbers also appear in [j + prefix, i] subarray, we have total 1 + prefix good subarrays. For example, there are 3 unique numers in [1, 2, 1, 2, 3]. First two numbers also appear in the remaining subarray [1, 2, 3], so we have 1 + 2 good subarrays: [1, 2, 1, 2, 3], [2, 1, 2, 3] and [1, 2, 3].Linear Solution
We can iterate through the array and use two pointers for our sliding window (
[j, i]). The back of the window is always the current position in the array (i). The front of the window (j) is moved so that A[j] appear only once in the sliding window. In other words, we are trying to shrink our sliding window while maintaining the same number of unique elements.
To do that, we keep tabs on how many times each number appears in our window (
m). After we add next number to the back of our window, we try to remove as many as possible numbers from the front, until the number in the front appears only once. While removing numbers, we are increasing prefix.
If we collected
K unique numbers, then we found 1 + prefix sequences, as each removed number would also form a sequence.
If our window reached
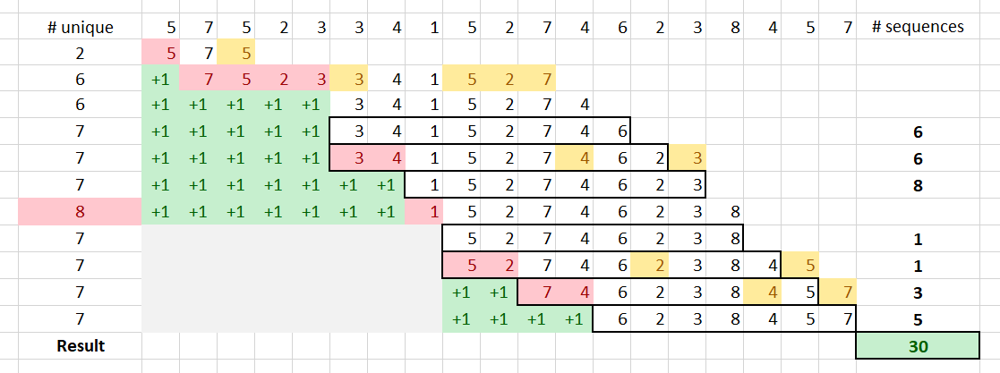
K + 1 unique numbers, we remove one number from the head (again, that number appears only in the front), and reset prefix as now we are starting a new sequence. This process is demonstrated step-by-step for the test case below; prefix are shown as +1 in the green background.[5,7,5,2,3,3,4,1,5,2,7,4,6,2,3,8,4,5,7]
7

In the code below, we use
cnt to track unique numbers. Since 1 <= A[i] <= A.size(), we can use an array instead of hash map to improve the performance.public int subarraysWithKDistinct(int[] A, int K) {
int res = 0, prefix = 0;
int[] m = new int[A.length + 1];
for (int i = 0, j = 0, cnt = 0; i < A.length; ++i) {
if (m[A[i]]++ == 0) ++cnt;
if (cnt > K) {
--m[A[j++]]; --cnt; prefix = 0;
}
while (m[A[j]] > 1) {
++prefix; --m[A[j++]];
}
if (cnt == K) res += prefix + 1;
}
return res;
} X. https://leetcode.com/problems/subarrays-with-k-different-integers/discuss/234482/JavaC%2B%2BPython-Sliding-Window-with-Video
Write a helper using sliding window,
to get the number of subarrays with at most K distinct elements.
Then f(exactly K) = f(atMost K) - f(atMost K-1).
to get the number of subarrays with at most K distinct elements.
Then f(exactly K) = f(atMost K) - f(atMost K-1).
Of course, you can merge 2 for loop into ones, if you like.
Time Complexity:
O(N)
O(N)
public int subarraysWithKDistinct(int[] A, int K) {
return atMostK(A, K) - atMostK(A, K - 1);
}
int atMostK(int[] A, int K) {
int i = 0, res = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> count = new HashMap<>();
for (int j = 0; j < A.length; ++j) {
if (count.getOrDefault(A[j], 0) == 0) K--;
count.put(A[j], count.getOrDefault(A[j], 0) + 1);
while (K < 0) {
count.put(A[i], count.get(A[i]) - 1);
if (count.get(A[i]) == 0) K++;
i++;
}
res += j - i + 1;
}
return res;
}res += j - i + 1:the total number of subarrays ending at
j that contain at most K distinct. // all subarrays with <= K distinct numbers are counted.
private int atMostK(int[] A, int K) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
int total = 0;
int distinct = 0; // count of distinct numbers in the window.
Map<Integer, Integer> counter = new HashMap<>();
while (j < A.length) {
if (counter.getOrDefault(A[j], 0) == 0) {
distinct++;
}
counter.put(A[j], 1 + counter.getOrDefault(A[j], 0));
j++;
while (i < j && distinct > K) { // shrink the left boundary of window.
counter.put(A[i], counter.get(A[i]) - 1);
if (counter.get(A[i]) == 0) {
distinct--;
}
i++;
}
total += j - i;
}
return total;
}对于每一个位置 i,求出 lower[i] 表示达到正好 K 个不同数字的最小下标,和 upper[i] 表示达到正好 K - 1 个不同数字的最小下标。累计每个位置的 upper[i] - lower[i] 就是答案。
具体求的过程可以用双指针(滑动窗口)来求解。对于求 lower[i] 来说,如果 i > j,则显然有 lower[i] >= lower[j]。对于求 upper[i] 同理。
void find(vector<int> &last, const vector<int> &A, int K) {
int n = A.size();
int j = 0, cur = 0;
vector<int> vis(n + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (vis[A[i]] == 0)
cur++;
vis[A[i]]++;
while (cur == K + 1) {
if (vis[A[j]] == 1)
cur--;
vis[A[j]]--;
j++;
}
last[i] = j;
}
}
int subarraysWithKDistinct(vector<int>& A, int K) {
int n = A.size();
vector<int> lower(n, 0), upper(n, 0);
find(upper, A, K - 1);
find(lower, A, K);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ans += upper[i] - lower[i];
return ans;
}
X.
- 遍历数组元素
- 用指针
i和j分别表示从当前元素开始,含有k个不同元素的最短子数组的结尾元素和最长子数组的结尾元素 - 用两个
map分别维护这两个子数组中的元素 - 需要移动到下一个元素时,从
map中删除当前元素,并移动指针直到满足要求为止。显然i和j的位置是递增的
这就相当于维护了两个滑动窗口。显然每个元素最多进出每个集合一次,所以整体复杂度应该是
搞两个滑窗一个维护数目是k的一个维护数目是k+1的就行了。O(N)。(虽然常数实在很大……)https://leetcode.com/articles/subarrays-with-k-different-integers/
For convenience, let's denote subarrays by tuples:
(i,j) = [A[i], A[i+1], ..., A[j]], and call a subarray valid if it has K different integers.
For each
j, let's consider the set of all i such that the subarray (i, j) is valid.
Firstly, must be a contiguous interval. If
i1 < i2 < i3, (i1,j) and (i3,j) are valid, but (i2,j) is not valid, this is a contradiction because (i2,j) must contain more than K different elements [as (i3,j)contains K], but (i1,j) [which is a superset of (i2,j)] only contains K different integers.
So now let's write as intervals: .
The second observation is that the endpoints of these intervals must be monotone increeasing - namely, and are monotone increasing. With similar logic to the above, we could construct a proof of this fact, but the intuition is that after adding an extra element to our subarrays, they are already valid, or we need to shrink them a bit to keep them valid.
We'll maintain two sliding windows, corresponding to and . Each sliding window will be able to count how many different elements there are in the window, and add and remove elements in a queue-like fashion
public int subarraysWithKDistinct(int[] A, int K) {
Window window1 = new Window();
Window window2 = new Window();
int ans = 0, left1 = 0, left2 = 0;
for (int right = 0; right < A.length; ++right) {
int x = A[right];
window1.add(x);
window2.add(x);
while (window1.different() > K)
window1.remove(A[left1++]);
while (window2.different() >= K)
window2.remove(A[left2++]);
ans += left2 - left1;
}
return ans;
}
class Window {
Map<Integer, Integer> count;
int nonzero;
Window() {
count = new HashMap();
nonzero = 0;
}
void add(int x) {
count.put(x, count.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);
if (count.get(x) == 1)
nonzero++;
}
void remove(int x) {
count.put(x, count.get(x) - 1);
if (count.get(x) == 0)
nonzero--;
}
int different() {
return nonzero;
}
}
http://www.noteanddata.com/leetcode-992-Subarrays-with-K-Different-Integers-java-solution-note.html
public int subarraysWithKDistinct(int[] A, int K) {
int ret = 0;
int j = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int curcount = 0;
int prevcount = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; ++i) {
curcount = (map.size() == K && map.containsKey(A[i])) ? prevcount-1 : 0;
map.compute(A[i], (k,v)-> null == v ? 1 : v+1);
while(map.size() > K) {
map.compute(A[j], (k,v)-> 1==v?null:v-1);
j++;
}
while(map.size() == K) {
curcount++;
int jcount = map.get(A[j]);
if(jcount == 1) {
//cur.remove(A[j]);
break;
}
else {
map.put(A[j], jcount-1);
}
j++;
}
ret += curcount;
prevcount = curcount;
}
return ret;
}