https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-sum-of-averages/
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-sum-of-averages/discuss/122775/Java-bottom-up-DP-with-Explanation
https://leetcode.com/articles/largest-sum-of-averages/
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-sum-of-averages/discuss/122739/C%2B%2BJavaPython-Easy-Understood-Solution-with-Explanation
It's top-down solution and it keeps all process to memory.
So it's like a DP solution while DP is bottom-up.
I took suggestion from @MonnaGotIt and added a prunting:
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-sum-of-averages/discuss/126280/Naive-Detailed-Step-by-Step-Approach-from-Recursive-to-DP-O(N)-solution
We partition a row of numbers
A into at most K adjacent (non-empty) groups, then our score is the sum of the average of each group. What is the largest score we can achieve?
Note that our partition must use every number in A, and that scores are not necessarily integers.
Example: Input: A = [9,1,2,3,9] K = 3 Output: 20 Explanation: The best choice is to partition A into [9], [1, 2, 3], [9]. The answer is 9 + (1 + 2 + 3) / 3 + 9 = 20. We could have also partitioned A into [9, 1], [2], [3, 9], for example. That partition would lead to a score of 5 + 2 + 6 = 13, which is worse.
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 100.1 <= A[i] <= 10000.1 <= K <= A.length.- Answers within
10^-6of the correct answer will be accepted as correct.
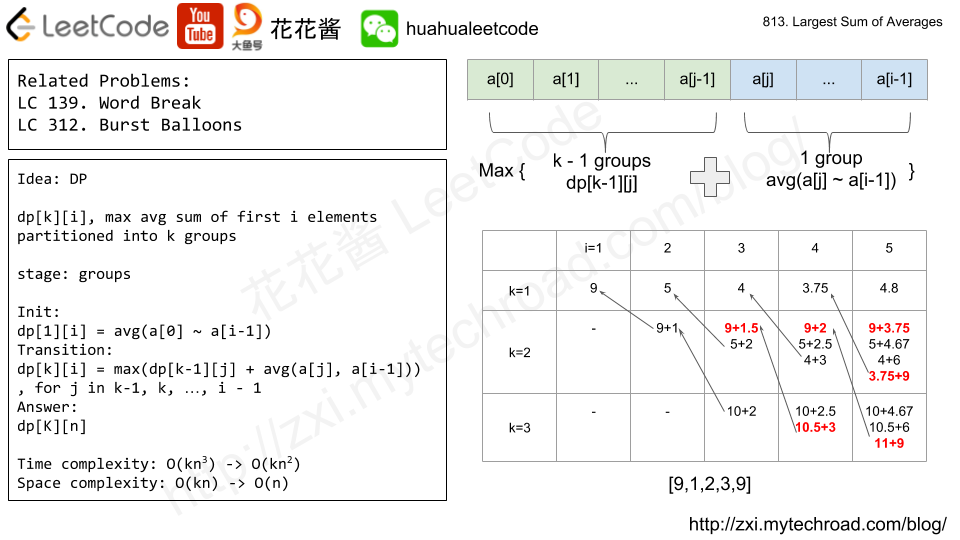
DP, use dp[k][i] to denote the largest average sum of partitioning first i elements into k groups.
Init
dp[1][i] = sum(a[0] ~ a[i – 1]) / i, for i in 1, 2, … , n.
Transition
dp[k][i] = max(dp[k – 1][j] + sum(a[j] ~ a[i – 1]) / (i – j)) for j in k – 1,…,i-1.
that is find the best j such that maximize dp[k][i]
largest sum of partitioning first j elements (a[0] ~ a[j – 1]) into k – 1 groups (already computed)
+ average of a[j] ~ a[i – 1] (partition a[j] ~ a[i – 1] into 1 group).
这道题给了我们一个数组,说是让我们将数组分成至多K个非空组,然后说需要统计的分数是各组的平均数之和,让我们求一个分割方法,使得这个分数值最大,当然这个分数值不一定是整型数。这道题限制了分割的组必须为非空组,那么就是说K值要小于等于数组的元素个数。但是实际上博主感觉这个必须为非空的限制有没有都一样,因为题目中说至多分成K组,也就是说可以根本不分组,那么比如你输入个A=[9,1], K=3,照样返回一个10,给人的感觉好像是分成了[9], [1], [] 这三组一样,但其实只是分成了两组[9] 和 [1]。但我们不必纠结这些,不是重点。没有啥思路的情况下我们就先想想brute force的解法呗,对于题目中给的那个例子,我们用最暴力的方法就是遍历所有的可能性,即遍历所有分割成三个组的情况,用三个for循环。貌似行的通,但问题来了,如果K大于3呢,每大一个,多加一个for循环么,总共K个for循环?如果K=100呢,100个for循环么?画面太美我不敢看!显然这道题用brute force是行不通的,那么换个方法呗!像这种求极值的题,又是玩数组的题,根据老夫行走江湖多年的经验,十有八九都是用Dynamic Programming来做的。玩子数组且跟极值有关的题天然适合用DP来做,想想为什么?DP的本质是什么,不就是状态转移方程,根据前面的状态来更新当前的状态。而子数组不就是整个数组的前一个状态,不停的更新的使得我们最终能得到极值。
好,下面进入正题。DP走起,首先来考虑dp数组的定义,我们如何定义dp数组有时候很关键,定义的不好,那么就无法写出正确的状态转移方程。对于这道题,我们很容易直接用一个一维数组dp,其中dp[i]表示范围为[0, i]的子数组分成三组能得到的最大分数。用这样定义的dp数组的话,状态转移方程将会非常难写,因为我们忽略了一个重要的信息,即K。dp数组不把K加进去的话就不知道当前要分几组,这个Hidden Information是解题的关键。这是DP中比较难的一类,有些DP题的隐藏信息藏的更深,不挖出来就无法解题。这道题的dp数组应该是个二维数组,其中dp[i][k]表示范围是[i, n-1]的子数组分成k组的最大得分。那么这里你就会纳闷了,为啥范围是[i, n-1]而不是[0, i],为啥要取后半段呢,不着急,听博主慢慢道来。由于把[i, n-1]范围内的子数组分成k组,那么suppose我们已经知道了任意范围内分成k-1组的最大分数,这是此类型题目的破题关键所在,要求状态k,一定要先求出所有的状态k-1,那么问题就转换成了从k-1组变成k组,即多分出一组,那么在范围[i, n-1]多分出一组,实际上就是将其分成两部分,一部分是一组,另一部分是k-1组,怎么分,就用一个变量j,遍历范围(i, n-1)中的每一个位置,那么分成的这两部分的分数如何计算呢?第一部分[i, j),由于是一组,那么直接求出平均值即可,另一部分由于是k-1组,由于我们已经知道了所有k-1的情况,可以直接从cache中读出来dp[j][k-1],二者相加即可 avg(i, j) + dp[j][k-1],所以我们可以得出状态转移方程如下:
dp[i][k] = max(avg(i, n) + max_{j > i} (avg(i, j) + dp[j][k-1]))
这里的avg(i, n)是其可能出现的情况,由于是至多分为k组,所以我们可以不分组,所以直接计算范围[i, n-1]内的平均值,然后用j来遍历区间(i, n-1)中的每一个位置,最终得到的dp[i][k]就即为所求。注意这里我们通过建立累加和数组sums来快速计算某个区间之和。博主觉得这道题十分的经典,考察点非常的多,很具有代表性,标为Hard都不过分,前面提到了dp[i][k]表示的是范围[i, n-1]的子数组分成k组的最大得分,现在想想貌似定义为[0, i]范围内的子数组分成k组的最大得分应该也是可以的,那么此时j就是遍历(0, i)中的每个位置了,好像也没什么不妥的地方,有兴趣的童鞋可以尝试的写一下~
Let
f[i][j]be the largest sum of averages for first i + 1 numbers(A[0], A[1], ... , A[i]) tojgroups. f[i][j] consists of two parts: first j-1 groups' averages and the last group' s average. Considering the last group, its last number must be A[i] and its first number can be from A[0] to A[i]. Suppose the last group starts from A[p+1], we can easily get the average form A[p+1] to A[i]. The sum of first j-1 groups' average is f[p][j-1] which we have got before. So now we can write the DP equation:f[i][j] = max {f[p][j-1] + (A[p+1] + A[p+2] + ... + A[i]) / (i - p)}, p = 0,1,...,i-1 public double largestSumOfAverages(int[] A, int K) {
if (K == 0 || A.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int l = A.length;
double[][] f = new double[l][K + 1];
double[] s = new double[l + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= l; i++) {
s[i] = s[i - 1] + A[i - 1];
f[i - 1][1] = s[i] / i;
}
for (int j = 2; j <= K; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
double max = Double.MIN_VALUE;
for (int p = 0; p < i; p++) {
double sum = f[p][j - 1] + (s[i + 1] - s[p + 1]) / (i - p);
max = Double.max(sum, max);
}
f[i][j] = max;
}
}
return f[l - 1][K];
}double largestSumOfAverages(vector<int>& A, int K) { int n = A.size(); vector<double> sums(n + 1); vector<vector<double>> dp(n, vector<double>(K)); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { sums[i + 1] = sums[i] + A[i]; } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { dp[i][0] = (sums[n] - sums[i]) / (n - i); } for (int k = 1; k < K; ++k) { for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { dp[i][k] = max(dp[i][k], (sums[j] - sums[i]) / (j - i) + dp[j][k - 1]); } } } return dp[0][K - 1]; }
我们可以对空间进行优化,由于每次的状态k,只跟前一个状态k-1有关,所以我们不需要将所有的状态都保存起来,只需要保存前一个状态的值就行了,那么我们就用一个一维数组就可以了,不断的进行覆盖,从而达到了节省空间的目的
double largestSumOfAverages(vector<int>& A, int K) { int n = A.size(); vector<double> sums(n + 1); vector<double> dp(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { sums[i + 1] = sums[i] + A[i]; } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { dp[i] = (sums[n] - sums[i]) / (n - i); } for (int k = 1; k < K; ++k) { for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { dp[i] = max(dp[i], (sums[j] - sums[i]) / (j - i) + dp[j]); } } } return dp[0]; }
The best score partitioning
A[i:] into at most K parts depends on answers to paritioning A[j:] (j > i) into less parts. We can use dynamic programming as the states form a directed acyclic graph.
Let
dp(i, k) be the best score partioning A[i:] into at most K parts.
If the first group we partition
A[i:] into ends before j, then our candidate partition has score average(i, j) + dp(j, k-1)), where average(i, j) = (A[i] + A[i+1] + ... + A[j-1]) / (j - i) (floating point division). We take the highest score of these, keeping in mind we don't necessarily need to partition - dp(i, k) can also be just average(i, N).
In total, our recursion in the general case is
dp(i, k) = max(average(i, N), max_{j > i}(average(i, j) + dp(j, k-1))).
We can calculate
average a little bit faster by remembering prefix sums. If P[x+1] = A[0] + A[1] + ... + A[x], then average(i, j) = (P[j] - P[i]) / (j - i).
Our implementation showcases a "bottom-up" style of dp. Here at loop number
k in our outer-most loop, dp[i] represents dp(i, k) from the discussion above, and we are calculating the next layer dp(i, k+1). The end of our second loop for i = 0..N-1 represents finishing the calculation of the correct value for dp(i, t), and the inner-most loop performs the calculation max_{j > i}(average(i, j) + dp(j, k)).
Time Complexity: , where is the length of
A.
public double largestSumOfAverages(int[] A, int K) {
int N = A.length;
double[] P = new double[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
P[i + 1] = P[i] + A[i];
double[] dp = new double[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
dp[i] = (P[N] - P[i]) / (N - i);
for (int k = 0; k < K - 1; ++k)
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; ++j)
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], (P[j] - P[i]) / (j - i) + dp[j]);
return dp[0];
}
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-sum-of-averages/discuss/122739/C%2B%2BJavaPython-Easy-Understood-Solution-with-Explanation
search return the result for n first numbers to k groups.It's top-down solution and it keeps all process to memory.
So it's like a DP solution while DP is bottom-up.
I took suggestion from @MonnaGotIt and added a prunting:
if (n < k) return 0; public double largestSumOfAverages(int[] A, int K) {
int N = A.length;
double[][] memo = new double[N+1][N+1];
double cur = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cur += A[i];
memo[i + 1][1] = cur / (i + 1);
}
return search(N, K, A, memo);
}
public double search(int n, int k, int[] A, double[][] memo) {
if (memo[n][k] > 0) return memo[n][k];
if (n < k) return 0;
double cur = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; --i) {
cur += A[i];
memo[n][k] = Math.max(memo[n][k], search(i, k - 1, A, memo) + cur / (n - i));
}
return memo[n][k];
}
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-sum-of-averages/discuss/126280/Naive-Detailed-Step-by-Step-Approach-from-Recursive-to-DP-O(N)-solution