https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/
is very import to find that we should find the answer from target to begin
if we start from sx and sy, there is two possibility
sx + sy, sy / sx, sx + xy
but if we start from target, there is only one possibility
if (tx > ty)
tx - ty, ty
else
tx, ty -tx
because the question say that all input are positive integer, so we must use the bigger one to subtract the smaller one
This is the crux but can't get you accepted because in worst case {sx = 1,sy = 1} and {tx = 10^9, ty = 1}, you have to make 10^9 iterations.
https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/discuss/230588/Easy-to-understand-diagram-and-recursive-solution
https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/discuss/114726/C%2B%2B-Simple-iterative.
https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/discuss/114732/Java-Simple-solution-with-explanation
X.
https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/discuss/114728/Java-Easy-to-understand-recursion-
solution
A move consists of taking a point
(x, y) and transforming it to either (x, x+y) or (x+y, y).
Given a starting point
(sx, sy) and a target point (tx, ty), return True if and only if a sequence of moves exists to transform the point (sx, sy) to (tx, ty). Otherwise, return False.Examples: Input: sx = 1, sy = 1, tx = 3, ty = 5 Output: True Explanation: One series of moves that transforms the starting point to the target is: (1, 1) -> (1, 2) (1, 2) -> (3, 2) (3, 2) -> (3, 5) Input: sx = 1, sy = 1, tx = 2, ty = 2 Output: False Input: sx = 1, sy = 1, tx = 1, ty = 1 Output: True
Note:
sx, sy, tx, tywill all be integers in the range[1, 10^9]
is very import to find that we should find the answer from target to begin
if we start from sx and sy, there is two possibility
sx + sy, sy / sx, sx + xy
but if we start from target, there is only one possibility
if (tx > ty)
tx - ty, ty
else
tx, ty -tx
because the question say that all input are positive integer, so we must use the bigger one to subtract the smaller one
This is the crux but can't get you accepted because in worst case {sx = 1,sy = 1} and {tx = 10^9, ty = 1}, you have to make 10^9 iterations.
https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/discuss/230588/Easy-to-understand-diagram-and-recursive-solution

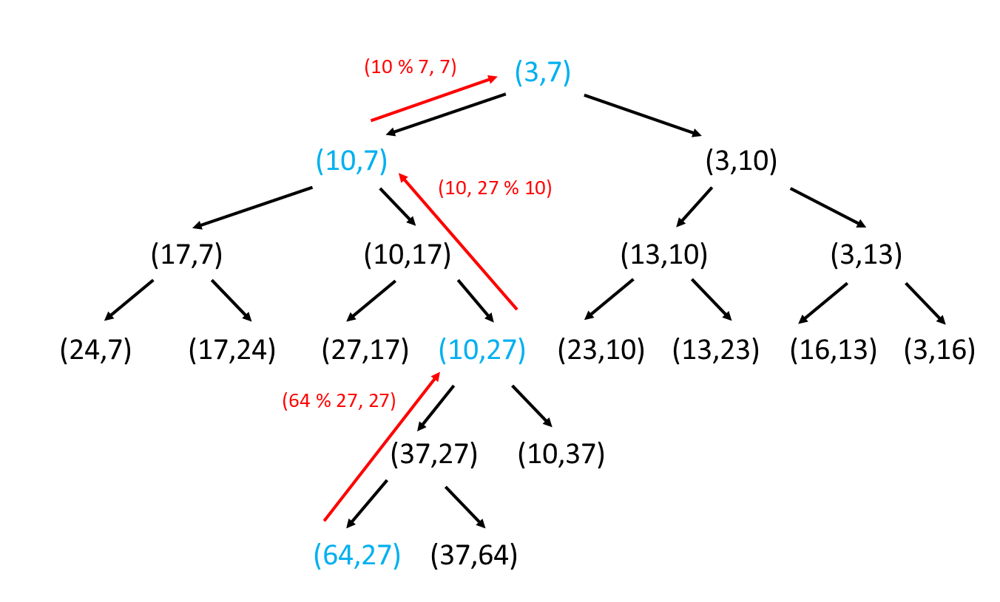
The above image shows the path that is taken from (64, 27) to the root node (3, 7) within the tree of all pairs that can be generated from the root.
Note that this is essentially https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_algorithm with different initial conditions.
bool recurse(int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) {
if (tx < sx) {
return false;
}
else if (tx == sx) {
return ((ty - sy) % sx) == 0;
}
else {
return recurse(sy, sx, ty % tx, tx);
}
}
bool reachingPoints(int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) {
if (tx < ty) {
return recurse(sx, sy, tx, ty);
}
else {
return recurse(sy, sx, ty, tx);
}
}
If we start from
If we start from
I cut down one by one at first and I got TLE. So I came up with remainder.
sx,sy, it will be hard to find tx, ty.If we start from
tx,ty, we can find only one path to go back to sx, sy.I cut down one by one at first and I got TLE. So I came up with remainder.
First line:
if 2 target points are still bigger than 2 starting point, we reduce target points.
Second line:
check if we reduce target points to (x, y+kx) or (x+ky, y)
if 2 target points are still bigger than 2 starting point, we reduce target points.
Second line:
check if we reduce target points to (x, y+kx) or (x+ky, y)
Time complexity
I will say
I will say
O(logN) where N = max(tx,ty). public boolean reachingPoints(int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) {
while (sx < tx && sy < ty)
if (tx < ty) ty %= tx;
else tx %= ty;
return sx == tx && sy <= ty && (ty - sy) % sx == 0 ||
sy == ty && sx <= tx && (tx - sx) % sy == 0;
}https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/discuss/114726/C%2B%2B-Simple-iterative.
f
sx,sy occurs in the path of Euclidean method to get GCD (by subtracting lesser value from greater value) of tx,ty, then return true.
To see why this is true, consider how the
tx, ty could have been formed if tx > ty. Let ax, ay be the pair in previous step. It cannot be ax, ax+ay because both ax and ay are greater than 0. So the only other possibility is ax+ay, ay. This means ay = ty and ax = tx-ty. Now we can optimize this subtraction a bit by doing ax = tx % ty since we will keep subtracting ty from tx until tx > ty.
One special case we need to handle during this optimization is when
Similar argument applies for
tx=9,ty=3,sx=6, sy=3 which can be covered using the condition if(sy == ty) return (tx - sx) % ty == 0;Similar argument applies for
tx <= ty. bool reachingPoints(int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) {
while(tx >= sx && ty >= sy){
if(tx > ty){
if(sy == ty) return (tx - sx) % ty == 0;
tx %= ty;
}else{
if(sx == tx) return (ty - sy) % tx == 0;
ty %= tx;
}
}
return false;
}https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/discuss/114732/Java-Simple-solution-with-explanation
We can solve this problem recursively from tx and ty.
In each recursive call, if tx > ty, it should derive from (tx % ty, ty), otherwise, from (tx, ty % tx) because the bigger one must come from last transformation from (tx - ty, ty) or (tx, ty - tx) until it is less than the smaller number.
We only need to care about the situation where (sx, sy) transforms to (sx + n * sy, sy) or (sx, sy + m * sx) in the first time because sx > sy is not the result of (sx % sy + m * sy). Hence, if sx > sy, (sx + n * sy) % sy will give a smaller number which is wrong.
public boolean reachingPoints(int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) {
if (sx > tx || sy > ty) return false;
if (sx == tx && (ty - sy) % sx == 0) return true;
if (sy == ty && (tx - sx) % sy == 0) return true;
return reachingPoints(sx, sy, tx % ty, ty % tx);
}X.
https://leetcode.com/problems/reaching-points/discuss/114728/Java-Easy-to-understand-recursion-
solution
public boolean reachingPoints(int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) {
if (sx == tx && sy == ty) {
return true;
} else if (tx == ty || sx > tx || sy > ty) {
return false;
} else if (tx > ty) {
int subtract = Math.max(1, (tx - sx)/ty);
return reachingPoints(sx, sy, tx - subtract * ty, ty);
} else {
int subtract = Math.max(1, (ty - sy)/tx);
return reachingPoints(sx, sy, tx, ty - subtract * tx);
}
}