https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/
https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/discuss/146786/Simple-recursive-Java-Solution
Given a binary tree rooted at
root, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
A node is deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Return the node with the largest depth such that it contains all the deepest nodes in its subtree.
Example 1:
Input: [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] Output: [2,7,4] Explanation: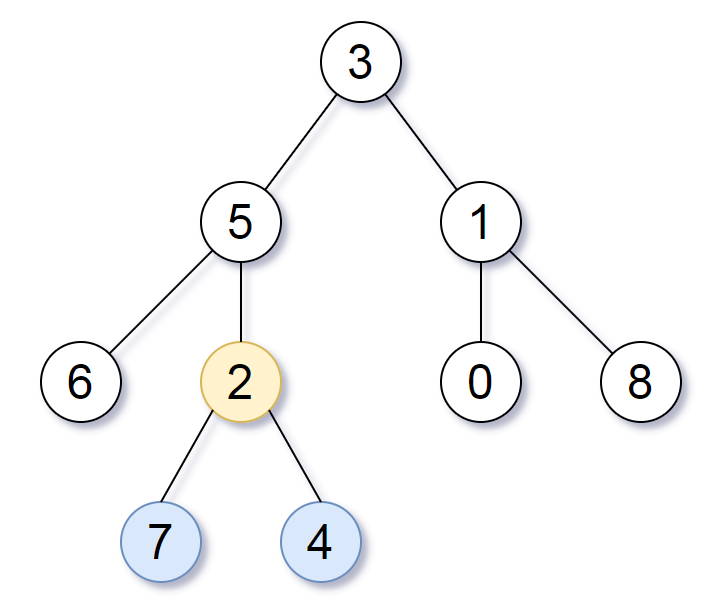
We can combine both depth first searches in Approach #1 into an approach that does both steps in one pass. We will have some function
dfs(node) that returns both the answer for this subtree, and the distance from node to the deepest nodes in this subtree.
Algorithm
The
Result (on some subtree) returned by our (depth-first search) recursion will have two parts:Result.node: the largest depth node that is equal to or an ancestor of all the deepest nodes of this subtree.Result.dist: the number of nodes in the path from the root of this subtree, to the deepest node in this subtree.
We can calculate these answers disjointly for
dfs(node):- To calculate the
Result.nodeof our answer:- If one
childResulthas deeper nodes, thenchildResult.nodewill be the answer. - If they both have the same depth nodes, then
nodewill be the answer.
- The
Result.distof our answer is always 1 more than the largestchildResult.distwe have.
public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root).node;
}
// Return the result of the subtree at this node.
public Result dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return new Result(null, 0);
Result L = dfs(node.left),
R = dfs(node.right);
if (L.dist > R.dist) return new Result(L.node, L.dist + 1);
if (L.dist < R.dist) return new Result(R.node, R.dist + 1);
return new Result(node, L.dist + 1);
}
}
/**
* The result of a subtree is:
* Result.node: the largest depth node that is equal to or
* an ancestor of all the deepest nodes of this subtree.
* Result.dist: the number of nodes in the path from the root
* of this subtree, to the deepest node in this subtree.
*/
class Result {
TreeNode node;
int dist;
Result(TreeNode n, int d) {
node = n;
dist = d;
}
Write a sub function
Return a
deep(TreeNode root).Return a
pair(int depth, TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest)
In sub function
deep(TreeNode root):
if root == null, return pair(0, null)
left = deep(root.left)
right = deep(root.left)
left = deep(root.left)
right = deep(root.left)
if left depth == right depth,
deepest nodes both in the left and right subtree,
return pair (left.depth + 1, root)
deepest nodes both in the left and right subtree,
return pair (left.depth + 1, root)
if left depth > right depth,
deepest nodes only in the left subtree,
return pair (left.depth + 1, left subtree)
deepest nodes only in the left subtree,
return pair (left.depth + 1, left subtree)
if left depth < right depth,
deepest nodes only in the right subtree,
return pair (right.depth + 1, right subtree)
deepest nodes only in the right subtree,
return pair (right.depth + 1, right subtree)
We try a straightforward approach that has two phases.
The first phase is to identify the nodes of the tree that are deepest. To do this, we have to annotate the depth of each node. We can do this with a depth first search.
Afterwards, we will use that annotation to help us find the answer:
- If the
nodein question has maximum depth, it is the answer. - If both the left and right child of a
nodehave a deepest descendant, then the answer is this parentnode. - Otherwise, if some child has a deepest descendant, then the answer is that child.
- Otherwise, the answer for this subtree doesn't exist.
Algorithm
In the first phase, we use a depth first search
dfs to annotate our nodes.
In the second phase, we also use a depth first search
answer(node), returning the answer for the subtree at that node, and using the rules above to build our answer from the answers of the children of node.
Note that in this approach, the
answer function returns answers that have the deepest nodes of the entiretree, not just the subtree being considered.
Map<TreeNode, Integer> depth;
int max_depth;
public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) {
depth = new HashMap();
depth.put(null, -1);
dfs(root, null);
max_depth = -1;
for (Integer d : depth.values())
max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, d);
return answer(root);
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent) {
if (node != null) {
depth.put(node, depth.get(parent) + 1);
dfs(node.left, node);
dfs(node.right, node);
}
}
public TreeNode answer(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null || depth.get(node) == max_depth)
return node;
TreeNode L = answer(node.left), R = answer(node.right);
if (L != null && R != null)
return node;
if (L != null)
return L;
if (R != null)
return R;
return null;
}
https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/discuss/146786/Simple-recursive-Java-Solution
public int depth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null ) return 0;
return Math.max(depth(root.left),depth(root.right))+1;
}
public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) {
if( root == null ) return null;
int left = depth(root.left);
int right = depth(root.right);
if( left == right ) return root;
if( left > right ) return subtreeWithAllDeepest(root.left);
return subtreeWithAllDeepest(root.right);
}
The time complexity of above code is O(N^2) since a binary tree can degenerate to a linked list, the worst complexity to calculate depth is O(N) and so the overall time complexity is O(N^2). Here is the memoized version:
Time complexity: O(N)
public int depth(TreeNode root,HashMap<TreeNode,Integer> map){
if(root == null ) return 0;
if( map.containsKey(root) ) return map.get(root);
int max = Math.max(depth(root.left,map),depth(root.right,map))+1;
map.put(root,max);
return max;
}
public TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root, HashMap<TreeNode,Integer> map){
int left = depth(root.left,map);
int right = depth(root.right,map);
if( left == right ) return root;
if( left > right ) return dfs(root.left,map);
return dfs(root.right,map);
}
public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) {
if( root == null ) return null;
HashMap<TreeNode,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
depth(root,map);
return dfs(root,map);
}