https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/discuss/189293/C%2B%2B-BFS-Island-Expansion-%2B-UF-Bonus
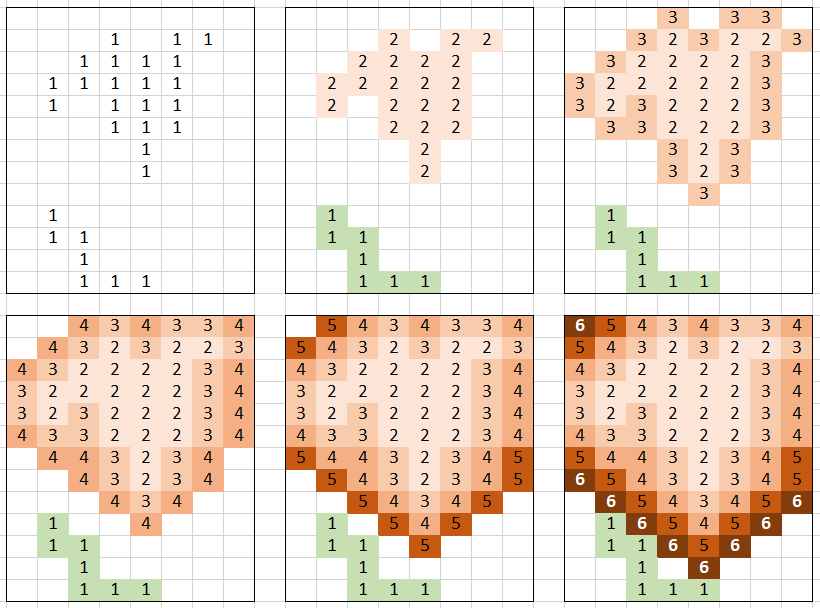
We first paint one of the islands using DFS with color 2, so we can easily identify island #1 and island #2. Thanks @davidluoyes for pointing out that we only need to paint one island.
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/discuss/189315/Java-DFS%2BBFS-traverse-the-2D-array-once
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/discuss/189321/Java-DFS-find-the-island-greater-BFS-expand-the-island
Approach 1: Find and Grow
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/discuss/189235/Java-Bidirectional-BFS
In a given 2D binary array
A, there are two islands. (An island is a 4-directionally connected group of 1s not connected to any other 1s.)
Now, we may change
0s to 1s so as to connect the two islands together to form 1 island.
Return the smallest number of
0s that must be flipped. (It is guaranteed that the answer is at least 1.)
Example 1:
Input: [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: [[0,1,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 2
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/discuss/189293/C%2B%2B-BFS-Island-Expansion-%2B-UF-Bonus
We first paint one of the islands using DFS with color 2, so we can easily identify island #1 and island #2. Thanks @davidluoyes for pointing out that we only need to paint one island.
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/discuss/189315/Java-DFS%2BBFS-traverse-the-2D-array-once
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/discuss/189321/Java-DFS-find-the-island-greater-BFS-expand-the-island
public int shortestBridge(int[][] A) {
int m = A.length, n = A[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
boolean found = false;
// 1. dfs to find an island, mark it in `visited`
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (found) {
break;
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (A[i][j] == 1) {
dfs(A, visited, q, i, j, dirs);
found = true;
break;
}
}
}
// 2. bfs to expand this island
int step = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
int[] cur = q.poll();
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int i = cur[0] + dir[0];
int j = cur[1] + dir[1];
if (i >= 0 && j >= 0 && i < m && j < n && !visited[i][j]) {
if (A[i][j] == 1) {
return step;
}
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
visited[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
private void dfs(int[][] A, boolean[][] visited, Queue<int[]> q, int i, int j, int[][] dirs) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= A.length || j >= A[0].length || visited[i][j] || A[i][j] == 0) {
return;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
dfs(A, visited, q, i + dir[0], j + dir[1], dirs);
}
}Approach 1: Find and Grow
Conceptually, our method is very straightforward: find both islands, then for one of the islands, keep "growing" it by 1 until we touch the second island.
We can use a depth-first search to find the islands, and a breadth-first search to "grow" one of them. This leads to a verbose but correct solution.
Algorithm
To find both islands, look for a square with a
1 we haven't visited, and dfs to get the component of that region. Do this twice. After, we have two components source and target.
To find the shortest bridge, do a BFS from the nodes
source. When we reach any node in target, we will have found the shortest distance.
Please see the code for more implementation details.
public int shortestBridge(int[][] A) {
int R = A.length, C = A[0].length;
int[][] colors = getComponents(A);
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList();
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet();
Set<Integer> target = new HashSet();
for (int r = 0; r < R; ++r)
for (int c = 0; c < C; ++c) {
if (colors[r][c] == 1) {
seen.add(r * R + c);
queue.add(new Node(r, c, 0));
} else if (colors[r][c] == 2) {
target.add(r * R + c);
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
if (target.contains(node.r * R + node.c))
return node.depth - 1;
for (int nei : neighbors(A, node.r, node.c)) {
int nr = nei / R, nc = nei % R;
if (colors[nr][nc] != 1) {
queue.add(new Node(nr, nc, node.depth + 1));
colors[nr][nc] = 1;
}
}
}
throw null;
}
public int[][] getComponents(int[][] A) {
int R = A.length, C = A[0].length;
int[][] colors = new int[R][C];
int t = 0;
for (int r0 = 0; r0 < R; ++r0)
for (int c0 = 0; c0 < C; ++c0)
if (colors[r0][c0] == 0 && A[r0][c0] == 1) {
// Start dfs
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
stack.push(r0 * R + c0);
colors[r0][c0] = ++t;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int node = stack.pop();
int r = node / R, c = node % R;
for (int nei : neighbors(A, r, c)) {
int nr = nei / R, nc = nei % R;
if (A[nr][nc] == 1 && colors[nr][nc] == 0) {
colors[nr][nc] = t;
stack.push(nr * R + nc);
}
}
}
}
return colors;
}
public List<Integer> neighbors(int[][] A, int r, int c) {
int R = A.length, C = A[0].length;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList();
if (0 <= r - 1)
ans.add((r - 1) * R + c);
if (0 <= c - 1)
ans.add(r * R + (c - 1));
if (r + 1 < R)
ans.add((r + 1) * R + c);
if (c + 1 < C)
ans.add(r * R + (c + 1));
return ans;
}
class Node {
int r, c, depth;
Node(int r, int c, int d) {
this.r = r;
this.c = c;
depth = d;
}
}
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-bridge/discuss/189235/Java-Bidirectional-BFS
A[x][y]=0: it is an unexplored empty cellA[x][y]=1: it is an island to be exploredA[x][y]=2: it is an island that has been exploredA[x][y]=3: this cell is already captured by island aA[x][y]=4: this cell is already captured by island b
First there are only 0 and 1 in board, we store island A in
3,4的更新非常聪明,有点儿像交叉染色 如果不加这个smart的处理的话,那么对于其中一个island中的所有点都要进行一遍BFS 然后进行比较 就会超出时间限制 学习了!qa, and island B in qb. Then we do BFS from those 2 islands, step by step. When one island reaches a cell that has been captured by the other island, we return the cost stored in res. public int shortestBridge(int[][] A) {
Queue<int[]> qa= new LinkedList<>();
Queue<int[]> qb= new LinkedList<>();
int m=A.length, n=A[0].length;
for (int i=0; i<m; i++){
for (int j=0; j<n; j++){
if (A[i][j]==1) {
if (qa.isEmpty()) dfs(A, i, j, qa);
else dfs(A, i, j, qb);
}
}
}
int res=0;
int[] d= new int[]{0,1,0,-1,0};
while (!qa.isEmpty() && !qb.isEmpty()){
for (int size=qa.size(); size>0; size--){
int[] cur= qa.poll();
for (int k=0; k<4; k++){
int x= cur[0]+d[k], y= cur[1]+d[k+1];
if (x<0 || x>=m || y<0 || y>=n || A[x][y]==3 || A[x][y]==2) continue; // Thanks Evolut1on for pointing this out, we can also skip A[x][y]==2
if (A[x][y]==4) return res;
A[x][y]=3;
qa.add(new int[]{x, y});
}
}
for (int size=qb.size(); size>0; size--){
int[] cur= qb.poll();
for (int k=0; k<4; k++){
int x= cur[0]+d[k], y= cur[1]+d[k+1];
if (x<0 || x>=m || y<0 || y>=n || A[x][y]==4 || A[x][y]==2) continue;
if (A[x][y]==3) return res+1;
A[x][y]=4;
qb.add(new int[]{x, y});
}
}
res+=2;
}
return 1;
}
public void dfs(int[][] A, int i, int j, Queue<int[]> q){
int m=A.length, n=A[0].length;
if (i<0 || i>=m || j<0 || j>=n || A[i][j]!=1) return;
q.add(new int[]{i, j});
A[i][j]=2;
dfs(A, i+1, j, q);
dfs(A, i-1, j, q);
dfs(A, i, j+1, q);
dfs(A, i, j-1, q);
}