https://leetcode.com/problems/mirror-reflection/description/
https://leetcode.com/problems/mirror-reflection/discuss/141790/The-Most-Straight-Forward-Solution.Pure-Math.Only-13ms
Approach 1: Simulation
https://www.acwing.com/solution/LeetCode/content/810/
解法一:
其实我们可以进一步化简,将三种情况融为一个表达式即可,即 1 - p%2 + q%2,不信的话可以带数字验证一下,碉堡了有木有,参见代码如下:
解法二:
其实不光是p和q同时为偶数的时候可以化简,只要p和q的最大公约数 Greatest Common Divisor 大于1时,都可以化简,比如,若 p = 6, q = 3 时跟 p = 2, q = 1 的情况也是一样,那我们就可以先求出p和q的最大公约数,然后用p和q分别除以这个最大公约数,再带入上面的那个一行公式求解即可,参见代码如下:
解法三:
There is a special square room with mirrors on each of the four walls. Except for the southwest corner, there are receptors on each of the remaining corners, numbered
0, 1, and 2.
The square room has walls of length
p, and a laser ray from the southwest corner first meets the east wall at a distance q from the 0th receptor.
Return the number of the receptor that the ray meets first. (It is guaranteed that the ray will meet a receptor eventually.)
Example 1:
Input: p = 2, q = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: The ray meets receptor 2 the first time it gets reflected back to the left wall.
First, think about the case p = 3 & q = 2.

So, this problem can be transformed into finding

So, this problem can be transformed into finding
m * p = n * q, wherem = the number of room extension + 1.n = the number of light reflection + 1.- If the number of light reflection is odd (which means
nis even), it means the corner is on the left-hand side. The possible corner is2.
Otherwise, the corner is on the right-hand side. The possible corners are0and1. - Given the corner is on the right-hand side.
If the number of room extension is even (which meansmis odd), it means the corner is1. Otherwise, the corner is0.
So, we can conclude:
m is even & n is odd => return 0.
m is odd & n is odd => return 1.
m is odd & n is even => return 2.
Note: The case
m is even & n is even is impossible. Because in the equation m * q = n * p, if m and n are even, we can divide both m and n by 2. Then, m or n must be odd.
--
Because we want to find
https://leetcode.com/problems/mirror-reflection/discuss/141773/C%2B%2BJavaPython-1-line-without-using-any-package-orBecause we want to find
m * p = n * q, where either m or n is odd, we can do it this way.
Here is my first solution. When I did it, I just code without any thinking.
def mirrorReflection(self, p, q):
k = 1
while (q * k % p): k += 1
if q * k / p % 2 and k % 2: return 1
if q * k / p % 2 == 0 and k % 2: return 0
if q * k / p % 2 and k % 2 == 0: return 2
return -1
When I reviewed the problems for my discuss article, I finaly realised only odd or even matter.
Divide
p,q by 2 until at least one odd.
If
If
If
I summary it as
p = odd, q = even: return 0If
p = even, q = odd: return 2If
p = odd, q = odd: return 1I summary it as
return 1 - p % 2 + q % 2 public int mirrorReflection(int p, int q) {
while (p % 2 == 0 && q % 2 == 0) {p >>= 1; q >>= 1;}
return 1 - p % 2 + q % 2;
}
Instead of modelling the ray as a bouncing line, model it as a straight line through reflections of the room.
For example, if
p = 2, q = 1, then we can reflect the room horizontally, and draw a straight line from (0, 0) to (4, 2). The ray meets the receptor 2, which was reflected from (0, 2) to (4, 2).
In general, the ray goes to the first integer point
(kp, kq) where k is an integer, and kp and kq are multiples of p. Thus, the goal is just to find the smallest k for which kq is a multiple of p.
The mathematical answer is
Time Complexity: , the complexity of the k = p / gcd(p, q).gcd operation.
public int mirrorReflection(int p, int q) {
int g = gcd(p, q);
p /= g;
p %= 2;
q /= g;
q %= 2;
if (p == 1 && q == 1)
return 1;
return p == 1 ? 0 : 2;
}
public int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (a == 0)
return b;
return gcd(b % a, a);
}
Approach 1: Simulation
The initial ray can be described as going from an origin
(x, y) = (0, 0) in the direction (rx, ry) = (p, q). From this, we can figure out which wall it will meet and where, and what the appropriate new ray will be (based on reflection.) We keep simulating the ray until it finds it's destination.
Algorithm
The parameterized position of the laser after time
t will be (x + rx * t, y + ry * t). From there, we know when it will meet the east wall (if x + rx * t == p), and so on. For a positive (and nonnegligible) time t, it meets the next wall.
We can then calculate how the ray reflects. If it hits an east or west wall, then
rx *= -1, else ry *= -1.
In Java, care must be taken with floating point operations.
Time Complexity: . We can prove (using Approach #2) that the number of bounces is bounded by this.
double EPS = 1e-6;
public int mirrorReflection(int p, int q) {
double x = 0, y = 0;
double rx = p, ry = q;
// While it hasn't reached a receptor,...
while (!(close(x, p) && (close(y, 0) || close(y, p)) || close(x, 0) && close(y, p))) {
// Want smallest t so that some x + rx, y + ry is 0 or p
// x + rxt = 0, then t = -x/rx etc.
double t = 1e9;
if ((-x / rx) > EPS)
t = Math.min(t, -x / rx);
if ((-y / ry) > EPS)
t = Math.min(t, -y / ry);
if (((p - x) / rx) > EPS)
t = Math.min(t, (p - x) / rx);
if (((p - y) / ry) > EPS)
t = Math.min(t, (p - y) / ry);
x += rx * t;
y += ry * t;
if (close(x, p) || close(x, 0))
rx *= -1;
if (close(y, p) || close(y, 0))
ry *= -1;
}
if (close(x, p) && close(y, p))
return 1;
return close(x, p) ? 0 : 2;
}
public boolean close(double x, double y) {
return Math.abs(x - y) < EPS;
}
https://www.acwing.com/solution/LeetCode/content/810/
有一个特殊的正方形房间,每面墙上都有一面镜子。除西南角以外,每个角落都放有一个接受器,编号为
0,1,以及 2。
正方形房间的墙壁长度为
p,一束激光从西南角射出,首先会与东墙相遇,入射点到接收器 0 的距离为 q。
返回光线最先遇到的接收器的编号(保证光线最终会遇到一个接收器)。
样例
输入:p = 2, q = 1
输出:2
解释:这条光线在第一次被反射回左边的墙时就遇到了接收器 2。
不管光线在里面怎么折射,光线在水平方向走p,那么在垂直方向必定走q. 找最小公倍数。
(找规律)
- 求出
p和q的最小公倍数lcm,令x = lcm / p,y = lcm / q。 - 如果
y为奇数,则说明最终会被右墙的接收器接收,此时若x也为奇数,则说明是右上角,否则是右下角。 - 如果
y为偶数,如果题目保证了一定能被接收,则一定是左上角的接收器。
时间复杂度
- 算法核心在求最大公约数,时间复杂度为 。
空间复杂度
- 由于使用了递归辗转相处,故需要额外的 的栈空间。
这道题给了我们一个正方形的房间,说是四面都是镜子墙,然后在西南角有一个激光发射器,其余三个角都有接收装置,问我们最终激光会被哪个接收器接收。第一次读题时这句 "Return the number of the receptor that the ray meets first." 让博主理解错误了,以为是让返回接收器的个数,以为接收器也能反射激光到其对角的接收器,那么接收器2和0互相反射,就是返回经过了2个接收器,接收器1返回到反射点,就是返回经过了1个接收点,想的是一套一套的,结果人家让返回的是接收器的标号,个人觉得将 number 改为 index 会减少些歧义。无所谓了,反正最终搞懂了题意就行了。其实这道题的正确解法还挺难想的,因为大家很容易走进的误区就是研究反射角啥的,然后算具体反射到了哪一个位置,再算下一个位置,其实这样都将题目变复杂了。博主把这一类型归为脑筋急转弯 Brain Teaser,一般都有很巧妙的数学解法,并不需要太复杂的算法。
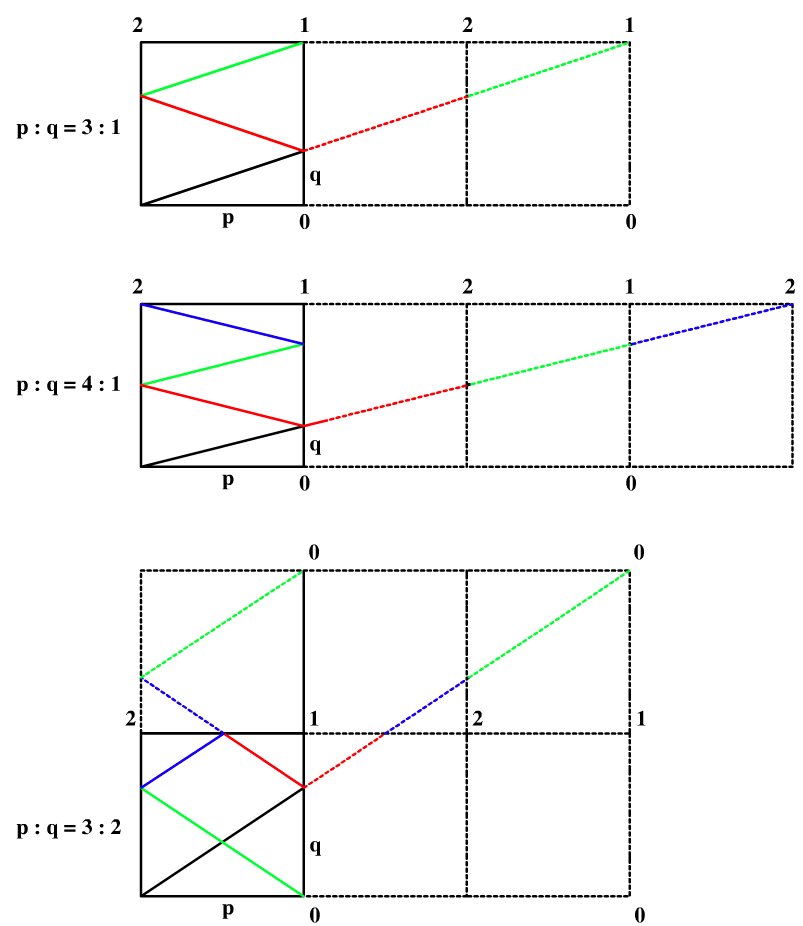
首先从最简单的情况开始分析,当p和q相等的时候,那么激光直接到达接收器1,当 p/q = 2 的时候,就如例子中所示,经过右边的镜面反射后到达左上角的接受器2。那么我们再来考虑下这三种情况 p/q = 3, p/q = 4, p/q = 3/2,并画出折射情况如下所示:

这里就有些比较好玩的规律了,我们知道激光遇到镜面是会发生折射的,但是假如没有镜面,就会仍然沿直线前进,那么对于 p/q = 3 时,若我们在右边增加大小相同的2个房间,则激光会到达右上角,由于第二个房间和原始房间是镜面对称的,而第三个房间和第二个房间也是镜面对称的,则第三个房间和原始房间就是一样的了,那么就可以假设一下,奇数房间和原始房间的布局相同。再来看上图中的 p/q = 4 时,我们在右边复制了三个房间,在第四个房间的时候,激光到达了右上角,而第偶数个房间的布局是跟原始房间称镜面反射的,则就是接受器2了。其实有些时候,我们不止要在右边复制房间,还需要在上面复制房间,比如当 p/q = 3/2 时,我们需要复制出一个 2x3 大小的矩阵出来,在水平方向共有三个房间,是奇数则水平方向和原始房间布局一致,但是竖直方向也复制了房间,那么竖直方向有偶数个房间,则竖直方向和原始房间成镜面反射,则最右上角为接收器0。
分析到这里,我们应该已经能总结出规律如下了:
- p为奇数,q为奇数时,到达接收器1。
- p为奇数,q为偶数时,到达接收器0。
- p为偶数,q为奇数时,到达接收器2。
那你可能会有疑问了,为啥没有p和q均为偶数的情况呢?比如 p = 4, q = 2,其实只要我们画个图就知道,这个跟 p = 2, q = 1 的情况是一摸一样的,若p和q均为偶数,那么那么一定可以同时除以2,那么其实我们可以先对p和q进行判断,若二者同为偶数,则同时除以2,直到不同时为偶数时,然后再带入上面归纳的三种情况求解即可,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
int mirrorReflection(int p, int q) {
while (p % 2 == 0 && q % 2 == 0) {
p /= 2; q /= 2;
}
if (p % 2 == 0) return 2;
if (q % 2 == 0) return 0;
return 1;
}
};其实我们可以进一步化简,将三种情况融为一个表达式即可,即 1 - p%2 + q%2,不信的话可以带数字验证一下,碉堡了有木有,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
int mirrorReflection(int p, int q) {
while (p % 2 == 0 && q % 2 == 0) {
p /= 2; q /= 2;
}
return 1 - p % 2 + q % 2;
}
};其实不光是p和q同时为偶数的时候可以化简,只要p和q的最大公约数 Greatest Common Divisor 大于1时,都可以化简,比如,若 p = 6, q = 3 时跟 p = 2, q = 1 的情况也是一样,那我们就可以先求出p和q的最大公约数,然后用p和q分别除以这个最大公约数,再带入上面的那个一行公式求解即可,参见代码如下:
解法三:
class Solution {
public:
int mirrorReflection(int p, int q) {
return 1 - p / gcd(p, q) % 2 + q / gcd(p, q) % 2;
}
int gcd(int p, int q) {
return q ? gcd(q, p % q) : p;
}
};
X. Video
leetcode 858. Mirror Reflection 算法讲解