https://www.hackerearth.com/problem/algorithm/subarrays-xor/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/subarray-xor-less-k/
https://www.cnblogs.com/1pha/p/8726928.html
https://discuss.codechef.com/questions/38108/subbxor-editorial
https://www.codechef.com/CDCRFT14/problems/SUBBXOR
https://github.com/fernandoBRS/SBC-Programming-Contests/blob/master/Algorithms/XOR/subarray_xor.cpp
class Node {
public:
int lCount,rCount;
Node *lChild,*rChild;
Node() {
lCount = rCount = 0;
lChild = rChild = NULL;
}
};
void addBit(Node *root,int n) {
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) {
int x= (n>>i) & 1;
if(x) {
root->rCount++;
if(root->rChild == NULL)
root->rChild = new Node();
root = root->rChild;
} else {
root->lCount++;
if(root->lChild == NULL)
root->lChild = new Node();
root = root->lChild;
}
}
}
int query(Node *root,int n,int k) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) {
bool ch1=(k>>i) & 1;
bool ch2=(n>>i) & 1;
if(ch1) {
if(ch2) {
res+=root->rCount;
if(root->lChild == NULL) return res;
root = root->lChild;
} else {
res+=root->lCount;
if(root->rChild == NULL) return res;
root = root->rChild;
}
} else {
if(ch2) {
if(root->rChild == NULL) return res;
root= root->rChild;
} else {
if(root->lChild == NULL) return res;
root= root->lChild;
}
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
int t;
//scanf("%d",&t);
t = next_int();
while(t--) {
int n,k;
n = next_int();
k = next_int();
int temp,temp1,temp2=0;
Node *root = new Node();
addBit(root,0);
long long total =0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp = next_int();
temp1= temp2^temp;
total+=(long long)query(root,temp1,k);
addBit(root , temp1);
temp2 = temp1;
}
printf("%lld\n",total);
}
return 0;
}
https://github.com/tr0j4n034/SPOJ/blob/master/SUBXOR.cpp
int get(pnode &p) {
return p ? p->sum : 0;
}
pnode initialize(int value) {
pnode p = (pnode)malloc(sizeof(node));
p->sum = value;
p->l = NULL;
p->r = NULL;
return p;
}
void add(pnode &p, int value) {
pnode current = p;
for (int i = MAX_BITS; i >= 0; i --) {
int bit = (value >> i) & 1;
if (!bit) {
if (!current->l) {
current->l = initialize(0);
}
current = current->l;
}
else {
if (!current->r) {
current->r = initialize(0);
}
current = current->r;
}
current->sum ++;
}
}
int get(pnode &p, int prefix, int value) {
int result = 0;
pnode current = p;
for (int i = MAX_BITS; i >= 0; i --) {
if (!current) {
break;
}
int prefixBit = (prefix >> i) & 1;
int bit = (value >> i) & 1;
if (prefixBit == bit) {
if (prefixBit == 1) {
result += get(current->r);
}
current = current->l;
}
else {
if (prefixBit == 0) {
result += get(current->l);
}
current = current->r;
}
}
return result;
}
int T, N, K;
int data[MAX], prefix[MAX];
pnode root;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
cin >> N >> K;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i ++) {
cin >> data[i];
}
root = initialize(0);
add(root, 0);
long long result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i ++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i - 1] ^ data[i];
result += get(root, prefix[i], K);
add(root, prefix[i]);
}
cout << result << endl;
}
return 0;
}
X. Brute Force - O(N^2)
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/subarray-xor-less-k/
Given an array of n numbers and a number k. You have to write a program to find the number of subarrays with xor less than k.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {8, 9, 10, 11, 12}, k=3
Output: 4
Sub-arrays [1:3], [2:3], [2:5], [4:5] have xor
values 2, 1, 0, 1 respectively.
Efficient Approach: An efficient approach will be to calculate all of the prefix xor values i.e. a[1:i] for all i.
It can be verified that the xor of a subarray a[l:r] can be written as (a[1:l-1] xor a[1:r]), where a[i, j] is the xor of all the elements with index such that, i <= index <= j.
Explanation:
We will store a number as binary number in trie. The left child will shows that the next bit is 0 and the right child will show the next bit is 1.
For example, given picture below shows number 1001 and 1010 in trie.
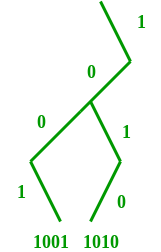
It can be verified that the xor of a subarray a[l:r] can be written as (a[1:l-1] xor a[1:r]), where a[i, j] is the xor of all the elements with index such that, i <= index <= j.
Explanation:
We will store a number as binary number in trie. The left child will shows that the next bit is 0 and the right child will show the next bit is 1.
For example, given picture below shows number 1001 and 1010 in trie.

If xor[i, j] represents the xor of all elements in the subarray a[i, j], then at an index i what we have is, a trie which has xor[1:1], xor[1:2]…..xor[1:i-1] already inserted. Now we somehow count how many of these (numbers in trie) are such that its xor with xor[1:i] is smaller than k. This will cover all the subarrays ending at the index i and having xor i.e. xor[j, i] <=k;
Now the problem remains, how to count the numbers with xor smaller than k. So, for example take the current bit of the ith index element is p, current bit of number k be q and the current node in trie be node.
Take the case when p=1, k=1. Then if we go to the right child the current xor would be 0 (as the right child means 1 and p=1, 1(xor)1=0).As k=1, all the numbers that are to the right child of this node would give xor value smaller than k. So, we would count the numbers that are right to this node.
If we go to the left child, the current xor would be 1 (as the left child means 0 and p=1, 0(xor)1=1). So, if we go to the left child we can still find number with xor smaller than k, therefore we move on to the left child.
Take the case when p=1, k=1. Then if we go to the right child the current xor would be 0 (as the right child means 1 and p=1, 1(xor)1=0).As k=1, all the numbers that are to the right child of this node would give xor value smaller than k. So, we would count the numbers that are right to this node.
If we go to the left child, the current xor would be 1 (as the left child means 0 and p=1, 0(xor)1=1). So, if we go to the left child we can still find number with xor smaller than k, therefore we move on to the left child.
So, to count the numbers that are below a given node, we modify the trie and each node will also store the number of leafs in that subtree and this would be modified after each insertion.
Other three cases for different values of p and k can be solved in the same way to the count the number of numbers with xor less than k.
Time complexity: O(n*log(max)), where max is the maximum element in the array.
Related Articles:
假设答案区间为 [L, R], XOR[L, R] 等价于 XOR[1, L - 1] ^ XOR[1, R], 可以使用 01Trie 保存目前已有的 前缀异或和, 对于每一个新的前缀插入之前, 在 01Trie 中查询 与 新的前缀 异或值 小于 K 的 已有前缀和的个数.
对于每个TrieNode 的定义为
struct TrieNode {
TrieNode* next[2];
int cnt;
TrieNode() {
next[0] = next[1] = NULL;
// 保存当前前缀的个数
cnt = 0;
}
};
在进行查询时, 比较 新的前缀和 and k 的每一位
| 已有前缀和的第 i 位 | indexPre( 新的前缀和的第 i 位) | indexK( K 的第 i 位) | 相应操作 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 递归求解左子树 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 统计左子树叶子节点个数, 递归求解右子树 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 递归求解右子树 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 统计右子树叶子节点个数, 递归求解左子树 |
对于 indexPre == 0, indexK == 0 的情况来说, 已有前缀和为 0 时满足条件, 因此需要递归求解左子树. 当已有前缀和为 1 时, indexK == 1, 大于要求的值, 所以不继续递归.
对于 indexPre == 0, indexK == 1 的情况来说, 已有前缀和为 1 时满足条件, 但 右子树 中可能有 值大于等于 K 的叶子节点, 因此需要递归求解右子树. 当已有前缀和为 0 时, indexK == 0, 所有左子树的叶子节点的值均小于 K, 因此统计左子树叶子节点的个数
struct TrieNode {
TrieNode* next[2];
int cnt;
TrieNode() {
next[0] = next[1] = NULL;
cnt = 0;
}
};
void insertNum(TrieNode* root, unsigned num) {
TrieNode* p = root;
for(int i = 31; i >= 0; i--) {
int index = (num >> i) & 1;
if(!p->next[index])
p->next[index] = new TrieNode();
p = p->next[index];
p->cnt++;
}
}
int getCnt(TrieNode* root) {
return root ? root->cnt : 0;
}
int queryLessThanK(TrieNode* root, int pre, int k) {
TrieNode* p = root;
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 31; i >= 0; i--) {
if(p == NULL)
break;
int indexPre = (pre >> i) & 1; // prefiexbit
int indexK = (k >> i) & 1; // bit
if(indexPre == indexK) {
if(indexK)
ret += getCnt(p->next[1]);
p = p->next[0];
}
else if(indexPre != indexK) {
if(indexK)
ret += getCnt(p->next[0]);
p = p->next[1];
}
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
int nTest; scanf("%d", &nTest);
while(nTest--) {
int nNum, k;
scanf("%d %u", &nNum, &k);
TrieNode* root = new TrieNode();
// insertNum(root, 0) 保证了前缀异或和 pre 自身 可以小于 k
insertNum(root, 0);
unsigned pre = 0;
long long ans = 0;
while(nNum--) {
unsigned num; scanf("%u", &num);
pre = pre ^ num;
ans += queryLessThanK(root, pre, k);
insertNum(root, pre);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
https://www.codechef.com/CDCRFT14/problems/SUBBXOR
Normal O(N^2) solution would time out. Let f(L,R) = XOR of subarray a[L..R], then f(L,R) = f(1,R) XOR f(1,L-1). For each index i=1 to N, we can count how many subarrays ending at ith position satisfy the given condition. Now, suppose, that we have a data structure that allows us to perform this two operations: insert some integer into this structure and for given two integers X and K finds the number of elements already in structure whose XOR with X is less than K.
Then we can solve the task like this:
Answer = 0;
XorOnPrefix = 0;
Structure.insert(0);
for i = 1 to n
XorOnPrefix = XorOnPrefix xor a_i;
Structure.insert(XorOnPrefix);
Answer + = Structure.query(XorOnPrefix,k);
return Answer;
Now, about the data structure. It can be implemented as trie (prefix tree), if we consider integers as binary strings of length logA = 20. Then insertion can be done in O(logA) time. But we also need to keep at each node the number of leaves we will encounter if we go to left side from that node and similarly for right. How do we do query(x,k)?
Structure.query(root,x,k,level)
{
if level==-1 or root==NULL: return 0
q=level'th bit of k
p=level'th bit of x
if q>0:
if p==0: // means that all leaves on left of this node will always satisfy
// + queries on right side
return root.count_left + Structure.query(root.right,x,k,level-1);
else: // all leave on right of this node will always satisfy
// + queries on left of this node
return root.count_right + Structure.query(root.left,x,k,level-1);
else:
if p==0: return Structure.query(root.left,x,k,level-1);
else: return Structure.query(root.right,x,k,level-1);
}
The sign  is used for the binary operation for bitwise exclusive or.
is used for the binary operation for bitwise exclusive or.
Let si be the xor of the first i elements on the prefix of a. Then the interval (i, j] is beautiful if  . Let's iterate over j from 1 ton and consider the values sj as the binary strings. On each iteration we should increase the answer by the value zj — the number of numbers si (i < j) so
. Let's iterate over j from 1 ton and consider the values sj as the binary strings. On each iteration we should increase the answer by the value zj — the number of numbers si (i < j) so  . To do that we can use the trie data structure. Let's store in the trie all the values si for i < j. Besides the structure of the trie we should also store in each vertex the number of leaves in the subtree of that vertex (it can be easily done during adding of each binary string). To calculate the value zj let's go down by the trie from the root. Let's accumulate the value curequals to the xor of the prefix of the value sj with the already passed in the trie path. Let the current bit in sj be equal to b and i be the depth of the current vertex in the trie. If the number cur + 2i ≥ k then we can increase zj by the number of leaves in vertex
. To do that we can use the trie data structure. Let's store in the trie all the values si for i < j. Besides the structure of the trie we should also store in each vertex the number of leaves in the subtree of that vertex (it can be easily done during adding of each binary string). To calculate the value zj let's go down by the trie from the root. Let's accumulate the value curequals to the xor of the prefix of the value sj with the already passed in the trie path. Let the current bit in sj be equal to b and i be the depth of the current vertex in the trie. If the number cur + 2i ≥ k then we can increase zj by the number of leaves in vertex  , because all the leaves in the subtree of tha vertex correspond to the values si that for sure gives
, because all the leaves in the subtree of tha vertex correspond to the values si that for sure gives  . After that we should go down in the subtree b. Otherwise if cur + 2i < k then we should simply go down to the subtree
. After that we should go down in the subtree b. Otherwise if cur + 2i < k then we should simply go down to the subtree  and recalculate the valuecur = cur + 2i.
and recalculate the valuecur = cur + 2i.
ll a[1000010]; class node { public: node *lt,*rt; int sub; node() { lt=NULL; rt=NULL; sub=0; } }; void insert(node *root,ll val) { for(int i=32;i>=0;i--) { if(val>>i&1) { if(root->rt==NULL) { root->rt=new node(); } root=root->rt; root->sub++; } else { if(root->lt==NULL) { root->lt=new node(); } root=root->lt; root->sub++; } } } ll query(node *root,ll val,ll K) { ll ret=0; for(int i=32;i>=0;i--) { int v=val>>i&1; int k=K>>i&1; node *temp; if(v==1 && k==0) { temp=root->lt; if(temp!=NULL) { ret+=temp->sub; // cout<<"ad ledt subtree "<<endl; } if(root->rt!=NULL) { root=root->rt; // cout<<"go to rt "<<endl; } else { //cout<<"direct ret "<<endl; return ret; } } else if(v==1 && k==1) { if(root->lt!=NULL) { // cout<<"only option go to lt "<<endl; root=root->lt; } else { //cout<<"return ret "<<endl; return ret; } } else if(v==0 && k==0) { temp=root->rt; if(temp!=NULL) { //cout<<"add values on rt subtree "<<endl; ret+=temp->sub; } if(root->lt!=NULL) { //cout<<"go to lefct "<<endl; root=root->lt; } else { //cout<<"else return ret "<<endl; return ret; } } else { if(root->rt!=NULL) { // cout<<"tru and go to rt "<<endl; root=root->rt; } else { // cout<<"elset return ret "<<endl; return ret; } } if(i==0) { ret+=root->sub; } } return ret; } int main() { int n; cin>>n; ll k; cin>>k; node *root=new node(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%lld",&a[i]); } insert(root,0); // cout<<" inserted "<<endl; int pre=0; ll ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { pre=pre^a[i]; ans+=query(root,pre,k); insert(root,pre); } cout<<ans<<endl; }
class Node {
public:
int lCount,rCount;
Node *lChild,*rChild;
Node() {
lCount = rCount = 0;
lChild = rChild = NULL;
}
};
void addBit(Node *root,int n) {
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) {
int x= (n>>i) & 1;
if(x) {
root->rCount++;
if(root->rChild == NULL)
root->rChild = new Node();
root = root->rChild;
} else {
root->lCount++;
if(root->lChild == NULL)
root->lChild = new Node();
root = root->lChild;
}
}
}
int query(Node *root,int n,int k) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) {
bool ch1=(k>>i) & 1;
bool ch2=(n>>i) & 1;
if(ch1) {
if(ch2) {
res+=root->rCount;
if(root->lChild == NULL) return res;
root = root->lChild;
} else {
res+=root->lCount;
if(root->rChild == NULL) return res;
root = root->rChild;
}
} else {
if(ch2) {
if(root->rChild == NULL) return res;
root= root->rChild;
} else {
if(root->lChild == NULL) return res;
root= root->lChild;
}
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
int t;
//scanf("%d",&t);
t = next_int();
while(t--) {
int n,k;
n = next_int();
k = next_int();
int temp,temp1,temp2=0;
Node *root = new Node();
addBit(root,0);
long long total =0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp = next_int();
temp1= temp2^temp;
total+=(long long)query(root,temp1,k);
addBit(root , temp1);
temp2 = temp1;
}
printf("%lld\n",total);
}
return 0;
}
int get(pnode &p) {
return p ? p->sum : 0;
}
pnode initialize(int value) {
pnode p = (pnode)malloc(sizeof(node));
p->sum = value;
p->l = NULL;
p->r = NULL;
return p;
}
void add(pnode &p, int value) {
pnode current = p;
for (int i = MAX_BITS; i >= 0; i --) {
int bit = (value >> i) & 1;
if (!bit) {
if (!current->l) {
current->l = initialize(0);
}
current = current->l;
}
else {
if (!current->r) {
current->r = initialize(0);
}
current = current->r;
}
current->sum ++;
}
}
int get(pnode &p, int prefix, int value) {
int result = 0;
pnode current = p;
for (int i = MAX_BITS; i >= 0; i --) {
if (!current) {
break;
}
int prefixBit = (prefix >> i) & 1;
int bit = (value >> i) & 1;
if (prefixBit == bit) {
if (prefixBit == 1) {
result += get(current->r);
}
current = current->l;
}
else {
if (prefixBit == 0) {
result += get(current->l);
}
current = current->r;
}
}
return result;
}
int T, N, K;
int data[MAX], prefix[MAX];
pnode root;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
cin >> N >> K;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i ++) {
cin >> data[i];
}
root = initialize(0);
add(root, 0);
long long result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i ++) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i - 1] ^ data[i];
result += get(root, prefix[i], K);
add(root, prefix[i]);
}
cout << result << endl;
}
return 0;
}
X. Brute Force - O(N^2)