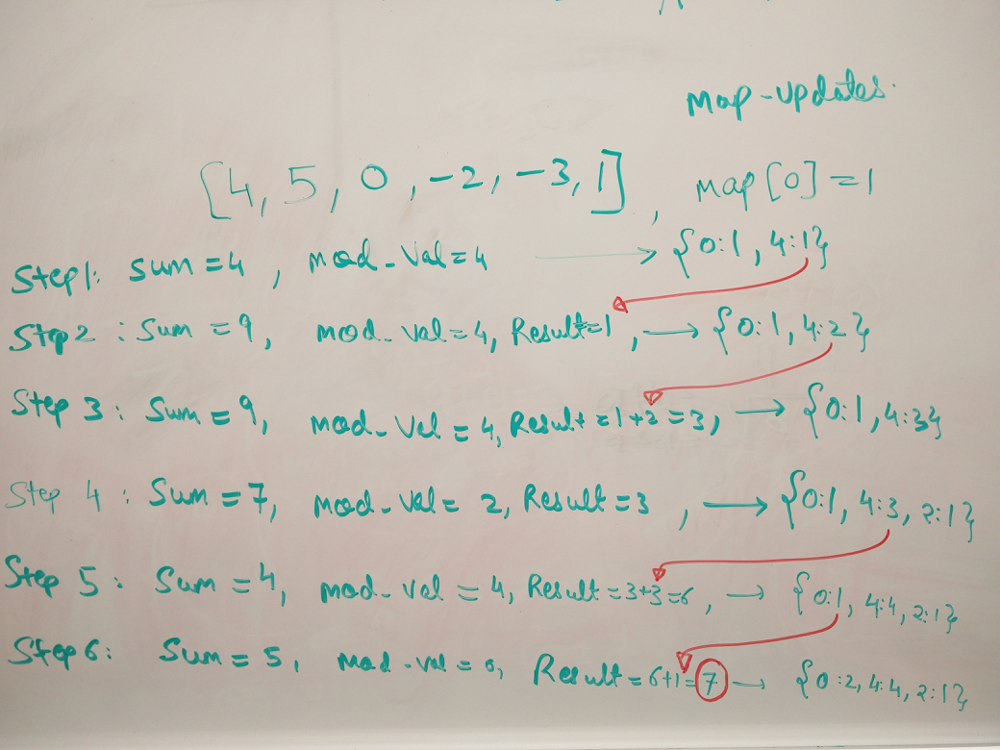https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-sums-divisible-by-k/
Approach 1: Prefix Sums and Counting
https://www.jianshu.com/p/7d9479ffcd5a
https://blog.csdn.net/dong_beijing/article/details/86444647
大致思路:比如数组A = [1,2,1], K=2,那么1%2 =1,(1+2)%2=1,所以 {2}是符合条件的子数组,而{1}和{1,2}的特点是有共同的余数1。类似的{}和{1,2,1}有共同的余数0,所以{1,2,1}是满足条件的数组。
详细思路:
(1)统计0到A.size()累计和的余数;
(2)统计相同余数的数量;
(3)相同余数的数量累加;
补充,由于题目A为整数,那么要处理负数的情况,负数的余数是A[i]%K+K。
int subarraysDivByK(vector<int>& a, int k) {
int as =a.size();
vector<int> remain(as+1,0);
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<as;i++)
{
sum+=a[i];//statistac for remainer
remain[i]=(sum%k+k)%k;//+k for neg
}
vector<int> stat(k,0);
int ret=0;
for(int i=0;i<=as;i++)
{
ret+=stat[remain[i]];//get same remainer counts
stat[remain[i]]++;
}
return ret;
}
X. https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-sums-divisible-by-k/discuss/217985/JavaC%2B%2B-Count-the-Remainder
https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-sums-divisible-by-k/discuss/217962/Java-Clean-O(n)-Number-Theory-%2B-Prefix-Sums
X. https://blog.csdn.net/fuxuemingzhu/article/details/86438244
定义DP数组,其中dp[i]代表以i结尾的能被K整除的子数组的最多个数。既然要求子数组的和,那么我们知道,肯定需要求数组累积和sums的。那么,对于sums每个位置i向前找,找到第一个差能被K整除的位置j,就停止即可。此时的dp[i] = dp[j] + 1. 题目要求的结果是sum(dp).
下面分析这个递推公式怎么来的。dp[j]表示以j位置结尾的子数组,该子数组的和能被K整除。那么当我们寻找到(sums[i] - sums[j]) % K == 0的时候,说明子数组sums[i, j]也能被K整除,那么,以i结尾的所有子数组个数等于以j结尾的子数组后面拼接上[i,j]子数组,加上[i,j]子数组.即dp[i] = dp[j] + 1。那么,为什么会break掉呢?这是因为,我们dp的状态是以i结尾的子数组的最大个数,再往前搜索则不是最大的。
这个代码的时间复杂度是O(N^2)的,也AC了,我认为主要是break的功劳。
int subarraysDivByK(vector<int>& A, int K) {
const int N = A.size();
vector<int> sums = {0};
for (int a : A)
sums.push_back(a + sums.back());
vector<int> dp(N + 1, 0);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if ((sums[i] - sums[j]) % K == 0) {
dp[i] = dp[j] + 1;
res += dp[i];
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
前缀和求余
其实,在上面这个做法当中,我们对于每个i位置都向前去查询(sums[i] - sums[j]) % K == 0的j,找到之后立马break,这一步可以更加简化,只要我们使用前缀和,并且相同余数的和。
如果(sums[i] - sums[j]) % K == 0,说明sums[i]和sums[j]都是K的倍数,所以得出sums[i] % K == sums[j] % K。也就是说,我们找到sums[i] % K这个数字的之前的状态即可。根据上面的DP,我们知道只需要找到最后的这个结果,然后break掉的意思就是,我们只需要保存最后的状态。总之,我们需要维护一个hash_map,保存每个余数在每个位置前面,出现的次数。
刚开始时,m[0] = 1,即假设0的出现了1次。然后遍历每个数字,对前缀和+当前数字再求余,在C++里面由于负数求余得到的是负数,所以要把负余数+K才行。把字典中保存的之前的结果累计,就是结果。
想了很久为什么是加的当前数字之前的结果,而不是现在的结果?这是因为,我们当前再次遇到了这个数字,才能说明形成了一个同余的区间。所以加的永远是前面的余数存在了多少次。这样,当某个余数只出现了1次时,并不会计入到结果里。
int subarraysDivByK(vector<int>& A, int K) {
unordered_map<int, int> m;
int preSum = 0;
int res = 0;
m[0] = 1;
for (int a : A) {
preSum = (preSum + a) % K;
if (preSum < 0) preSum += K;
res += m[preSum]++;
}
return res;
}
Given an array
A of integers, return the number of (contiguous, non-empty) subarrays that have a sum divisible by K.
Example 1:
Input: A = [4,5,0,-2,-3,1], K = 5 Output: 7 Explanation: There are 7 subarrays with a sum divisible by K = 5: [4, 5, 0, -2, -3, 1], [5], [5, 0], [5, 0, -2, -3], [0], [0, -2, -3], [-2, -3]
Note:
1 <= A.length <= 30000-10000 <= A[i] <= 100002 <= K <= 10000
Approach 1: Prefix Sums and Counting
As is typical with problems involving subarrays, we use prefix sums to add each subarray. Let
P[i+1] = A[0] + A[1] + ... + A[i]. Then, each subarray can be written as P[j] - P[i] (for j > i). Thus, we have P[j] - P[i] equal to 0 modulo K, or equivalently P[i] and P[j] are the same value modulo K.
Algorithm
Count all the
P[i]'s modulo K. Let's say there are values . Then, there are possible subarrays.
For example, take
A = [4,5,0,-2,-3,1]. Then P = [0,4,9,9,7,4,5], and :- With (at , ), it indicates subarray with sum divisible by , namely .
- With (at , , , ), it indicates subarrays with sum divisible by , namely , , , , , .
- Time Complexity: , where is the length of
A. - Space Complexity: . (However, the solution can be modified to use space by storing only
count.)
public int subarraysDivByK(int[] A, int K) {
int N = A.length;
int[] P = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
P[i + 1] = P[i] + A[i];
int[] count = new int[K];
for (int x : P)
count[(x % K + K) % K]++;
int ans = 0;
for (int v : count)
ans += v * (v - 1) / 2;
return ans;
}
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/count-sub-arrays-sum-divisible-k/
其实上面的解法已经很接近了,但是思考一下为什么会超时?比如K=5,当sum[0]=4时,后面的sum[i]=5*n + 4都符合要求,即不需要判断每个和,只需要判断sum[i]%5的值就好了。
假设:
所以这道题就变成了求对K的每个模的个数,然后对于每个0~i,分别两两组合,假设mod[i]=n,那么其i的个数为n*(n-1)/2.
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(K)
假设:
sum[i]=p*K+ri
sum[j]=q*K+rj
sum[j]-sum[i]=(q-p)*K+rj-ri
所以这道题就变成了求对K的每个模的个数,然后对于每个0~i,分别两两组合,假设mod[i]=n,那么其i的个数为n*(n-1)/2.
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(K)
public int subarraysDivByK(int[] A, int K) {
int mod[] = new int[K];
int cumSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
cumSum += A[i];
// countSum % K 可能是负数,需要 +K
mod[((cumSum % K) + K) % K]++;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
if (mod[i] > 1) {
ans += (mod[i] * (mod[i] - 1)) / 2;
}
}
ans += mod[0];
return ans;
}
大致思路:比如数组A = [1,2,1], K=2,那么1%2 =1,(1+2)%2=1,所以 {2}是符合条件的子数组,而{1}和{1,2}的特点是有共同的余数1。类似的{}和{1,2,1}有共同的余数0,所以{1,2,1}是满足条件的数组。
详细思路:
(1)统计0到A.size()累计和的余数;
(2)统计相同余数的数量;
(3)相同余数的数量累加;
补充,由于题目A为整数,那么要处理负数的情况,负数的余数是A[i]%K+K。
int subarraysDivByK(vector<int>& a, int k) {
int as =a.size();
vector<int> remain(as+1,0);
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<as;i++)
{
sum+=a[i];//statistac for remainer
remain[i]=(sum%k+k)%k;//+k for neg
}
vector<int> stat(k,0);
int ret=0;
for(int i=0;i<=as;i++)
{
ret+=stat[remain[i]];//get same remainer counts
stat[remain[i]]++;
}
return ret;
}
X. https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-sums-divisible-by-k/discuss/217985/JavaC%2B%2B-Count-the-Remainder
Calculate the prefix sum and count it.
Java, use HashMap
public int subarraysDivByK(int[] A, int K) {
Map<Integer, Integer> count = new HashMap<>();
count.put(0, 1);
int prefix = 0, res = 0;
for (int a : A) {
prefix = (prefix + a % K + K) % K;
res += count.getOrDefault(prefix, 0);
count.put(prefix, count.getOrDefault(prefix, 0) + 1);
}
return res;
}
Java, Use Array
public int subarraysDivByK(int[] A, int K) {
int[] count = new int[K];
count[0] = 1;
int prefix = 0, res = 0;
for (int a : A) {
prefix = (prefix + a % K + K) % K;
res += count[prefix]++;
}
return res;
}
About the problems - sum of contiguous subarray , prefix sum is a common technique.
Another thing is if sum[0, i] % K == sum[0, j] % K, sum[i + 1, j] is divisible by by K.
So for current index j, we need to find out how many index i (i < j) exit that has the same mod of K.
Now it easy to come up with HashMap <mod, frequency>
Another thing is if sum[0, i] % K == sum[0, j] % K, sum[i + 1, j] is divisible by by K.
So for current index j, we need to find out how many index i (i < j) exit that has the same mod of K.
Now it easy to come up with HashMap <mod, frequency>
Time Complexity: O(N)
Space Complexity: O(K)
Space Complexity: O(K)
Very clever solution with map.put(0,1) to deal with "remainder = 0" situation
public int subarraysDivByK(int[] A, int K) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(0, 1);//\\
int count = 0, sum = 0;
for(int a : A) {
sum = (sum + a) % K;
if(sum < 0) sum += K; // Because -1 % 5 = -1, but we need the positive mod 4
count += map.getOrDefault(sum, 0);
map.put(sum, map.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);
}
return count;
}
we can just use array, which is faster than HashMap.
public int subarraysDivByK(int[] A, int K) {
int[] map = new int[K];
map[0] = 1;
int count = 0, sum = 0;
for(int a : A) {
sum = (sum + a) % K;
if(sum < 0) sum += K; // Because -1 % 5 = -1, but we need the positive mod 4
count += map[sum];
map[sum]++;
}
return count;
}
I am already going to assume that you know about prefix sums before you read this.
We can all agree that for an array int[] A, where N = len(A), that there are N prefix sums.
prefix[0] = A[0], prefix[1] = A[0] + A[1], ... prefix[i] = prefix[0] + ... + prefix[i].
We can all agree that for an array int[] A, where N = len(A), that there are N prefix sums.
prefix[0] = A[0], prefix[1] = A[0] + A[1], ... prefix[i] = prefix[0] + ... + prefix[i].
Then to calculate how many subarrays are divisible by K is logically equivalent to saying, how many ways can we pair up all prefix sum pairs (i,j) where i < j
such that (prefix[j] - prefix[i]) % K == 0.
such that (prefix[j] - prefix[i]) % K == 0.
Just from that information alone we easily get a O(n^2) solution.
Compute all prefix sums, then check all pair to see if k divides the difference between them.
Compute all prefix sums, then check all pair to see if k divides the difference between them.
However, if we just exploit some information w.r.t to the remainder of each prefix sum we can manipulate this into a linear algorithm. Here's how.
Number Theory Part
I noted above that we need to find all prefix sum pairs (i,j) such tha (p[j] - p[i]) % K == 0.
But this is only true, if and only if
Why is this?
I noted above that we need to find all prefix sum pairs (i,j) such tha (p[j] - p[i]) % K == 0.
But this is only true, if and only if
p[j] % K == p[i] % KWhy is this?
According the the division algorithm we can express p[j] and p[i] in the following way.
p[j] = bK + r0 where 0 <= r0 < K
p[i] = aK + r1 where 0<= r1 < K
p[j] = bK + r0 where 0 <= r0 < K
p[i] = aK + r1 where 0<= r1 < K
Then
Again:
p[j] - p[i] = (b*K + r0) - (a*K + r1)= b*K - a*K + r0 - r1 = K*(b-a) + r0 - r1Again:
p[j] - p[i] = K*(b-a) + (r0-r1), in other wordsK only divides p[j] - p[i] iff r0-r1 = 0 <-> r0 = r1 QED
But we should not forget about elements in the array that do not need a pairing, namely those that are are divisible by K. That's why I add mod[0] at the end.
Also counting pairs => N choose 2 = > n*(n-1) / 2.
https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-sums-divisible-by-k/discuss/217979/Pictured-Explanation-Python-O(n)-Clean-Solution-8-Lines!
Running Sum[i]%K == Running Sum[j]%k that means we have sum(i,j) which is divisible by K.
Thus, we keep HashMap = {RunningSum%K : Frequency_Count}
Time Complexity : O(n)
Space Complexity : O(K) - As map keys are always Modulus of K with running sum.
Thus, we keep HashMap = {RunningSum%K : Frequency_Count}
Time Complexity : O(n)
Space Complexity : O(K) - As map keys are always Modulus of K with running sum.
X. https://blog.csdn.net/fuxuemingzhu/article/details/86438244
定义DP数组,其中dp[i]代表以i结尾的能被K整除的子数组的最多个数。既然要求子数组的和,那么我们知道,肯定需要求数组累积和sums的。那么,对于sums每个位置i向前找,找到第一个差能被K整除的位置j,就停止即可。此时的dp[i] = dp[j] + 1. 题目要求的结果是sum(dp).
下面分析这个递推公式怎么来的。dp[j]表示以j位置结尾的子数组,该子数组的和能被K整除。那么当我们寻找到(sums[i] - sums[j]) % K == 0的时候,说明子数组sums[i, j]也能被K整除,那么,以i结尾的所有子数组个数等于以j结尾的子数组后面拼接上[i,j]子数组,加上[i,j]子数组.即dp[i] = dp[j] + 1。那么,为什么会break掉呢?这是因为,我们dp的状态是以i结尾的子数组的最大个数,再往前搜索则不是最大的。
这个代码的时间复杂度是O(N^2)的,也AC了,我认为主要是break的功劳。
int subarraysDivByK(vector<int>& A, int K) {
const int N = A.size();
vector<int> sums = {0};
for (int a : A)
sums.push_back(a + sums.back());
vector<int> dp(N + 1, 0);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if ((sums[i] - sums[j]) % K == 0) {
dp[i] = dp[j] + 1;
res += dp[i];
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
前缀和求余
其实,在上面这个做法当中,我们对于每个i位置都向前去查询(sums[i] - sums[j]) % K == 0的j,找到之后立马break,这一步可以更加简化,只要我们使用前缀和,并且相同余数的和。
如果(sums[i] - sums[j]) % K == 0,说明sums[i]和sums[j]都是K的倍数,所以得出sums[i] % K == sums[j] % K。也就是说,我们找到sums[i] % K这个数字的之前的状态即可。根据上面的DP,我们知道只需要找到最后的这个结果,然后break掉的意思就是,我们只需要保存最后的状态。总之,我们需要维护一个hash_map,保存每个余数在每个位置前面,出现的次数。
刚开始时,m[0] = 1,即假设0的出现了1次。然后遍历每个数字,对前缀和+当前数字再求余,在C++里面由于负数求余得到的是负数,所以要把负余数+K才行。把字典中保存的之前的结果累计,就是结果。
想了很久为什么是加的当前数字之前的结果,而不是现在的结果?这是因为,我们当前再次遇到了这个数字,才能说明形成了一个同余的区间。所以加的永远是前面的余数存在了多少次。这样,当某个余数只出现了1次时,并不会计入到结果里。
int subarraysDivByK(vector<int>& A, int K) {
unordered_map<int, int> m;
int preSum = 0;
int res = 0;
m[0] = 1;
for (int a : A) {
preSum = (preSum + a) % K;
if (preSum < 0) preSum += K;
res += m[preSum]++;
}
return res;
}