https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/convert-a-binary-tree-into-doubly-linked-list-in-spiral-fashion/
Convert Binary Tree to Double Linked List in Zig-Zag Order | Code Samurai
Question: given a binary tree, write an algorithm to convert the tree into a double-linked list. The list must be as if the tree is traversed in zig-zag and level order.
Solution: let's first understand what the objective is. By zig-zag level order, the question means that we need to traverse the tree in level order, a.k.a breadth first, such that the next level is traversed in the oposite direction to the current level. For example, take a look at this tree:
A zig-zag level-order traversal creates the list 1, 2, 3, 5, 4. It doesn't matter which direction the root is printed because there is only one node. However, since the second level is printed left to right, 2 then 3, the third level is printed from right to left, 5 then 4.
Given a Binary Tree, convert it into Doubly Linked List where the nodes are represented Spirally. The left pointer of the binary tree node should act as a previous node for created DLL and right pointer should act as next node.
The solution should not allocate extra memory for DLL nodes. It should use binary tree nodes for creating DLL i.e. only change of pointers is allowed
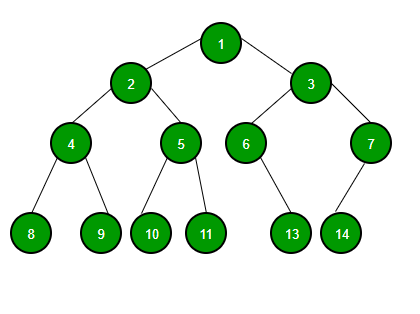

For example, for the tree on left side, Doubly Linked List can be,
1 2 3 7 6 5 4 8 9 10 11 13 14 or
1 3 2 4 5 6 7 14 13 11 10 9 8.
We can do this by doing a spiral order traversal in O(n) time and O(n) extra space. The idea is to use deque (Double-ended queue) that can be expanded or contracted on both ends (either its front or its back). We do something similar to level order traversal but to maintain spiral order, for every odd level, we dequeue node from the front and inserts its left and right children in the back of the deque data structure. And for each even level, we dequeue node from the back and inserts its right and left children in the front of deque. We also maintain a stack to store Binary Tree nodes. Whenever we pop nodes from deque, we push that node into stack. Later, we pop all nodes from stack and push the nodes in the beginning of the list. We can avoid use of stack if we maintain a tail pointer that always points to last node of DLL and inserts nodes in O(1) time in the end.
Question: given a binary tree, write an algorithm to convert the tree into a double-linked list. The list must be as if the tree is traversed in zig-zag and level order.
Solution: let's first understand what the objective is. By zig-zag level order, the question means that we need to traverse the tree in level order, a.k.a breadth first, such that the next level is traversed in the oposite direction to the current level. For example, take a look at this tree:
A zig-zag level-order traversal creates the list 1, 2, 3, 5, 4. It doesn't matter which direction the root is printed because there is only one node. However, since the second level is printed left to right, 2 then 3, the third level is printed from right to left, 5 then 4.
struct Node* bt2ZigZagDoubleLinkedList(struct Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Node* head = root;
struct Node* listIT = NULL;
struct Node* prevNode = NULL;
stack left2RightStack;
stack right2LeftStack;
left2RightStack.push(root);
while (!left2RightStack.empty())
{
//add nodes from left to right to the list
while (!left2RightStack.empty())
{
//set previous node
prevNode = listIT;
//pop a node in left2RightStack and add it to list
listIT = left2RightStack.top();
left2RightStack.pop();
//add child nodes of the newly node in right to left direction
if (listIT->left != NULL)
right2LeftStack.push(listIT->left);
if (listIT->right != NULL)
right2LeftStack.push(listIT->right);
//set left pointer of current node to the node in front of it
listIT->left = prevNode;
//the previous node points to the current node in list
if (prevNode != NULL)
prevNode->right = listIT;
}
//add nodes from right to left to the list
while (!right2LeftStack.empty())
{
prevNode = listIT;
listIT = right2LeftStack.top();
right2LeftStack.pop();
if(listIT->right != NULL)
left2RightStack.push(listIT->right);
if(listIT->left != NULL)
left2RightStack.push(listIT->left);
listIT->left = prevNode;
if (prevNode != NULL)
prevNode->right = listIT;
}
}
//connect linked the end node of list to NULL and the node in front of it
listIT->right = NULL;
listIT->left = prevNode;
return head;
}
- After the first inner loop traverses a level from left to right, the second inner while loop traverses the next level from right to left. The process is similar to that of left-to-right traversal. The only difference is that we add right children to the stack before left children.
- Once all nodes have been added into the double linked list, we'll connect the end node of the list to the node before it and to a null node as the node after it.
- Lastly, we return head. In the beginning, we have already assigned head to the root node which is the first node of the list, so head is point at the first node in the list.
