cracking-the-coding-interview chap18-Q12.java
Given a 2D binary matrix filled with 0's and 1's, find the largest rectangle containing all ones and return its area.
http://prismoskills.appspot.com/lessons/Dynamic_Programming/Chapter_07_-_Submatrix_with_largest_sum.jsp
int findMaxSum (int matrix[numRows][numCols])
{
int maxSum=0;
for (int left = 0; left < numCols; left++)
{
int temp[numRows] = {0};
for (int right = left; right < numCols; right++)
{
// Find sum of every mini-row between left and right columns and save it into temp[]
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; ++i)
temp[i] += matrix[i][right];
// Find the maximum sum subarray in temp[].
int sum = kadane(temp, numRows);
if (sum > maxSum)
maxSum = sum;
}
}
return maxSum;
}
How the algorithm executes:

http://www.shuatiblog.com/blog/2014/08/01/Max-Sum-In-2D-Array/
O(n3)
https://tianrunhe.wordpress.com/category/questions-from-careercup/
O(n^4)
Go through each submatrix (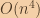 of them) and compute their sums, keeping track of the curren maximum. Without additional optimization, the computation of sums cost
of them) and compute their sums, keeping track of the curren maximum. Without additional optimization, the computation of sums cost 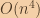 , giving total a
, giving total a  algorithm. We can precompute some sums to reduce the total costs to
algorithm. We can precompute some sums to reduce the total costs to 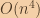 :
:
Let’s say we need to compute the sum of the submatrix (startRow, startCol) -> (endRow, endCol), . We can first pre-compute the sum of (0,0) -> (endRow, endCol) denote as
. We can first pre-compute the sum of (0,0) -> (endRow, endCol) denote as 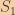 , the sum of (0,0) -> (endRow, startCol-1) denote as
, the sum of (0,0) -> (endRow, startCol-1) denote as 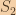 , the sum of (0,0) -> (startRow-1, endCol) denote as
, the sum of (0,0) -> (startRow-1, endCol) denote as  and the sum of (0,0) -> (startRow-1, startCol-1) denote as
and the sum of (0,0) -> (startRow-1, startCol-1) denote as 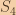 , then
, then 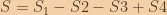 . Hence, we can pre-compute sums of (0,0) -> (i,j) for every pair of (i,j). Then we searching, the computation of sum of submatrix will only need a single operation.
. Hence, we can pre-compute sums of (0,0) -> (i,j) for every pair of (i,j). Then we searching, the computation of sum of submatrix will only need a single operation.
https://github.com/wzhishen/cracking-the-coding-interview/blob/master/src/chap18/Q12.java
Code http://analgorithmist.blogspot.com/2012/10/applying-kadanes-algorithm-to-2-d-array.html
http://alexeigor.wikidot.com/kadane
Maximum Rectangle | N00tc0d3r
Also check http://ihaventyetdecided.blogspot.com/2010/10/kadanes-2d-algorithm.html
http://massivealgorithms.blogspot.com/2014/08/find-max-sum-in-2d-array-programming.html
Read full article from Dynamic Programming | Set 27 (Maximum sum rectangle in a 2D matrix)
Given a 2D binary matrix filled with 0's and 1's, find the largest rectangle containing all ones and return its area.
This problem is mainly an extension of Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray for 1D array.
The naive solution for this problem is to check every possible rectangle in given 2D array. This solution requires 4 nested loops and time complexity of this solution would be O(n^4).
The idea is to fix the left and right columns one by one and find the maximum sum contiguous rows for every left and right column pair.
We basically find top and bottom row numbers (which have maximum sum) for every fixed left and right column pair. To find the top and bottom row numbers, calculate sun of elements in every row from left to right and store these sums in an array say temp[]. So temp[i] indicates sum of elements from left to right in row i. If we apply Kadane’s 1D algorithm on temp[], and get the maximum sum subarray of temp, this maximum sum would be the maximum possible sum with left and right as boundary columns.
Explanation from http://www.algorithmist.com/index.php/UVa_108- First, calculate the vertical prefix sum for all columns (an O(n2) algorithm).
- Second, assume that the maximum sub-array will be between row a and row b, inclusive. There are only O(n2) a, b pairs such that a < b. Try each of them.
- Since we already have the vertical prefix sum for all columns, the sum of elements in arr[a..b][c] for column c can be computed in O(1) time. This allows us to imagine each column sum as if it is a single element of a one-dimensional array across all columns (one dimensional array with one row and n columns).
- There’s an O(n) algorithm to compute the maximum sub-array for a one-dimensional array, known as Kadane’s Algorithm.
- Applying the Kadane’s algorithm inside each a and b combination gives the total complexity of O(n3)
void findMaxSum(int M[][COL]){ // Variables to store the final output int maxSum = INT_MIN, finalLeft, finalRight, finalTop, finalBottom; int left, right, i; int temp[ROW], sum, start, finish; // Set the left column for (left = 0; left < COL; ++left) { // Initialize all elements of temp as 0 memset(temp, 0, sizeof(temp)); // Set the right column for the left column set by outer loop for (right = left; right < COL; ++right) { // Calculate sum between current left and right for every row 'i' for (i = 0; i < ROW; ++i) temp[i] += M[i][right]; // Find the maximum sum subarray in temp[]. The kadane() function // also sets values of start and finish. So 'sum' is sum of // rectangle between (start, left) and (finish, right) which is the // maximum sum with boundary columns strictly as left and right. sum = kadane(temp, &start, &finish, ROW); // Compare sum with maximum sum so far. If sum is more, then update // maxSum and other output values if (sum > maxSum) { maxSum = sum; finalLeft = left; finalRight = right; finalTop = start; finalBottom = finish; } } } // Print final values printf("(Top, Left) (%d, %d)\n", finalTop, finalLeft); printf("(Bottom, Right) (%d, %d)\n", finalBottom, finalRight); printf("Max sum is: %d\n", maxSum);}int kadane(int* arr, int* start, int* finish, int n){ // initialize sum, maxSum and int sum = 0, maxSum = INT_MIN, i; // Just some initial value to check for all negative values case *finish = -1; // local variable int local_start = 0; for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { sum += arr[i]; if (sum < 0) { sum = 0; local_start = i+1; } else if (sum > maxSum) { maxSum = sum; *start = local_start; *finish = i; } } // There is at-least one non-negative number if (*finish != -1) return maxSum; // Special Case: When all numbers in arr[] are negative maxSum = arr[0]; *start = *finish = 0; // Find the maximum element in array for (i = 1; i < n; i++) { if (arr[i] > maxSum) { maxSum = arr[i]; *start = *finish = i; } } return maxSum;}int findMaxSum (int matrix[numRows][numCols])
{
int maxSum=0;
for (int left = 0; left < numCols; left++)
{
int temp[numRows] = {0};
for (int right = left; right < numCols; right++)
{
// Find sum of every mini-row between left and right columns and save it into temp[]
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; ++i)
temp[i] += matrix[i][right];
// Find the maximum sum subarray in temp[].
int sum = kadane(temp, numRows);
if (sum > maxSum)
maxSum = sum;
}
}
return maxSum;
}
How the algorithm executes:
http://www.shuatiblog.com/blog/2014/08/01/Max-Sum-In-2D-Array/
O(n3)
Try convert this question to “max sum in 1D array” by sum up all numbers in the same column. (we know that in 1D array, the algo runs O(n) time)
There’s in total O(n2) combinations of ways to sum up a column. So the total time complexity is O(n3).
public int maxSum(int[][] A) {
int m = A.length;
int n = A[0].length;
int maxResult = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int[] temp = new int[n];
for (int j = i; j < m; j++) {
// from row#i to row#(m-1), add the number into temp[]
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
temp[k] += A[j][k];
}
// find max sum for 1D array
maxResult = Math.max(maxResult, maxSum(temp));
}
}
return maxResult;
}
private int maxSum(int[] B) {
int sumSoFar = 0;
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < B.length; i++) {
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, sumSoFar + B[i]);
sumSoFar = Math.max(0, sumSoFar + B[i]);
}
return maxSum;
}https://tianrunhe.wordpress.com/category/questions-from-careercup/
O(n^4)
Go through each submatrix (
Let’s say we need to compute the sum of the submatrix (startRow, startCol) -> (endRow, endCol),
private static int[][] sums;private static void preComputeSums(int[][] matrix) { sums = new int[matrix.length][matrix[0].length]; for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; ++j) { if (i == 0 && j == 0) sums[i][j] = matrix[i][j]; else if (j == 0) sums[i][j] = sums[i - 1][j] + matrix[i][j]; else if (i == 0) sums[i][j] = sums[i][j - 1] + matrix[i][j]; else sums[i][j] = sums[i - 1][j] + sums[i][j - 1] - sums[i - 1][j - 1] + matrix[i][j]; } }}private static int computeSum(int[][] matrix, int startRow, int endRow, int startCol, int endCol) { if (startRow == 0 && startCol == 0) return sums[endRow][endCol]; else if (startRow == 0) return sums[endRow][endCol] - sums[endRow][startCol - 1]; else if (startCol == 0) return sums[endRow][endCol] - sums[startRow - 1][endCol]; else return sums[endRow][endCol] - sums[endRow][startCol - 1] - sums[startRow - 1][endCol] + sums[startRow - 1][startCol - 1];}public static int[][] findSubmatrixWithMaxSum(int[][] matrix) { preComputeSums(matrix); int startRow = 0, endRow = 0; int startCol = 0, endCol = 0; int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; ++j) { for (int rowPtr = i; rowPtr < matrix.length; ++rowPtr) { for (int colPtr = j; colPtr < matrix[rowPtr].length; ++colPtr) { int sum = computeSum(matrix, i, rowPtr, j, colPtr); if (sum > maxSum) { maxSum = sum; startRow = i; endRow = rowPtr; startCol = j; endCol = colPtr; } } } } } int[][] subMatrix = new int[endRow - startRow + 1][endCol - startCol + 1]; for (int i = startRow; i <= endRow; ++i) System.arraycopy(matrix[i], startCol, subMatrix[i - startRow], 0, endCol - startCol + 1); return subMatrix;}| //brute force: O(n^6) time. //returns [r1, c1, r2, c2, sum] where (r1,c1),(r2,c2) represents //the diagonal of submatrix | |
| static int[] findLargestSubmatrix(int[][] matrix) { | |
| int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; | |
| int[] ret = {-1, -1, -1, -1, 0}; | |
| for (int r1 = 0; r1 < matrix.length; ++r1) { | |
| for (int r2 = r1; r2 < matrix.length; ++r2) { | |
| for (int c1 = 0; c1 < matrix[0].length; ++c1) { | |
| for (int c2 = c1; c2 < matrix[0].length; ++c2) { | |
| int sum = getSum(matrix, r1, c1, r2, c2); | |
| if (sum > maxSum) { | |
| maxSum = sum; | |
| ret = new int[] {r1, c1, r2, c2, sum}; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| return ret; | |
| } |
Code http://analgorithmist.blogspot.com/2012/10/applying-kadanes-algorithm-to-2-d-array.html
http://alexeigor.wikidot.com/kadane
Maximum Rectangle | N00tc0d3r
Also check http://ihaventyetdecided.blogspot.com/2010/10/kadanes-2d-algorithm.html
http://massivealgorithms.blogspot.com/2014/08/find-max-sum-in-2d-array-programming.html
Read full article from Dynamic Programming | Set 27 (Maximum sum rectangle in a 2D matrix)