http://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/hashtable/leetcode-737-sentence-similarity-ii/
X. DFS
Time complexity: O(|Pairs| + |words1|)
Space complexity: O(|Pairs|)
C++ / DFS Optimized
X. BFS
http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/8053934.html
https://protegejj.gitbooks.io/algorithm-practice/content/737-sentence-similarity-ii.html
Space complexity: O(|Pairs|)
https://gist.github.com/aquawj/1d8b62533b7a5d6633013cd0d5a47a43
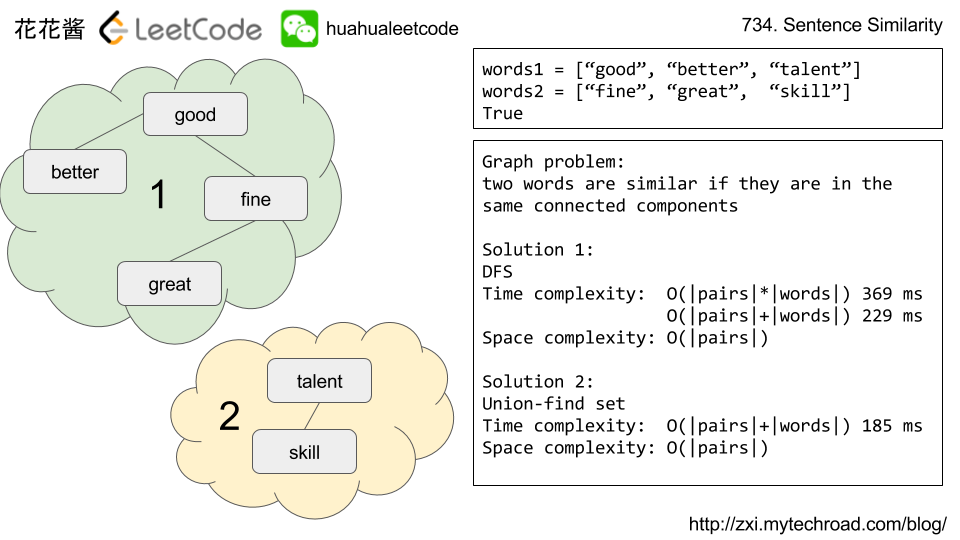
Given two sentences
words1, words2 (each represented as an array of strings), and a list of similar word pairs pairs, determine if two sentences are similar.
For example,
words1 = ["great", "acting", "skills"] and words2 = ["fine", "drama", "talent"] are similar, if the similar word pairs are pairs = [["great", "good"], ["fine", "good"], ["acting","drama"], ["skills","talent"]].
Note that the similarity relation is transitive. For example, if “great” and “good” are similar, and “fine” and “good” are similar, then “great” and “fine” are similar.
Similarity is also symmetric. For example, “great” and “fine” being similar is the same as “fine” and “great” being similar.
Also, a word is always similar with itself. For example, the sentences
words1 = ["great"], words2 = ["great"], pairs = [] are similar, even though there are no specified similar word pairs.
Finally, sentences can only be similar if they have the same number of words. So a sentence like
words1 = ["great"] can never be similar to words2 = ["doubleplus","good"].
Note:
- The length of
words1andwords2will not exceed1000. - The length of
pairswill not exceed2000. - The length of each
pairs[i]will be2. - The length of each
words[i]andpairs[i][j]will be in the range[1, 20].
Time complexity: O(|Pairs| + |words1|)
Space complexity: O(|Pairs|)
X. Time complexity: O(|Pairs| * |words1|)
Space complexity: O(|Pairs|)
public boolean areSentencesSimilarTwo(String[] words1, String[] words2, String[][] pairs) {
if (words1.length != words2.length) {
return false;
}
// Build the graph of pairs
HashMap<String, Set<String>> pairMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String[] pair : pairs) {
// Create keys(words in [][]pairs without duplication) and empty set
if (!pairMap.containsKey(pair[0])) {
pairMap.put(pair[0], new HashSet<String>());
}
if (!pairMap.containsKey(pair[1])) {
pairMap.put(pair[1], new HashSet<String>());
}
// Add the corresponding pairs to each other
pairMap.get(pair[0]).add(pair[1]);
pairMap.get(pair[1]).add(pair[0]);
}
// Iterate throught each word in both input strings and do DFS search
for (int i = 0; i < words1.length; i++) {
// If same, then we don't need to do DFS search
if (words1[i].equals(words2[i])) continue;
// If they are not the same and no such strings in the pairs
if (!pairMap.containsKey(words1[i]) || !pairMap.containsKey(words2[i])) return false;
// Do DFS search, initialize the set to prevent revisiting.
if (!dfs(words1[i], words2[i], pairMap, new HashSet<>())) return false;
}
return true;
}
public boolean dfs(String source, String target, HashMap<String, Set<String>> pairMap, HashSet<String> visited) {
if (pairMap.get(source).contains(target)) {
return true;
}
// Mark as visited
visited.add(source);
for (String next : pairMap.get(source)) {
// DFS other connected node, except the mirrowed string
if (!visited.contains(next) && next.equals(target) ||
!visited.contains(next) && dfs(next, target, pairMap, visited)) {
return true;
}
}
// We've done dfs still can't find the target
return false;
}
Time complexity: O(|Pairs| + |words1|)
Space complexity: O(|Pairs|)
C++ / DFS Optimized
bool areSentencesSimilarTwo(vector<string>& words1, vector<string>& words2, vector<pair<string, string>>& pairs) {
if (words1.size() != words2.size()) return false;
g_.clear();
ids_.clear();
for (const auto& p : pairs) {
g_[p.first].insert(p.second);
g_[p.second].insert(p.first);
}
int id = 0;
for (const auto& p : pairs) {
if(!ids_.count(p.first)) dfs(p.first, ++id);
if(!ids_.count(p.second)) dfs(p.second, ++id);
}
for (int i = 0; i < words1.size(); ++i) {
if (words1[i] == words2[i]) continue;
auto it1 = ids_.find(words1[i]);
auto it2 = ids_.find(words2[i]);
if (it1 == ids_.end() || it2 == ids_.end()) return false;
if (it1->second != it2->second) return false;
}
return true;
}
private:
bool dfs(const string& curr, int id) {
ids_[curr] = id;
for (const auto& next : g_[curr]) {
if (ids_.count(next)) continue;
if (dfs(next, id)) return true;
}
return false;
}
unordered_map<string, int> ids_;
unordered_map<string, unordered_set<string>> g_;
X. BFS
http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/8053934.html
这道题是之前那道Sentence Similarity的拓展,那道题说单词之间不可传递,于是乎这道题就变成可以传递了,那么难度就增加了。不过没有关系,还是用我们的经典老三样来解,BFS,DFS,和Union Find。我们先来看BFS的解法,其实这道题的本质是无向连通图的问题,那么首先要做的就是建立这个连通图的数据结构,对于每个结点来说,我们要记录所有和其相连的结点,所以我们建立每个结点和其所有相连结点集合之间的映射,比如对于这三个相似对(a, b), (b, c),和(c, d),我们有如下的映射关系:
a -> {b}
b -> {a, c}
c -> {b, d}
d -> {c}
那么如果我们要验证a和d是否相似,就需要用到传递关系,a只能找到b,b可以找到a,c,为了不陷入死循环,我们将访问过的结点加入一个集合visited,那么此时b只能去,c只能去d,那么说明a和d是相似的了。那么我们用for循环来比较对应位置上的两个单词,如果二者相同,那么直接跳过去比较接下来的。否则就建一个访问即可visited,建一个队列queue,然后把words1中的单词放入queue,建一个布尔型变量succ,标记是否找到,然后就是传统的BFS遍历的写法了,从队列中取元素,如果和其相连的结点中有words2中的对应单词,标记succ为true,并break掉。否则就将取出的结点加入队列queue,并且遍历其所有相连结点,将其中未访问过的结点加入队列queue继续循环
(1) 用union find的关键就是要给每个pair里的word分配一个unique id,然后用map存string到id的关系
(2) 在遍历words1和words2,如果map里面没有words1或words2当前的词或者通过find我们发现当前word1和word2不在一个集合里,return false
Union Find: 时间复杂度O(k + n), 空间复杂度O(k)
class Solution {
public boolean areSentencesSimilarTwo(String[] words1, String[] words2, String[][] pairs) {
if (words1.length != words2.length) {
return false;
}
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(2 * pairs.length);
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int id = 0;
for (String[] pair : pairs) {
for (String word : pair) {
if (!map.containsKey(word)) {
map.put(word, id);
++id;
}
}
uf.union(map.get(pair[0]), map.get(pair[1]));
}
for (int i = 0; i < words1.length; i++) {
String word1 = words1[i];
String word2 = words2[i];
if (word1.equals(word2)) {
continue;
}
if (!map.containsKey(word1) || !map.containsKey(word2) || uf.find(map.get(word1)) != uf.find(map.get(word2))) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
class UnionFind {
int[] sets;
int[] size;
int count;
public UnionFind(int n) {
sets = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
count = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sets[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int node) {
while (node != sets[node]) {
node = sets[node];
}
return node;
}
public void union(int i, int j) {
int node1 = find(i);
int node2 = find(j);
if (node1 == node2) {
return;
}
if (size[node1] < size[node2]) {
sets[node1] = node2;
size[node2] += size[node1];
}
else {
sets[node2] = node1;
size[node1] += size[node2];
}
--count;
}
}
C++ / Union Find
Time complexity: O(|Pairs| + |words1|)Space complexity: O(|Pairs|)
bool Union(const string& word1, const string& word2) {
const string& p1 = Find(word1, true);
const string& p2 = Find(word2, true);
if (p1 == p2) return false;
parents_[p1] = p2;
return true;
}
const string& Find(const string& word, bool create = false) {
if (!parents_.count(word)) {
if (!create) return word;
return parents_[word] = word;
}
string w = word;
while (w != parents_[w]) {
parents_[w] = parents_[parents_[w]];
w = parents_[w];
}
return parents_[w];
}
private:
unordered_map<string, string> parents_;
};
class Solution {
public:
bool areSentencesSimilarTwo(vector<string>& words1, vector<string>& words2, vector<pair<string, string>>& pairs) {
if (words1.size() != words2.size()) return false;
UnionFindSet s;
for (const auto& pair : pairs)
s.Union(pair.first, pair.second);
for (int i = 0; i < words1.size(); ++i)
if (s.Find(words1[i]) != s.Find(words2[i])) return false;
return true;
}
https://www.jianshu.com/p/43fe7cc6797bhttps://gist.github.com/aquawj/1d8b62533b7a5d6633013cd0d5a47a43
public boolean areSentencesSimilarTwo(String[] a, String[] b, String[][] pairs) {
if (a.length != b.length)
return false;
Map<String, String> m = new HashMap<>();
for (String[] p : pairs) {
String parent1 = find(m, p[0]), parent2 = find(m, p[1]);
if (!parent1.equals(parent2))
m.put(parent1, parent2);
}
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (!a[i].equals(b[i]) && !find(m, a[i]).equals(find(m, b[i])))
return false;
return true;
}
private String find(Map<String, String> m, String s) {
if (!m.containsKey(s))
m.put(s, s);
return s.equals(m.get(s)) ? s : find(m, m.get(s));
}
题解:用map<String, String>来实现union and find
public boolean areSentencesSimilarTwo(String[] words1, String[] words2, String[][] pairs) {
if (words1.length != words2.length)
return false;
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String[] pair : pairs) {
String parent0 = find(pair[0], map);
String parent1 = find(pair[1], map);
if (!parent0.equals(parent1))
map.put(parent0, parent1);
}
int n = words1.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!words1[i].equals(words2[i]) && !find(words1[i], map).equals(find(words2[i], map)))
return false;
}
return true;
}
private String find(String word, Map<String, String> map) {
if (!map.containsKey(word))
return word;
String str = word;
while (map.containsKey(str)) {
str = map.get(str);
}
map.put(word, str);
return str;
}
X.
https://protegejj.gitbooks.io/algorithm-practice/content/737-sentence-similarity-ii.html
https://medium.com/@rebeccahezhang/leetcode-737-sentence-similarity-ii-2ca213f10115
https://medium.com/@rebeccahezhang/leetcode-737-sentence-similarity-ii-2ca213f10115
DFS: 时间复杂度O(nk), 其中n为words的长度, k为pairs的长度,空间复杂度O(k)
X.
public boolean areSentencesSimilarTwo(String[] words1, String[] words2, String[][] pairs) {
if (words1.length != words2.length) {
return false;
}
// Build the graph of pairs
HashMap<String, Set<String>> pairMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String[] pair : pairs) {
// Create keys(words in [][]pairs without duplication) and empty set
if (!pairMap.containsKey(pair[0])) {
pairMap.put(pair[0], new HashSet<String>());
}
if (!pairMap.containsKey(pair[1])) {
pairMap.put(pair[1], new HashSet<String>());
}
// Add the corresponding pairs to each other
pairMap.get(pair[0]).add(pair[1]);
pairMap.get(pair[1]).add(pair[0]);
}
// Iterate throught each word in both input strings and do DFS search
for (int i = 0; i < words1.length; i++) {
// If same, then we don't need to do DFS search
if (words1[i].equals(words2[i]))
continue;
// If they are not the same and no such strings in the pairs
if (!pairMap.containsKey(words1[i]) || !pairMap.containsKey(words2[i]))
return false;
// Do DFS search, initialize the set to prevent revisiting.
if (!dfs(words1[i], words2[i], pairMap, new HashSet<>()))
return false;
}
return true;
}
public boolean dfs(String source, String target, HashMap<String, Set<String>> pairMap, HashSet<String> visited) {
if (pairMap.get(source).contains(target)) {
return true;
}
// Mark as visited
visited.add(source);
for (String next : pairMap.get(source)) {
// DFS other connected node, except the mirrowed string
if (!visited.contains(next) && next.equals(target)
|| !visited.contains(next) && dfs(next, target, pairMap, visited)) {
return true;
}
}
// We've done dfs still can't find the target
return false;
}
http://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/hashtable/leetcode-737-sentence-similarity-ii/
Time complexity: O(|Pairs| + |words1|)
Space complexity: O(|Pairs|)
C++ / DFS Optimized
bool areSentencesSimilarTwo(vector<string>& words1, vector<string>& words2, vector<pair<string, string>>& pairs) {
if (words1.size() != words2.size()) return false;
g_.clear();
ids_.clear();
for (const auto& p : pairs) {
g_[p.first].insert(p.second);
g_[p.second].insert(p.first);
}
int id = 0;
for (const auto& p : pairs) {
if(!ids_.count(p.first)) dfs(p.first, ++id);
if(!ids_.count(p.second)) dfs(p.second, ++id);
}
for (int i = 0; i < words1.size(); ++i) {
if (words1[i] == words2[i]) continue;
auto it1 = ids_.find(words1[i]);
auto it2 = ids_.find(words2[i]);
if (it1 == ids_.end() || it2 == ids_.end()) return false;
if (it1->second != it2->second) return false;
}
return true;
}
private:
bool dfs(const string& curr, int id) {
ids_[curr] = id;
for (const auto& next : g_[curr]) {
if (ids_.count(next)) continue;
if (dfs(next, id)) return true;
}
return false;
}
unordered_map<string, int> ids_;
unordered_map<string, unordered_set<string>> g_;
bool areSentencesSimilarTwo(vector<string>& words1, vector<string>& words2, vector<pair<string, string>> pairs) { if (words1.size() != words2.size()) return false; unordered_map<string, unordered_set<string>> m; for (auto pair : pairs) { m[pair.first].insert(pair.second); m[pair.second].insert(pair.first); } for (int i = 0; i < words1.size(); ++i) { unordered_set<string> visited; if (!helper(m, words1[i], words2[i], visited)) return false; } return true; } bool helper(unordered_map<string, unordered_set<string>>& m, string& cur, string& target, unordered_set<string>& visited) { if (cur == target) return true; visited.insert(cur); for (string word : m[cur]) { if (!visited.count(word) && helper(m, word, target, visited)) return true; } return false; }