https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-array-for-maximum-sum/
Given an integer array
A, you partition the array into (contiguous) subarrays of length at most K. After partitioning, each subarray has their values changed to become the maximum value of that subarray.
Return the largest sum of the given array after partitioning.
Example 1:
Input: A = [1,15,7,9,2,5,10], K = 3 Output: 84 Explanation: A becomes [15,15,15,9,10,10,10]
Note:
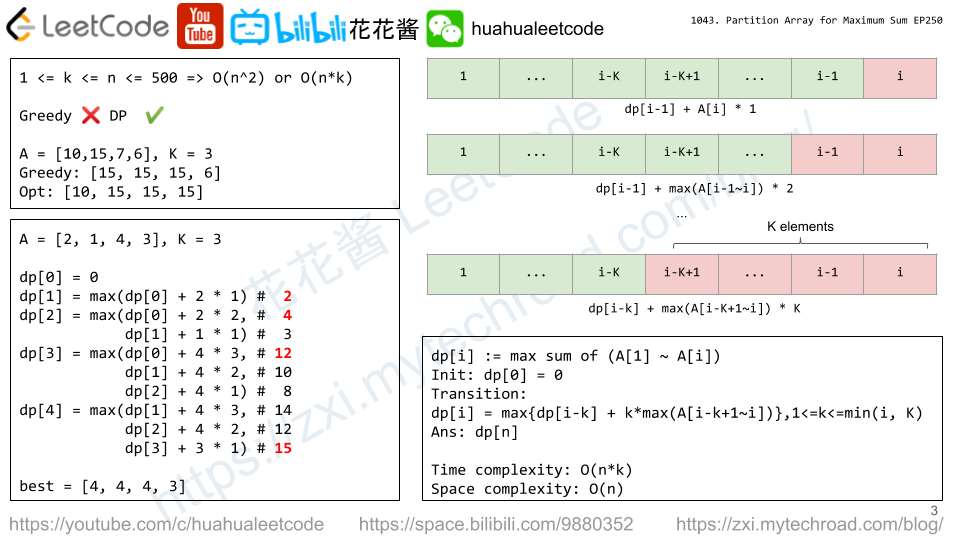
1 <= K <= A.length <= 5000 <= A[i] <= 10^6
X. DP
https://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/dynamic-programming/leetcode-1043-partition-array-for-maximum-sum/
Time complexity: O(n*k)
Space complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
dp[i] := max sum of A[1] ~ A[i]
init: dp[0] = 0
transition: dp[i] = max{dp[i – k] + max(A[i-k:i]) * k}, 1 <= k <= min(i, K)
ans: dp[n]
init: dp[0] = 0
transition: dp[i] = max{dp[i – k] + max(A[i-k:i]) * k}, 1 <= k <= min(i, K)
ans: dp[n]
A = | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | K = 3 dp[0] = 0 dp[1] = max(dp[0] + 2 * 1) = 2 dp[2] = max(dp[0] + 2 * 2, dp[1] + 1 * 1) = max(4, 3) = 4 dp[3] = max(dp[0] + 4 * 3, dp[1] + 4 * 2, dp[2] + 4 * 1) = max(12, 10, 8) = 12 dp[4] = max(dp[1] + 4 * 3, dp[2] + 4 * 2, dp[3] + 3 * 1) = max(14, 12, 15) = 15 best = | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-array-for-maximum-sum/discuss/291057/Java-visualize-the-pattern
// Let k be 2
// Focus on "growth" of the pattern
// Define A' to be a partition over A that gives max sum
// #0
// A = {1}
// A'= {1} => 1
// #1
// A = {1, 2}
// A'= {1}{2} => 1 + 2 => 3 X
// A'= {1, 2} => {2, 2} => 4 AC
// #2
// A = {1, 2, 9}
// A'= {1, 2}{9} => {2, 2}{9} => 4 + 9 => 13 X
// A'= {1}{2, 9} => {1}{9, 9} => 1 + 18 => 19 AC
// #3
// A = {1, 2, 9, 30}
// A'= {1}{2, 9}{30} => {1}{9, 9}{30} => 19 + 30 => 49 X
// A'= {1, 2}{9, 30} => {2, 2}{30, 30} => 4 + 60 => 64 AC
// Now, label each instance. Use F1() to represent how A is partitioned and use F2() to represent
// the AC value of that partition. F2() is the dp relation we are looking for.
// #4
// A = {1, 2, 9, 30, 5}
// A'= F1(#3){5} => F2(#3) + 5 => 69 X
// A'= F1(#2){30, 5} => F2(#2) + 30 + 30 => 79 AC
// => F2(#4) = 79
dp[i] record the maximum sum we can get considering A[0] ~ A[i]To get
dp[i], we will try to change k last numbers separately to the maximum of them,where
k = 1 to k = K.Complexity
Time
O(NK), Space O(N) public int maxSumAfterPartitioning(int[] A, int K) {
int N = A.length, dp[] = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int curMax = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <= K && i - k + 1 >= 0; ++k) {
curMax = Math.max(curMax, A[i - k + 1]);
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], (i >= k ? dp[i - k] : 0) + curMax * k);
}
}
return dp[N - 1];
}- 输入一个整数数组, 然后把这个整数数组划分成x个小数组, 每个小数组的长度不超过K,
- 划分完以后, 把每个小数组里面的元素的值替换成这个小数组里面的最大值
- 求替换完以后的数组的和的最大值
- 这个题目可以用动态规划做, 在之前的总结里面, 感悟到动态规划的核心是要定义一个连续的dp状态, 这样才可以把大状态切分成小状态, 形成重叠子问题
- 这里, 可以用dp[i][j]表示一个状态, 至于状态是什么, 我们可以先尝试表达最终结果, 看看是否可行; 如果不行, 再尝试表达中间结果。 比如, dp[i][j]就可以表示从[i,j]的partition后的最大sum;
- 考虑递推关系的时候, 通常可以先考虑到最后一步开始, 这里, 我们可以考虑尾部的几个数的partition,
那么, 最后一次的结果就可以和之前的结果形成一个递推关系
dp[i][j] = max{dp[i][t] + count * max(A[t+1], …, A[j])} for t = i…j-1 - 实际上, 这里的递推关系里面, dp变化的只是第二个维度, 第一个维度始终是i,
所以, dp[i] = max{dp[t] + count * max(A[t+1]….A[i])} for t = i-K…i-1 - 还有一个特殊情况就是前面k个元素, 需要直接取最大值然后计算
- 求区间最大值, 本来需要先计算一下保存结果, 但是如果我们从后往前遍历的话,直接就可以用一个变量保存结果
public int maxSumAfterPartitioning(int[] A, int K) { int[] dp = new int[A.length]; dp[0] = A[0]; int max = A[0]; for(int i = 0; i < A.length; ++i) { if(i-K >= 0) { max = A[i]; for(int j = i-1; j >= i-K; --j) { dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + (i-j) * max); max = Math.max(max, A[j]); } } else { max = Math.max(max, A[i]); dp[i] = max * (i+1); } } return dp[A.length-1]; }https://www.acwing.com/solution/LeetCode/content/2000/
(动态规划) O(nK)O(nK) f(i)f(i) 表示划分了前 ii 个数字产生的最大和。这里的 ii 下标从 1 开始。 初始时 f(0)=0f(0)=0,其余为 -1。转移时,考虑第 ii 个数字与之前多少个数字组成一个 subarray。故枚举 jj 从 1 到 KK,取 f(i−j)+curmax∗jf(i−j)+curmax∗j 的最大值。这里的 curmaxcurmax 为区间的最大值,可以在枚举转移的时候更新。 最终答案为 f(n)f(n)。 时间复杂度 状态数有 O(n)O(n) 个,转移有 O(K)O(K) 个,故需要 O(nK)O(nK) 的时间。 空间复杂度 只需要一个空间为 O(n)O(n) 的数组,故空间复杂度为 O(n)O(n)。X.
https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-array-for-maximum-sum/discuss/299443/Java-O(NK).-Faster-than-99.82.-Less-memory-than-100.-With-Explanation.
The dynamic programming solution works here because the problem has an optimal substructure and overlapping subproblems as in the following example:
Let
A = [9, 10, 2, 5] and K = 3
Let
The following are base cases to initialize the memo array:
S[n1, n2, ..., ni] be the solution to subarray [n1, n2, ..., ni].The following are base cases to initialize the memo array:
S[9] = 9 (i.e., memo[0] = 9)
S[9, 10] = 20 (i.e., memo[1] = 20)
S[9, 10, 2] = 30 (i.e., memo[2] = 30)
Here we do the real work, where you need to "loop" through a K-sized window before the new value to be considered, including the new value, which in this case the new value is 5:
S[9, 10, 2, 5] = max(S[9] + S[10, 2, 5], S[9, 10] + S[2, 5], S[9, 10, 2] + S[5]) = 39
The window we "looped" through above is [10, 2, 5].
From the formula above, we see that the overlapping subproblem is in using the solutions from previous solutions stored in the memo, e.g.,
S[9], S[9, 10], and S[9, 10, 2]. The optimal substructure comes from the fact that the solution to S[9, 10, 2, 5] is solved by using solutions to previously calculated solutions. public int maxSumAfterPartitioning(int[] A, int K) {
int[] memo = new int[A.length];
memo[0] = A[0];
int initMax = A[0];
for(int i = 1; i < K; ++i) {
if (A[i] > initMax) {
initMax = A[i];
}
memo[i] = (i+1) * initMax;
}
for (int i = K; i < A.length; ++i) {
int cur = 0;
int kIntervalMax = A[i];
// Backtrack up to K-1 indices to calculate current maximum for memo[i].
for (int j = 1; j <= K; ++j) {
// Keep track of the current maximum in the window [i-j+1, i].
if (A[i-j+1] > kIntervalMax) {
kIntervalMax = A[i-j+1];
}
// cur is the candidate for the solution to memo[i] as we backtrack the K-1 window.
cur = memo[i-j] + j * kIntervalMax;
if (cur > memo[i]) {
memo[i] = cur;
}
}
}
return memo[A.length-1];
}