[CC150v4] 4.7 Check Subtree - Shuatiblog.com
Updated on Jan 26th, 2015: do we have to use sentinals for this purpose? Well, the answer is NO, cuz a preorder and a inorder can uniquely define a binary tree.
However, this solution is very memory intensive.
Time complexity:
If k is the number of occurrences of T2's root in T1, the worst case runtime can be characterized as O(n + k * m).
However, there can be a lot of pruning for this solution, so it's NOT necessarily slower than Solution 1.
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/check-if-a-binary-tree-is-subtree-of-another-binary-tree/
The algorithm is essentially the same as given in the book, except that I first preprocess the large tree to collect a set of subtrees whose size is the same as the small binary tree. The intuition is that since T2 is much smaller than T1, it is better to check the subtrees from lower levels (nodes at higher level might have too many nodes in their subtree, hence cannot match with T2). The extreme cases are complete binary trees and a linked-list like trees. The time complexity is , where
, where 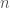 is the size of the large binary tree and
is the size of the large binary tree and 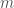 is the size of the small binary tree. The space complexity is
is the size of the small binary tree. The space complexity is 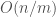 for storing the roots of the possible subtrees from T1 that might match with T2.
for storing the roots of the possible subtrees from T1 that might match with T2.
http://blog.csdn.net/navyifanr/article/details/19234825
http://www.careercup.com/question?id=5164767748554752
Read full article from [CC150v4] 4.7 Check Subtree - Shuatiblog.com
You have two very large binary trees: T1, with millions of nodes, and T2, with hundreds of nodes. Create an algorithm to decide if T2 is a subtree of T1.
Solution 1
The best solution is to print inorder and preorder traversal of both trees. Find whether the 2 traversal string of T2 is substring of the traversal of T1. This is a very good idea of checking subtree of a Binary Tree.Updated on Jan 26th, 2015: do we have to use sentinals for this purpose? Well, the answer is NO, cuz a preorder and a inorder can uniquely define a binary tree.
However, this solution is very memory intensive.
Solution 2
The alternative solution simply checks the tree similarity for each and every node.Time complexity:
If k is the number of occurrences of T2's root in T1, the worst case runtime can be characterized as O(n + k * m).
However, there can be a lot of pruning for this solution, so it's NOT necessarily slower than Solution 1.
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/check-if-a-binary-tree-is-subtree-of-another-binary-tree/
bool areIdentical(struct node * root1, struct node *root2){ /* base cases */ if (root1 == NULL && root2 == NULL) return true; if (root1 == NULL || root2 == NULL) return false; /* Check if the data of both roots is same and data of left and right subtrees are also same */ return (root1->data == root2->data && areIdentical(root1->left, root2->left) && areIdentical(root1->right, root2->right) );}/* This function returns true if S is a subtree of T, otherwise false */bool isSubtree(struct node *T, struct node *S){ /* base cases */ if (S == NULL) return true; if (T == NULL) return false; /* Check the tree with root as current node */ if (areIdentical(T, S)) return true; /* If the tree with root as current node doesn't match then try left and right subtrees one by one */ return isSubtree(T->left, S) || isSubtree(T->right, S);}public static boolean containsTree(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null) {
return false;
} else if (matchTree(t1, t2)) {
return true;
} else {
return containsTree(t1.left, t2) || containsTree(t1.right, t2);
}
}
private static boolean matchTree(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t2 == null) {
return true;
} else if (t1 == null) {
return false;
} else if (t1.data != t2.data) {
return false;
} else {
return matchTree(t1.left, t2.left) && matchTree(t1.right, t2.right);
}
}The algorithm is essentially the same as given in the book, except that I first preprocess the large tree to collect a set of subtrees whose size is the same as the small binary tree. The intuition is that since T2 is much smaller than T1, it is better to check the subtrees from lower levels (nodes at higher level might have too many nodes in their subtree, hence cannot match with T2). The extreme cases are complete binary trees and a linked-list like trees. The time complexity is
int findcandidatesubtree(shared_ptr<Binarytree> root, int size, vector<shared_ptr<Binarytree>> &candidate){ if (!root) return {}; auto l = findcandidatesubtree(root->left, size, candidate); auto r = findcandidatesubtree(root->right, size, candidate); if (l + r + 1 == size) candidate.push_back(root); return l+r+1;}int subtreesize(shared_ptr<Binarytree> root){ if (!root) return {}; return subtreesize(root->left) + 1 + subtreesize(root->right);}bool issametree(shared_ptr<Binarytree> t1, shared_ptr<Binarytree> t2){ if (!t1 && !t2) return true; else if (!t1 && t2 || t1 && !t2) return false; return (t1->key == t2->key) && issametree(t1->left, t2->left) && issametree(t1->right, t2->right);}shared_ptr<Binarytree> subtree(shared_ptr<Binarytree> root, shared_ptr<Binarytree> small){ if (!small || !root) return {}; vector<shared_ptr<Binarytree>> candidate; int smalltreesize = subtreesize(small); findcandidatesubtree(root, smalltreesize, candidate); for (auto i = candidate.begin(); i != candidate.end(); ++i) if (issametree(*i, small)) return *i; return {};}
方法2:对T1,T2中的每个节点生成一个hash值,hash值由当前节点和左右子树共同决定;
We don't need to store the hash values into hashset, we can compare hash value at the same time when traverse tn1.
If the hash value is same, we may compare them to check whether they are really same tree.
public static boolean method1(TreeNode tn1,TreeNode tn2){
hash(tn1);
hash(tn2);
HashSet<Integer> set=new HashSet<Integer>();
preTraverse(tn1,set);
if(set.contains(tn2.hashValue))
return true;
else
return false;
}
private static void preTraverse(TreeNode tn1,HashSet<Integer> set){
if(tn1==null) return;
set.add(tn1.hashValue);
preTraverse(tn1.lchild,set);
preTraverse(tn1.rchild,set);
}
private static int hash(TreeNode tnode){
if(tnode==null) return 0;
if(tnode.lchild==null&&tnode.rchild==null)
tnode.hashValue=tnode.value;
else
tnode.hashValue=3*tnode.value+5*hash(tnode.lchild)+7*hash(tnode.rchild);
return tnode.hashValue;
}
class TreeNode{
int value;
TreeNode lchild;
TreeNode rchild;
TreeNode parent;
int hashValue;
}
http://www.careercup.com/question?id=5164767748554752
Read full article from [CC150v4] 4.7 Check Subtree - Shuatiblog.com