http://bookshadow.com/weblog/2016/09/11/leetcode-evaluate-division/
Google Interview Questions Deconstructed
X. DFS
https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-division/discuss/171649/1ms-DFS-with-Explanations
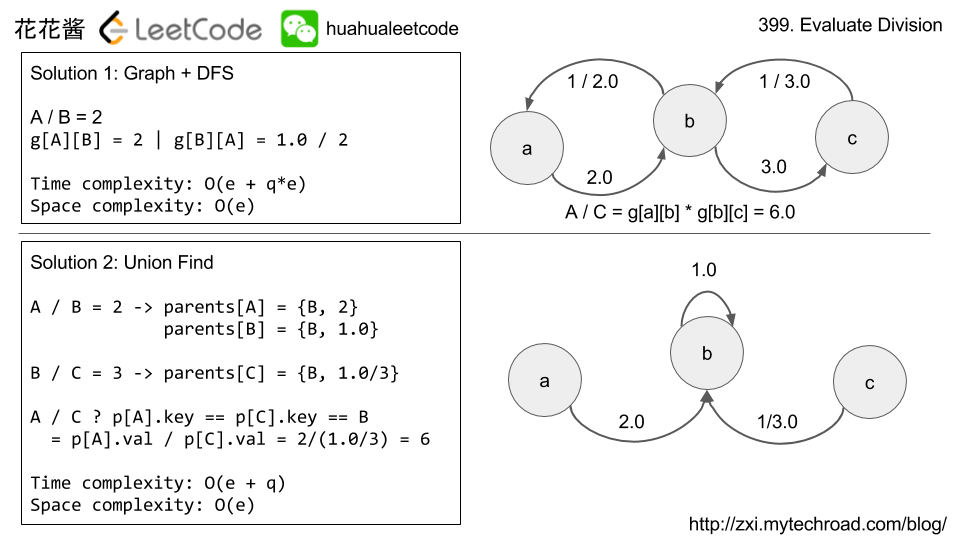
If a/b = 2.0 and b/c = 3.0, we can treat a,b,c as vertices.
edge(a,b) weight 2.0, edge(b,c) weight 3.0
backward edge(b,a) weight 1/2.0, edge(c,b) weight 1/3.0
query a,c is a path from a to c, distance (a,c) = weight(a,b) * weight(b,c)
String to;
double weight;
Edge(String t, double w){
to = t;
weight = w;
}
}
https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-division/discuss/88228/java-ac-solution-with-explanation
https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-division/discuss/88346/java-solution-using-hashmap-and-dfs
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/58399/share-my-straightforward-java-dfs-solution-very-similar-to-the-332-reconstruct-itinerary
http://blog.csdn.net/yeqiuzs/article/details/52506433
X. BFS
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26658823/article/details/78470306
http://edlinlink.github.io/Leetcode_Evaluate_Division.html
http://xiadong.info/2016/09/leetcode-399-evaluate-division/
X. Floyd–Warshall DP
https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-division/discuss/88207/java-solution-using-floydu2013warshall-algorithm
functional programming in java is very slow
Google Interview Questions Deconstructed
Equations are given in the format
A / B = k, where A and B are variables represented as strings, and k is a real number (floating point number). Given some queries, return the answers. If the answer does not exist, return -1.0.
Example:
Given
queries are:
return
Given
a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0.queries are:
a / c = ?, b / a = ?, a / e = ?, a / a = ?, x / x = ? .return
[6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ].
The input is:
The example above:
vector<pair<string, string>> euqations, vector<double>& values, vector<pair<string, string>> query . where equations.size() == values.size(),the values are positive. this represents the equations.return vector<double>. .The example above:
equations = [ ["a", "b"], ["b", "c"] ]. values = [2.0, 3.0]. queries = [ ["a", "c"], ["b", "a"], ["a", "e"], ["a", "a"], ["x", "x"] ].
The input is always valid. You may assume that evaluating the queries will result in no division by zero and there is no contradiction.
Floyd算法求解传递闭包
输入等式可以看做一个有向图
例如等式a / b = 2.0,可以转化为两条边:<a, b>,<b, a>,其长度分别为2.0,0.5
遍历equations与values,利用g数组保存有向图中各边的长度,利用vset记录顶点集合
最后调用Floyd算法即可
def calcEquation(self, equations, values, query):
"""
:type equations: List[List[str]]
:type values: List[float]
:type query: List[List[str]]
:rtype: List[float]
"""
g = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(int))
vset = set()
for e, v in zip(equations, values):
g[e[0]][e[1]] = v
g[e[1]][e[0]] = 1.0 / v
vset.add(e[0])
vset.add(e[1])
for k in vset:
g[k][k] = 1.0
for s in vset:
for t in vset:
if g[s][k] and g[k][t]:
g[s][t] = g[s][k] * g[k][t]
ans = []
for s, t in query:
ans.append(g[s][t] if g[s][t] else -1.0)
return ans
X. DFS
https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-division/discuss/171649/1ms-DFS-with-Explanations
Binary relationship is represented as a graph usually.
Does the direction of an edge matters? -- Yes. Take a / b = 2 for example, it indicates
Thus, it is a directed weighted graph.
In this graph, how do we evaluate division?
Take a / b = 2, b / c = 3, a / c = ? for example,
Does the direction of an edge matters? -- Yes. Take a / b = 2 for example, it indicates
a --2--> b as well as b --1/2--> a.Thus, it is a directed weighted graph.
In this graph, how do we evaluate division?
Take a / b = 2, b / c = 3, a / c = ? for example,
a --2--> b --3--> c
We simply find a path using DFS from node
a to node c and multiply the weights of edges passed, i.e. 2 * 3 = 6.
Please note that during DFS,
- Rejection case should be checked before accepting case.
- Accepting case is
(graph.get(u).containsKey(v))rather than(u.equals(v))for it takes O(1) but(u.equals(v))takes O(n) for n is the length of the longer one between u and v.
public double[] calcEquation(String[][] equations, double[] values, String[][] queries) {
/* Build graph. */
Map<String, Map<String, Double>> graph = buildGraph(equations, values);
double[] result = new double[queries.length];
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
result[i] = getPathWeight(queries[i][0], queries[i][1], new HashSet<>(), graph);
}
return result;
}
private double getPathWeight(String start, String end, Set<String> visited, Map<String, Map<String, Double>> graph) {
/* Rejection case. */
if (!graph.containsKey(start))
return -1.0;
/* Accepting case. */
if (graph.get(start).containsKey(end))
return graph.get(start).get(end);
visited.add(start);
for (Map.Entry<String, Double> neighbour : graph.get(start).entrySet()) {
if (!visited.contains(neighbour.getKey())) {
double productWeight = getPathWeight(neighbour.getKey(), end, visited, graph);
if (productWeight != -1.0)
return neighbour.getValue() * productWeight;
}
}
return -1.0;
}
private Map<String, Map<String, Double>> buildGraph(String[][] equations, double[] values) {
Map<String, Map<String, Double>> graph = new HashMap<>();
String u, v;
for (int i = 0; i < equations.length; i++) {
u = equations[i][0];
v = equations[i][1];
graph.putIfAbsent(u, new HashMap<>());
graph.get(u).put(v, values[i]);
graph.putIfAbsent(v, new HashMap<>());
graph.get(v).put(u, 1 / values[i]);
}
return graph;
}
这道题首先需要做的工作是,已知a/b=x的情况下,推断出b/a=1/x的情况。将所有a作为被除数的情况下能作为除数的全部集合起来。
然后就有搜索的方式(如DFS),搜索有没有一个这样的链:
a/c = a/x1 x1/x2 x2/x3*…..*xn/c
这样就能推导出最终的结果了
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/59146/java-ac-solution-using-graph这样就能推导出最终的结果了
If a/b = 2.0 and b/c = 3.0, we can treat a,b,c as vertices.
edge(a,b) weight 2.0, edge(b,c) weight 3.0
backward edge(b,a) weight 1/2.0, edge(c,b) weight 1/3.0
query a,c is a path from a to c, distance (a,c) = weight(a,b) * weight(b,c)
public double[] calcEquation(String[][] equations, double[] values, String[][] queries) {
double[] res = new double[queries.length];
if(equations.length == 0) return res;
Map<String, List<Edge>> adjs = new HashMap();
for(int i=0;i<equations.length;i++){
String v = equations[i][0];
String u = equations[i][1];
Edge ef = new Edge(u, values[i]);
Edge eb = new Edge(v, 1.0/values[i]);
if(adjs.containsKey(v)){
adjs.get(v).add(ef);
} else {
List<Edge> adjsV = new ArrayList();
adjsV.add(ef);
adjs.put(v, adjsV);
}
if(adjs.containsKey(u)){
adjs.get(u).add(eb);
} else {
List<Edge> adjsU = new ArrayList();
adjsU.add(eb);
adjs.put(u, adjsU);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<queries.length;i++){
String s = queries[i][0];
String t = queries[i][1];
Set<String> visited = new HashSet();
dfs(adjs,visited, s, t, 1.0,i, res);
if(res[i] == 0 && s != t) res[i] = -1.0;
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(Map<String, List<Edge>> adjs,Set<String> visited, String s, String t, double distance, int index, double[] res){
if(s.equals(t)) { // start, end, result,
res[index] = distance;
}
if(visited.contains(s)) return;
visited.add(s);
if(!adjs.containsKey(s) || !adjs.containsKey(t)) {
res[index] = -1.0;
return;
}
List<Edge> adjsV = adjs.get(s);
Iterator<Edge> iter = adjsV.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
Edge e = iter.next();
dfs(adjs,visited, e.to, t, distance * e.weight,index, res);
}String to;
double weight;
Edge(String t, double w){
to = t;
weight = w;
}
}
https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-division/discuss/88228/java-ac-solution-with-explanation
The logic I have used is to construct a Map of maps, that contains all possible a/b and b/a from the given input and their values.
For the given input
equations = [ ["a", "b"], ["b", "c"] ]. values = [2.0, 3.0]
equations = [ ["a", "b"], ["b", "c"] ]. values = [2.0, 3.0]
The map that gets constructed is :
[a: [b:2.0]
b: [a:0.5], [c:3.0]
c: [b:0.333]]
b: [a:0.5], [c:3.0]
c: [b:0.333]]
For each key in the outer map, the value represents a map, that denotes all possible denominators for the key and the corresponding key/value.
With this map constructed, the logic for evaluating a query is simple in a dfs style:
To find any m/n, if the map of m contains x1, x2, x3
then
m/n = m/x1 * x1/n if this gives a valid result or m/x2 * x2/n or m/x3 * x3/n
then
m/n = m/x1 * x1/n if this gives a valid result or m/x2 * x2/n or m/x3 * x3/n
public static double[] calcEquation(String[][] equations, double[] values, String[][] query) {
Map<String, Map<String, Double>> numMap = new HashMap<>();
int i = 0;
for(String[] str : equations) {
insertPairs(numMap, str[0], str[1], values[i]);
insertPairs(numMap, str[1], str[0], 1.0/values[i]);
i++;
}
double[] res = new double[query.length];
i = 0;
for(String[] q: query) {
Double resObj = handleQuery(q[0], q[1], numMap, new HashSet<>());
res[i++] = (resObj != null) ? resObj : -1.0;
}
return res;
}
public static void insertPairs(Map<String, Map<String, Double>> numMap, String num, String denom, Double value) {
Map<String, Double> denomMap = numMap.get(num);
if(denomMap == null) {
denomMap = new HashMap<>();
numMap.put(num, denomMap);
}
denomMap.put(denom, value);
}
public static Double handleQuery(String num, String denom, Map<String, Map<String, Double>> numMap, Set<String> visitedSet) {
String dupeKey = num+":"+denom;
if(visitedSet.contains(dupeKey)) return null;
if(!numMap.containsKey(num) || !numMap.containsKey(denom)) return null;
if(num.equals(denom)) return 1.0;
Map<String, Double> denomMap = numMap.get(num);
for(String key : denomMap.keySet()) {
visitedSet.add(dupeKey);
Double res = handleQuery(key, denom, numMap, visitedSet);
if(res != null) {
return denomMap.get(key) * res;
}
visitedSet.remove(dupeKey);
}
return null;
}
(1) Build the map, the key is dividend, the value is also a map whose key is divisor and value is its parameter. For example,
(2) for each query, use DFS to search divisors recursively
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/58321/java-ac-solution-with-explanationa / b = 2.0, the map entry is <"a", <"b", 2.0>>. To make searching and calculation easier, we also put b / a = 0.5 into the map.(2) for each query, use DFS to search divisors recursively
public static double[] calcEquation(String[][] equations, double[] values, String[][] query) {
Map<String, Map<String, Double>> numMap = new HashMap<>();
int i = 0;
for(String[] str : equations) {
insertPairs(numMap, str[0], str[1], values[i]);
insertPairs(numMap, str[1], str[0], 1.0/values[i]);
i++;
}
double[] res = new double[query.length];
i = 0;
for(String[] q: query) {
Double resObj = handleQuery(q[0], q[1], numMap, new HashSet<>());
res[i++] = (resObj != null) ? resObj : -1.0;
}
return res;
}
public static void insertPairs(Map<String, Map<String, Double>> numMap, String num, String denom, Double value) {
Map<String, Double> denomMap = numMap.get(num);
if(denomMap == null) {
denomMap = new HashMap<>();
numMap.put(num, denomMap);
}
denomMap.put(denom, value);
}
public static Double handleQuery(String num, String denom, Map<String, Map<String, Double>> numMap, Set<String> visitedSet) {
String dupeKey = num+":"+denom;
if(visitedSet.contains(dupeKey)) return null;
if(!numMap.containsKey(num) || !numMap.containsKey(denom)) return null;
if(num.equals(denom)) return 1.0;
Map<String, Double> denomMap = numMap.get(num);
visitedSet.add(dupeKey);
for(String key : denomMap.keySet()) {
Double res = handleQuery(key, denom, numMap, visitedSet);
if(res != null) {//\\
return denomMap.get(key) * res;
}
}
visitedSet.remove(dupeKey);
return null;
}https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/58399/share-my-straightforward-java-dfs-solution-very-similar-to-the-332-reconstruct-itinerary
http://blog.csdn.net/yeqiuzs/article/details/52506433
用HashMap 存储图的邻接表,并用创建图节点的visited标记。这里是图节点value是string,用数组表示visited不合适,故用hashmap<string,boolean>
- Map<String, Map<String, Double>> map = new HashMap<>();//邻接表
- public double[] calcEquation(String[][] equations, double[] values, String[][] query) {
- Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>();//记录表达式中出现的字符串
- for (int i = 0; i < equations.length; i++) {//建图
- set.add(equations[i][0]);
- set.add(equations[i][1]);
- Map<String, Double> m;
- if (map.containsKey(equations[i][0])) {
- m = map.get(equations[i][0]);
- } else {
- m = new HashMap<String, Double>();
- }
- m.put(equations[i][1], values[i]);
- map.put(equations[i][0], m);
- if (map.containsKey(equations[i][1])) {
- m = map.get(equations[i][1]);
- } else {
- m = new HashMap<String, Double>();
- }
- m.put(equations[i][0], 1.0 / values[i]);
- map.put(equations[i][1], m);
- }
- double result[] = new double[query.length];
- for (int i = 0; i < query.length; i++) {
- //初始化visited标记
- Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();
- Map<String, Boolean> visited = new HashMap<String, Boolean>();
- while (it.hasNext()) {
- visited.put(it.next(), false);
- }
- if (query[i][0].equals(query[i][1]) && set.contains(query[i][0])) {
- result[i] = 1;
- continue;
- }
- //dfs
- double res = dfs(query[i][0], query[i][1], 1, visited);
- result[i] = res;
- }
- return result;
- }
- public double dfs(String s, String t, double res, Map<String, Boolean> visited) {
- if (map.containsKey(s) && !visited.get(s)) {
- visited.put(s, true);
- Map<String, Double> m = map.get(s);
- if (m.containsKey(t)) {
- return res * m.get(t);
- } else {
- Iterator<String> keys = m.keySet().iterator();
- while (keys.hasNext()) {
- String key = keys.next();
- double state = dfs(key, t, res * m.get(key), visited);
- if (state != -1.0) {
- return state;
- }
- }
- }
- } else {
- return -1.0;
- }
- return -1.0;
- }
X. BFS
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26658823/article/details/78470306
http://edlinlink.github.io/Leetcode_Evaluate_Division.html
struct Node{
string name;
double rate;
Node(string n, double r) : name(n), rate(r) {};
};
vector<double> calcEquation( vector<pair<string, string>> equations,
vector<double>& values,
vector<pair<string, string>> queries ) {
map< string, vector<Node> > graph;
for( int i=0; i<equations.size(); i++ ){
string a = equations[i].first;
string b = equations[i].second;
double value = values[i];
graph[a].push_back( Node(a,1));
graph[a].push_back( Node(b,value) );
if( value != 0 ){
graph[b].push_back( Node(a,1/value) );
graph[b].push_back( Node(b,1) );
}
}
vector<double> ret;
for( int i=0; i<queries.size(); i++ ){
string from = queries[i].first;
string dest = queries[i].second;
set<string> visit;
queue<Node> que; Node start(from,1);
que.push( start );
bool found = false;
while( !que.empty() && !found ){
Node node = que.front();
que.pop();
for( int j=0; j<graph[node.name].size() && !found; j++ ){
if( visit.count( graph[node.name][j].name ) == 0 ){
visit.insert( graph[node.name][j].name );
que.push( Node(graph[node.name][j].name, node.rate * graph[node.name][j].rate) );
}
if( dest == graph[node.name][j].name )
{
ret.push_back( node.rate * graph[node.name][j].rate );
found = true;
}
}
}
if( !found )
ret.push_back(-1.00000);
}
return ret;
} public void addArc(Map<String, Map<String, Double>> graph, String vexStart, String vexEnd, double value) {
Map<String, Double> arcMap;
if (graph.containsKey(vexStart)) {
arcMap = graph.get(vexStart);
} else {
arcMap = new HashMap<>();
}
arcMap.put(vexEnd, value);
graph.put(vexStart, arcMap);
}
public double getValue(Map<String, Map<String, Double>> graph, String vexStart, String vexEnd) {
if (graph.get(vexStart) == null || graph.get(vexEnd) == null) {
return -1;
}
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //queue uesd for bfs
Map<String, Double> value = new HashMap<>(); //distance from vexStart
Set<String> validation = new HashSet<>(); //check if the vertex has been in the queue
//init
queue.add(vexStart);
validation.add(vexStart);
value.put(vexStart, 1d);
String currentNode, nextNode;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
currentNode = queue.remove();
for (Map.Entry<String, Double> arc : graph.get(currentNode).entrySet()) {
nextNode = arc.getKey();
value.put(nextNode, value.get(currentNode) * arc.getValue());
if (nextNode.equals(vexEnd)) {
return value.get(vexEnd);
} else if (!validation.contains(nextNode)) {
queue.add(nextNode);
validation.add(nextNode);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public double[] calcEquation(String[][] equations, double[] values, String[][] queries) {
Map<String, Map<String, Double>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < equations.length; i++) {
//add arcs for both directions
addArc(graph, equations[i][0], equations[i][1], values[i]);
addArc(graph, equations[i][1], equations[i][0], 1 / values[i]);
}
double[] answer = new double[queries.length];
for (int i = 0; i < answer.length; i++) {
answer[i] = getValue(graph, queries[i][0], queries[i][1]);
}
return answer;
}
http://xiadong.info/2016/09/leetcode-399-evaluate-division/
// 由于对于string的比较等操作很费时, 所以用一个map把string与int对应起来.
unordered_map<string, int> nodes;
public:
vector<double> calcEquation(vector<pair<string, string>> equations, vector<double>& values, vector<pair<string, string>> queries) {
for(int i = 0; i < equations.size(); i++){
// 给每一个string分配一个下标
// 注意这里有个隐藏bug, 假如map/unordered_map对象m中不包含a,
// 那么在使用m[a]时实际上是已经创建一个a的key和对应的value, 导致size加1
// 所以如果我们想让第n个加入的元素的value为n-1的话,
// 需要赋值m.size() - 1而不是m.size()
if(!nodes.count(equations[i].first)){
nodes[equations[i].first] = nodes.size() - 1;
}
if(!nodes.count(equations[i].second)){
nodes[equations[i].second] = nodes.size() - 1;
}
}
vector<vector<double>> g(nodes.size(), vector<double>(nodes.size(), -1.0));
for(int i = 0; i < equations.size(); i++){
// 构建邻接矩阵
g[getNode(equations[i].first)][getNode(equations[i].second)] = values[i];
g[getNode(equations[i].second)][getNode(equations[i].first)] = 1 / values[i];
}
vector<double> ret(queries.size());
for(int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++){
string a = queries[i].first, b = queries[i].second;
if(!nodes.count(a) || !nodes.count(b)){
// 如果出现了不存在的节点
ret[i] = -1.0;
}
else{
// 使用BFS来搜索路径
ret[i] = BFS(g, getNode(a), getNode(b));
}
}
return ret;
}
int getNode(string s){
return nodes[s];
}
double BFS(vector<vector<double>> &g, int a, int b){
// 如果是同一个节点就直接返回
if(a == b) return 1.0;
int n = g.size();
vector<int> visited(n, 0); // 用于保存是否访问过节点
queue<int> q; // BFS队列, 保存节点下标
queue<double> v; // 用于保存从a到BFS队列中相应的节点的路径乘积
q.push(a);
visited[a] = 1;
v.push(1.0);
while(!q.empty()){
int node = q.front();
double value = v.front();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(visited[i] || g[node][i] == -1.0) continue; // 节点i已经访问过或者没有边到达i
visited[i] = 1;
q.push(i);
double len = value * g[node][i]; // 从a到i的路径权值乘积
// 添加新的边
g[a][i] = len;
g[i][a] = 1 / len;
if(i == b){ // 抵达b点
return len;
}
v.push(len);
}
q.pop();
v.pop();
}
return -1.0;
}
X. Floyd–Warshall DP
https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-division/discuss/88207/java-solution-using-floydu2013warshall-algorithm
functional programming in java is very slow
Using a variant of Floyd–Warshall algorithm, to find the distance between each reachable pair:
public double[] calcEquation(String[][] equations, double[] values, String[][] queries) {
HashMap<String, HashMap<String, Double>> graph = new HashMap<>();
Function<String, HashMap<String, Double>> function = s -> new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < equations.length; i++) {
graph.computeIfAbsent(equations[i][0], function).put(equations[i][0], 1.0);
graph.computeIfAbsent(equations[i][1], function).put(equations[i][1], 1.0);
graph.get(equations[i][0]).put(equations[i][1], values[i]);
graph.get(equations[i][1]).put(equations[i][0], 1 / values[i]);
}
for (String mid : graph.keySet()) {
for (String src : graph.get(mid).keySet()) {
for (String dst : graph.get(mid).keySet()) {
double val = graph.get(src).get(mid) * graph.get(mid).get(dst);
graph.get(src).put(dst, val);
}
}
}
double[] result = new double[queries.length];
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
if (!graph.containsKey(queries[i][0])) {
result[i] = -1;
} else {
result[i] = graph.get(queries[i][0]).getOrDefault(queries[i][1], -1.0);
}
}
return result;
}
In practice, we can use guava's
HashBasedTable, do not have to use HashMap<String,HashMap<String,Double>>,: public double[] calcEquation(String[][] equations, double[] values, String[][] queries) {
Table<String, String, Double> table = HashBasedTable.create();
for (int i = 0; i < equations.length; i++) {
String src = equations[i][0], dst = equations[i][1];
table.put(src, src, 1.0);
table.put(dst, dst, 1.0);
table.put(src, dst, values[i]);
table.put(dst, src, 1.0 / values[i]);
}
for (String mid : table.rowKeySet()) {
for (String src : table.row(mid).keySet()) {
for (String dst : table.row(mid).keySet()) {
double val = table.get(src, mid) * table.get(mid, dst);
table.put(src, dst, val);
}
}
}
double[] result = new double[queries.length];
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
result[i] = table.contains(queries[i][0], queries[i][1]) ? table.get(queries[i][0], queries[i][1]) : -1.0;
}
return result;
}