Vertex Cover Problem | Set 1 (Introduction and Approximate Algorithm) - GeeksforGeeks
A vertex cover of an undirected graph is a subset of its vertices such that for every edge (u, v) of the graph, either 'u' or 'v' is in vertex cover. Although the name is Vertex Cover, the set covers all edges of the given graph. Given an undirected graph, the vertex cover problem is to find minimum size vertex cover.
http://ideone.com/ItOB19
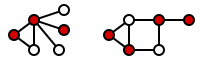
Formally, a vertex-cover of an undirected graph is a subset V′ of V such that if edge (u, v) is an edge of G, then u is in V′, or v is in V′, or both. The set V′ is said to "cover" the edges of G. The following figure shows examples of vertex covers in two graphs (and the set V' is marked with red).
is a subset V′ of V such that if edge (u, v) is an edge of G, then u is in V′, or v is in V′, or both. The set V′ is said to "cover" the edges of G. The following figure shows examples of vertex covers in two graphs (and the set V' is marked with red).
Approximate evaluation
https://code.google.com/p/gteditor/source/browse/trunk/externiallibsrc/org/jgrapht/alg/VertexCovers.java?r=11
Exact Algorithms:
Although the problem is NP complete, it can be solved in polynomial time for following types of graphs.
1) Bipartite Graph
2) Tree Graph
DP: http://massivealgorithms.blogspot.com/2015/05/vertex-cover-problem-set-2-dynamic.html
Read full article from Vertex Cover Problem | Set 1 (Introduction and Approximate Algorithm) - GeeksforGeeks
A vertex cover of an undirected graph is a subset of its vertices such that for every edge (u, v) of the graph, either 'u' or 'v' is in vertex cover. Although the name is Vertex Cover, the set covers all edges of the given graph. Given an undirected graph, the vertex cover problem is to find minimum size vertex cover.
Approximate Algorithm for Vertex Cover:
1) Initialize the result as {}
2) Consider a set of all edges in given graph. Let the set be E.
3) Do following while E is not empty
...a) Pick an arbitrary edge (u, v) from set E and add 'u' and 'v' to result
...b) Remove all edges from E which are either incident on u or v.
4) Return result
// The function to print vertex covervoid Graph::printVertexCover(){ // Initialize all vertices as not visited. bool visited[V]; for (int i=0; i<V; i++) visited[i] = false; list<int>::iterator i; // Consider all edges one by one for (int u=0; u<V; u++) { // An edge is only picked when both visited[u] and visited[v] // are false if (visited[u] == false) { // Go through all adjacents of u and pick the first not // yet visited vertex (We are basically picking an edge // (u, v) from remaining edges. for (i= adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i) { int v = *i; if (visited[v] == false) { // Add the vertices (u, v) to the result set. // We make the vertex u and v visited so that // all edges from/to them would be ignored visited[v] = true; visited[u] = true; break; } } } } // Print the vertex cover for (int i=0; i<V; i++) if (visited[i]) cout << i << " ";}- std::vector<bool> get_vertex_cover() {
- std::vector<bool> visited(vertex_count, false);
- for (int u = 0; u < vertex_count; u++) {
- if (visited[u]) continue;
- for (int v : adj[u]) {
- if (visited[v]) continue;
- visited[v] = visited[u] = true;
- break;
- }
- }
- return visited;
- }
Formally, a vertex-cover of an undirected graph
 is a subset V′ of V such that if edge (u, v) is an edge of G, then u is in V′, or v is in V′, or both. The set V′ is said to "cover" the edges of G. The following figure shows examples of vertex covers in two graphs (and the set V' is marked with red).
is a subset V′ of V such that if edge (u, v) is an edge of G, then u is in V′, or v is in V′, or both. The set V′ is said to "cover" the edges of G. The following figure shows examples of vertex covers in two graphs (and the set V' is marked with red).
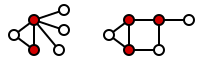
A minimum vertex cover is a vertex cover of smallest possible size. The vertex cover number  is the size of a minimum vertex cover. The following figure shows examples of minimum vertex covers in the previous graphs.
is the size of a minimum vertex cover. The following figure shows examples of minimum vertex covers in the previous graphs.
 is the size of a minimum vertex cover. The following figure shows examples of minimum vertex covers in the previous graphs.
is the size of a minimum vertex cover. The following figure shows examples of minimum vertex covers in the previous graphs.
图的覆盖是一些顶点(或边)的集合,使得图中的每一条边(每一个顶点)都至少接触集合中的一个顶点(边)。寻找最小的顶点覆盖的问题称为顶点覆盖问题,它是一个NP完全问题。
Approximate evaluation
One can find a factor-2 approximation by repeatedly taking both endpoints of an edge into the vertex cover, then removing them from the graph. Put otherwise, we find a maximal matching M with a greedy algorithm and construct a vertex cover C that consists of all endpoints of the edges in M. In the following figure, a maximal matching M is marked with red, and the vertex cover C is marked with blue.
The set C constructed this way is a vertex cover: suppose that an edge e is not covered by C; then M ∪ {e} is a matching and e ∉ M, which is a contradiction with the assumption that M is maximal. Furthermore, if e = {u, v} ∈ M, then any vertex cover – including an optimal vertex cover – must contain u or v (or both); otherwise the edge e is not covered. That is, an optimal cover contains at leastone endpoint of each edge in M; in total, the set C is at most 2 times as large as the optimal vertex cover.
http://mste.illinois.edu/mmckelve/applets/graphtheory/org/_3pq/jgrapht/alg/VertexCovers.javahttps://code.google.com/p/gteditor/source/browse/trunk/externiallibsrc/org/jgrapht/alg/VertexCovers.java?r=11
| * Finds a 2-approximation for a minimal vertex cover of the specified |
| * graph. The algorithm promises a cover that is at most double the size of |
| * a minimal cover. The algorithm takes O(|E|) time. |
| * |
| * <p> |
| * For more details see Jenny Walter, CMPU-240: Lecture notes for Language |
| * Theory and Computation, Fall 2002, Vassar College, <a |
| * href="http://www.cs.vassar.edu/~walter/cs241index/lectures/PDF/approx.pdf"> |
| * http://www.cs.vassar.edu/~walter/cs241index/lectures/PDF/approx.pdf</a>. |
| public static <V, E> Set<V> find2ApproximationCover(Graph<V, E> g) { |
| // C <-- {} |
| Set<V> cover = new HashSet<V>(); |
| // G'=(V',E') <-- G(V,E) |
| Subgraph<V, E, Graph<V, E>> sg = new Subgraph<V, E, Graph<V, E>>(g, |
| null, null); |
| // while E' is non-empty |
| while (sg.edgeSet().size() > 0) { |
| // let (u,v) be an arbitrary edge of E' |
| E e = sg.edgeSet().iterator().next(); |
| // C <-- C U {u,v} |
| V u = g.getEdgeSource(e); |
| V v = g.getEdgeTarget(e); |
| cover.add(u); |
| cover.add(v); |
| // remove from E' every edge incident on either u or v |
| sg.removeVertex(u); |
| sg.removeVertex(v); |
| } |
| return cover; // return C |
| } |
| * Finds a greedy approximation for a minimal vertex cover of a specified |
| * graph. At each iteration, the algorithm picks the vertex with the highest |
| * degree and adds it to the cover, until all edges are covered. |
| * |
| * <p> |
| * The algorithm works on undirected graphs, but can also work on directed |
| * graphs when their edge-directions are ignored. To ignore edge directions |
| * you can use {@link org.jgrapht.Graphs#undirectedGraph(Graph)} or |
| * {@link org.jgrapht.graph.AsUndirectedGraph}. |
| * @return a set of vertices which is a vertex cover for the specified |
| * graph. |
| */ |
| public static <V, E> Set<V> findGreedyCover(UndirectedGraph<V, E> g) { |
| // C <-- {} |
| Set<V> cover = new HashSet<V>(); |
| // G' <-- G |
| UndirectedGraph<V, E> sg = new UndirectedSubgraph<V, E>(g, null, null); |
| // compare vertices in descending order of degree |
| VertexDegreeComparator<V, E> comp = new VertexDegreeComparator<V, E>(sg); |
| // while G' != {} |
| while (sg.edgeSet().size() > 0) { |
| // v <-- vertex with maximum degree in G' |
| V v = Collections.max(sg.vertexSet(), comp); |
| // C <-- C U {v} |
| cover.add(v); |
| // remove from G' every edge incident on v, and v itself |
| sg.removeVertex(v); |
| } |
| return cover; |
| } |
Exact Algorithms:
Although the problem is NP complete, it can be solved in polynomial time for following types of graphs.
1) Bipartite Graph
2) Tree Graph
DP: http://massivealgorithms.blogspot.com/2015/05/vertex-cover-problem-set-2-dynamic.html
Read full article from Vertex Cover Problem | Set 1 (Introduction and Approximate Algorithm) - GeeksforGeeks