https://leetcode.com/problems/snapshot-array/
Implement a SnapshotArray that supports the following interface:
SnapshotArray(int length)initializes an array-like data structure with the given length. Initially, each element equals 0.void set(index, val)sets the element at the givenindexto be equal toval.int snap()takes a snapshot of the array and returns thesnap_id: the total number of times we calledsnap()minus1.int get(index, snap_id)returns the value at the givenindex, at the time we took the snapshot with the givensnap_id
Example 1:
Input: ["SnapshotArray","set","snap","set","get"] [[3],[0,5],[],[0,6],[0,0]] Output: [null,null,0,null,5] Explanation: SnapshotArray snapshotArr = new SnapshotArray(3); // set the length to be 3 snapshotArr.set(0,5); // Set array[0] = 5 snapshotArr.snap(); // Take a snapshot, return snap_id = 0 snapshotArr.set(0,6); snapshotArr.get(0,0); // Get the value of array[0] with snap_id = 0, return 5
Constraints:
1 <= length <= 50000- At most
50000calls will be made toset,snap, andget. 0 <= index < length0 <= snap_id <(the total number of times we callsnap())0 <= val <= 10^9
https://leetcode.com/problems/snapshot-array/discuss/350562/JavaPython-Binary-Search
TreeMap<Integer, Integer>[] A;
int snap_id = 0;
public SnapshotArray(int length) {
A = new TreeMap[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
A[i] = new TreeMap<Integer, Integer>();
A[i].put(0, 0);
}
}
public void set(int index, int val) {
A[index].put(snap_id, val);
}
public int snap() {
return snap_id++;
}
public int get(int index, int snap_id) {
return A[index].floorEntry(snap_id).getValue();
} List<TreeMap<Integer, Integer>> arr;
int currId = 0;
public SnapshotArray(int length) {
arr = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
arr.add(i, new TreeMap<Integer, Integer>());
arr.get(i).put(0, 0);
}
}
public void set(int index, int val) {
arr.get(index).put(currId, val);
}
public int snap() {
return currId++;
}
public int get(int index, int snap_id) {
return arr.get(index).floorEntry(snap_id).getValue();
}
Store to a HashMap the
set() results since previous snapshot.
Analysis:
Time: Each call of
Space: Total cost
Time: Each call of
get() cost O(snap_id), othersO(1);Space: Total cost
O(n), where n is number of calls of set(). private List<Map<Integer, Integer>> shot;
private Map<Integer, Integer> diff;
public SnapshotArray(int length) {
shot = new ArrayList<>(length);
diff = new HashMap<>(length);
}
public void set(int index, int val) {
diff.put(index, val);
}
public int snap() {
shot.add(diff);
diff = new HashMap<>();
return shot.size() - 1;
}
public int get(int index, int snap_id) {
for (int i = snap_id; i >= 0; --i)
if (shot.get(i).containsKey(index))
return shot.get(i).get(index);
return 0;
}
Method 2: TreeMap
Store the
Store the
set() result together with current snapshot count to the TreeMap of the specified index.
Analysis:
Time: Instantiation cost
Space: Total cost
Time: Instantiation cost
O(length), each call of get()/set() cost O(log(count)), snap() O(1);Space: Total cost
O(length + count). private int count;
private List<TreeMap<Integer, Integer>> shot = new ArrayList<>();
public SnapshotArray(int length) {
IntStream.range(0, length).forEach(i -> { shot.add(new TreeMap<>()); });
}
public void set(int index, int val) {
shot.get(index).put(count, val);
}
public int snap() {
return count++;
}
public int get(int index, int snap_id) {
Integer key = shot.get(index).floorKey(snap_id);
return key == null ? 0 : shot.get(index).get(key);
}
Each index has its own treemap to store all needed values of different snap ids information. For a key value pair(k, v) in an index's treemap, it means starting from snap id k, until there is a newer snap, the value is v. ThisInstead of copy the whole array,
we can only record the changes of
set.Explanation
The idea is, the whole array can be large,
and we may take the
(Like you may always ctrl + S twice)
and we may take the
snap tons of times.(Like you may always ctrl + S twice)
Instead of record the history of the whole array,
we will record the history of each cell.
And this is the minimum space that we need to record all information.
we will record the history of each cell.
And this is the minimum space that we need to record all information.
For each
With a
A[i], we will record its history.With a
snap_id and a its value.
When we want to
get the value in history, just binary search the time point.Complexity
Time
Space
where
O(logS)Space
O(S)where
S is the number of set called.SnapshotArray(int length) is O(N) timeset(int index, int val) is O(1) in Python and O(logSnap) in Javasnap() is O(1)get(int index, int snap_id) is O(logSnap) representation helps achieve the following properties.
1. O(N) init, O(logS) get and set, where N is the total number of indices and S is the total number of snaps for an index.
2. If there is no value update at index i for consecutive snap shots, there will be only a snap_id to value mapping. When setting a new value at index i, it first check the last entry of its map, this is the latest value prior to this update operation. Only insert a new mapping if the new value is the same with the previous value, which means starting from this new snap id, the value is the new value.
3. When calling the get method, it tries to find the a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key less than or equal to the given key snap id.
class SnapshotArray { private TreeMap<Integer, Integer>[] snapMap; private int snapId = 0; public SnapshotArray(int length) { snapMap = new TreeMap[length]; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { snapMap[i] = new TreeMap<Integer, Integer>(); snapMap[i].put(0, 0); } } public void set(int index, int val) { Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> lastEntry = snapMap[index].lastEntry(); if(val != lastEntry.getValue()) { snapMap[index].put(snapId, val); } } public int snap() { return snapId++; } public int get(int index, int snap_id) { return snapMap[index].floorEntry(snap_id).getValue(); }
https://www.acwing.com/solution/LeetCode/content/3431/
实现支持下列接口的快照数组:
SnapshotArray(int length)初始化一个与指定长度相等的类似于数组的数据结构。初始时,每个元素都等于 0。void set(index, val)会将指定索引index处的元素设置为val。int snap()获取该数组的快照,并返回快照的编号snap_id(快照号是调用snap()的总次数减去1)。int get(index, snap_id)根据指定的snap_id选择快照,并返回该快照指定索引index的值。
(数据结构,二分)
- 我们在普通数组的基础上进行改造,每个位置都存储一个新动态数组,存储每个版本(如果有)下的更改。
- 初始时,我们建立长度为
length的数组,每个位置是一个长度为 1 的数组,仅保存版本号 0 和 元素 0 的一个数对。 - 修改时,我们去
index位置的数组中的最后一个位置,如果那个位置的版本号等于当前计数器的版本号,则直接修改元素值;否则新插入一个数对,记录当前版本号和元素值。 - 快照时,直接更新计数器。
- 查询时,我们得到那个位置的数组,然后开始二分,找到小于等于待查询版本的最大版本的那个数对,返回数对的元素值即可。
时间复杂度
- 初始化时间复杂度为 。
- 修改元素的时间复杂度为 。
- 快照的时间复杂度为 。
- 查询的时间复杂度最坏为 ,其中 S 为快照的次数。
空间复杂度
- 最坏需要 的空间,其中 Q 为操作的总次数
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> arr;
int counter;
SnapshotArray(int length) {
arr.resize(length, vector<pair<int, int>>(1));
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
arr[i][0] = make_pair(0, 0);
counter = 0;
}
void set(int index, int val) {
auto &x = arr[index][arr[index].size() - 1];
if (x.first == counter)
x.second = val;
else {
arr[index].emplace_back(make_pair(counter, val));
}
}
int snap() {
return counter++;
}
int get(int index, int snap_id) {
auto &v = arr[index];
int l = 0, r = v.size() - 1;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (snap_id >= v[mid + 1].first)
l = mid + 1;
else
r = mid;
}
return v[l].second;
}X.
https://www.codetd.com/en/article/6973297
Each location to open up a space that is only saved in this location
because of the number of changes in each location is not the same
when you want value, they look for less input snap_id latest
变化because of the number of changes in each location is not the same
when you want value, they look for less input snap_id latest
变化- Use List + Map data structures to build an array of snapshots
List changes in store for each position
value after the change: TreeMap single storage changes in key: snapshot number value
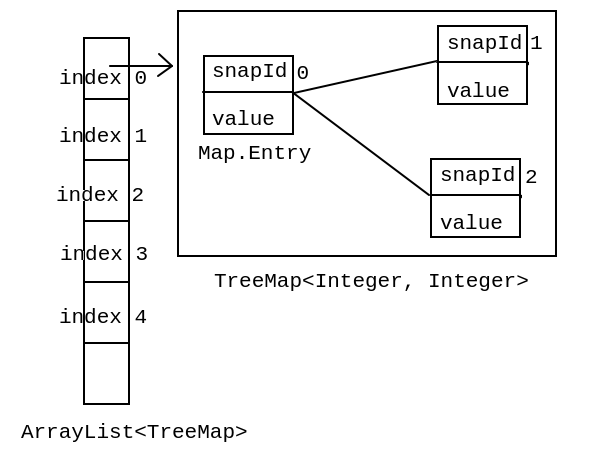
value after the change: TreeMap single storage changes in key: snapshot number value

- Examples of its structure
ArrayList + TreeMap
class SnapshotArray {
// List 存储每个位置的变动情况
// TreeMap 存储单次变动情况 key:快照编号 value:变动后的值
// [index,[(snapId, val), (snapId, val)...]]
List<TreeMap<Integer, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 当前快照编号
int snapId = 0;
// 初始化
public SnapshotArray(int length) {
snapId = 0;
// 开始每个位置全为0
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> t = new TreeMap<>();
t.put(snapId, 0);
list.add(t);
}
}
public void set(int index, int val) {
// 重复就覆盖
list.get(index).put(snapId, val);
}
public int snap() {
int res = snapId;
snapId++;
return res;
}
/**
* 难点
* 需要在TreeMap的key值中寻找小于快照编号snap_id的数据
*
* 这里取巧使用了自带的方法
* floorEntry(key) 找到key值接近snap_id的实体Entry
**/
public int get(int index, int snap_id) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> t = list.get(index);
return t.floorEntry(snap_id).getValue();
} // int[0]: snapId, int[1]:val
private List<int[]>[] snapshots;
private int snapId;
public SnapshotArray(int length) {
snapId = 0;
snapshots = new List[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
List<int[]> snapListEachItem = new ArrayList<>();
snapListEachItem.add(new int[] {0, 0});
snapshots[i] = snapListEachItem;
}
}
public void set(int index, int val) {
List<int[]> snapsOfIndex = snapshots[index];
int[] lastSnap = snapsOfIndex.get(snapsOfIndex.size() - 1);
// If last snap id is less than current id then add a new snap.
if (lastSnap[0] < snapId) {
snapsOfIndex.add(new int[] {snapId, val});
return;
}
lastSnap[0] = snapId;
lastSnap[1] = val;
}
public int snap() {
return snapId++;
}
public int get(int index, int snap_id) {
List<int[]> snaps = snapshots[index];
return binarySearch(snaps, snap_id);
}
private int binarySearch(List<int[]> snaps, int snapId) {
int low = 0, high = snaps.size() - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (snaps.get(mid)[0] < snapId) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (snaps.get(mid)[0] > snapId) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
return snaps.get(mid)[1];
}
}
return low == 0 ? snaps.get(0)[1] : snaps.get(low - 1)[1];
}