https://leetcode.com/problems/all-oone-data-structure/
http://shirleyisnotageek.blogspot.com/2016/11/first-pair-non-matching-leaves.html
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/65434/accepted-java-and-python-solution
http://yuanyuanzhangcs.blogspot.com/2017/02/all-oone-data-structure.html
X. TreeMap Not right answer:
https://blog.csdn.net/MebiuW/article/details/53436455
这道题关键在于如何保存数据形式:
1、使用一个Hashmap保存当前存入的key的频次frequency
2、倒序使用一个Treemap保存当前frequency为某个值时的所有key有哪些,Treemap按照key排序
因此在inc和dec时只需要正常的更新两个map就可以,在取最大最小的时候,直接用有序的treemap的第一个key和最后一个key就可以(分别对应最小的frequency和最大的frequency),然后再将数据取出来就好。
当然其实Treemap的排序开销才开始并不是O(1),但如果数据量大,其实也近似O(1)了。。数据量小又不影响~~~
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/65354/ac-java-solution-using-hashmap-and-two-heaps/3
http://blog.csdn.net/mebiuw/article/details/53436455
TreeMap O(logn) not O(1)
TreeMap<Integer,HashSet<String>> reversedIndex; HashMap<String,Integer> index; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public AllOne() { this.reversedIndex = new TreeMap<>(); this.index = new HashMap<>(); } /** Inserts a new key <Key> with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. */ public void inc(String key) { if (this.index.containsKey(key) == false){ this.index.put(key,1); if(this.reversedIndex.containsKey(1) == false) this.reversedIndex.put(1,new HashSet<String>()); this.reversedIndex.get(1).add(key); } else{ int currentCounts = this.index.get(key); this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts).remove(key); // 这里必须要做remove,因为treemap要直接firstkey()或者lastkey,下面dec同理 if(this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts).size() == 0){ this.reversedIndex.remove(currentCounts); } if(this.reversedIndex.containsKey(currentCounts + 1) == false){ this.reversedIndex.put(currentCounts + 1,new HashSet<>()); } this.index.put(key,currentCounts + 1); this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts + 1).add(key); } } /** Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. */ public void dec(String key) { if(this.index.containsKey(key)){ int currentCounts = this.index.get(key); this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts).remove(key); if(this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts).size() == 0){ this.reversedIndex.remove(currentCounts); } if(currentCounts == 1){ this.index.remove(key); } else{ if(this.reversedIndex.containsKey(currentCounts - 1) == false){ this.reversedIndex.put(currentCounts - 1,new HashSet<>()); } this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts -1).add(key); this.index.put(key,currentCounts - 1); } } } /** Returns one of the keys with maximal value. */ public String getMaxKey() { if (this.index.size() == 0 ) return ""; return this.reversedIndex.get(this.reversedIndex.lastKey()).iterator().next(); } /** Returns one of the keys with Minimal value. */ public String getMinKey() { if (this.index.size() == 0 ) return ""; return this.reversedIndex.get(this.reversedIndex.firstKey()).iterator().next(); }
http://bgmeow.xyz/2017/02/15/LeetCode-432/
X. https://www.cnblogs.com/EdwardLiu/p/6139859.html
PriorityQueue remove is O(n)
http://hellokenlee.tk/2017/03/12/leetcode-432/
Implement a data structure supporting the following operations:
- Inc(Key) - Inserts a new key
with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. Key is guaranteed to be a non-empty string. - Dec(Key) - Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. Key is guaranteed to be a non-empty string. If the key does not exist, this function does nothing.
- GetMaxKey() - Returns one of the keys with maximal value. If no element exists, return an empty string
"". - GetMinKey() - Returns one of the keys with minimal value. If no element exists, return an empty string
"".
Challenge: Perform all these in O(1) time complexity.
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/65439/an-accepted-java-solution-detailed-explanation-hashmap-double-linked-listhttp://shirleyisnotageek.blogspot.com/2016/11/first-pair-non-matching-leaves.html
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/65434/accepted-java-and-python-solution
http://yuanyuanzhangcs.blogspot.com/2017/02/all-oone-data-structure.html
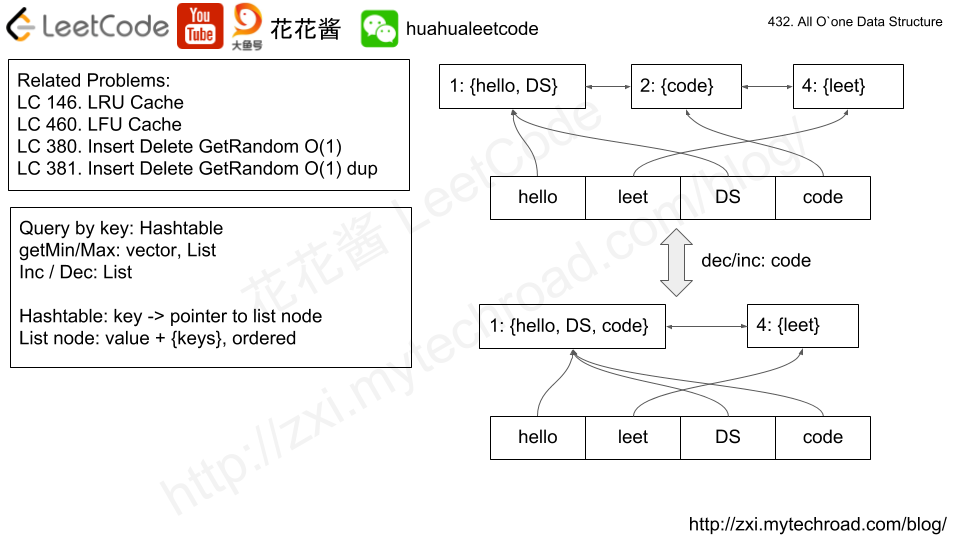
1. Similar to LRU, use double linked list to do change the position of element in O(1) time.
2. Since multiple strings might have the same value, we maintain a set of keys for each value.
3. A hash map is used to store the node (i.e. the bucket) in the double-linked list which a key
is mapped to.
is mapped to.
用bucket保存同一value的key,bucket是一个双向指针。bucket里面有keySet,有value。保存全局变量keyMap和bucketMap以便于在O(1)时间内找到bucket。
http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/6012229.html
这道题让我们实现一个全是O(1)复杂度的数据结构,包括了增加key,减少key,获取最大key,获取最小key,这几个函数。由于需要常数级的时间复杂度,我们首先第一反应就是要用哈希表来做,不仅如此,我们肯定还需要用list来保存所有的key,那么哈希表就是建立key和list中位置迭代器之间的映射,这不由得令人想到了之前那道LRU Cache,也是用了类似的方法来解,但是感觉此题还要更加复杂一些。由于每个key还要对应一个次数,所以list中不能只放key,而且相同的次数可能会对应多个key值,所以我们用unordered_set来保存次数相同的所有key值,我们建立一个Bucket的结构体来保存次数val,和保存key值的集合keys。解题思路主要参考了网友ivancjw的帖子,数据结构参考了史蒂芬大神的帖子,思路是,我们建立一个次数分层的结构,次数多的在顶层,每一层放相同次数的key值,例如下面这个例子:
"A": 4, "B": 4, "C": 2, "D": 1
那么用我们设计的结构保存出来就是:
row0: val = 4, keys = {"A", "B"}
row1: val = 2, keys = {"C"}
row2: val = 1, keys = {"D"}
row1: val = 2, keys = {"C"}
row2: val = 1, keys = {"D"}
好,我们现在来分析如何实现inc函数,我们来想,如果我们插入一个新的key,跟我们插入一个已经存在的key,情况是完全不一样的,那么我们就需要分情况来讨论:
- 如果我们插入一个新的key,那么由于该key没有出现过,所以加入后次数一定为1,那么就有两种情况了,如果list中没有val为1的这一行,那么我们需要插入该行,如果已经有了val为1的这行,我们直接将key加入集合keys中即可。
- 如果我们插入了一个已存在的key,那么由于个数增加了1个,所以该key值肯定不能在当前行继续待下去了,要往上升职啊,那么这里就有两种情况了,如果该key要升职到的那行不存在,我们需要手动添加那一行;如果那一行存在,我们之间将key加入集合keys中,记得都要将原来行中的key值删掉。
下面我们再来看dec函数如何实现,其实理解了上面的inc函数,那么dec函数也就没什么难度了:
- 如果我们要删除的key不存在,那么直接返回即可。
- 如果我们要删除的key存在,那么我们看其val值是否为1,如果为1的话,那么直接在keys中删除该key即可,然后还需要判断如果该key是集合中的唯一一个,那么该行也需要删除。如果key的次数val不为1的话,我们要考虑降级问题,跟之前的升职很类似,如果要降级的行不存在,我们手动添加上,如果存在,则直接将key值添加到keys集合中即可。
当我们搞懂了inc和dec的实现方法,那么getMaxKey()和getMinKey()简直就是福利啊,不要太简单啊,直接返回首层和尾层的key值即可
https://leetcode.com/problems/all-oone-data-structure/discuss/91416/java-ac-all-strict-o1-not-average-o1-easy-to-read
Main idea is to maintain a list of Bucket's, each Bucket contains all keys with the same count.
headandtailcan ensure bothgetMaxKey()andgetMaxKey()be done in O(1).keyCountMapmaintains the count of keys,countBucketMapprovides O(1) access to a specific Bucket with given count. Deleting and adding a Bucket in the Bucket list cost O(1), so bothinc()anddec()take strict O(1) time.
it will be fine with the INT_MIN and INT_MAX because the head and tail are only used as dummy nodes.
public class AllOne {
// maintain a doubly linked list of Buckets
private Bucket head;
private Bucket tail;
// for accessing a specific Bucket among the Bucket list in O(1) time
private Map<Integer, Bucket> countBucketMap;
// keep track of count of keys
private Map<String, Integer> keyCountMap;
// each Bucket contains all the keys with the same count
private class Bucket {
int count;
Set<String> keySet;
Bucket next;
Bucket pre;
public Bucket(int cnt) {
count = cnt;
keySet = new HashSet<>();
}
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public AllOne() {
head = new Bucket(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
tail = new Bucket(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
countBucketMap = new HashMap<>();
keyCountMap = new HashMap<>();
}
/** Inserts a new key <Key> with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. */
public void inc(String key) {
if (keyCountMap.containsKey(key)) {
changeKey(key, 1);
} else {
keyCountMap.put(key, 1);
if (head.next.count != 1)
addBucketAfter(new Bucket(1), head);
head.next.keySet.add(key);
countBucketMap.put(1, head.next);
}
}
/** Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. */
public void dec(String key) {
if (keyCountMap.containsKey(key)) {
int count = keyCountMap.get(key);
if (count == 1) {
keyCountMap.remove(key);
removeKeyFromBucket(countBucketMap.get(count), key);
} else {
changeKey(key, -1);
}
}
}
/** Returns one of the keys with maximal value. */
public String getMaxKey() {
return tail.pre == head ? "" : (String) tail.pre.keySet.iterator().next();
}
/** Returns one of the keys with Minimal value. */
public String getMinKey() {
return head.next == tail ? "" : (String) head.next.keySet.iterator().next();
}
// helper function to make change on given key according to offset
private void changeKey(String key, int offset) {
int count = keyCountMap.get(key);
keyCountMap.put(key, count + offset);
Bucket curBucket = countBucketMap.get(count);
Bucket newBucket;
if (countBucketMap.containsKey(count + offset)) {
// target Bucket already exists
newBucket = countBucketMap.get(count + offset);
} else {
// add new Bucket
newBucket = new Bucket(count + offset);
countBucketMap.put(count + offset, newBucket);
addBucketAfter(newBucket, offset == 1 ? curBucket : curBucket.pre);
}
newBucket.keySet.add(key);
removeKeyFromBucket(curBucket, key);
}
private void removeKeyFromBucket(Bucket bucket, String key) {
bucket.keySet.remove(key);
if (bucket.keySet.size() == 0) {
removeBucketFromList(bucket);
countBucketMap.remove(bucket.count);
}
}
private void removeBucketFromList(Bucket bucket) {
bucket.pre.next = bucket.next;
bucket.next.pre = bucket.pre;
bucket.next = null;
bucket.pre = null;
}
// add newBucket after preBucket
private void addBucketAfter(Bucket newBucket, Bucket preBucket) {
newBucket.pre = preBucket;
newBucket.next = preBucket.next;
preBucket.next.pre = newBucket;
preBucket.next = newBucket;
}
}
The main idea is to maintain an ordered two-dimensional doubly-linked list (let's call it matrix for convenience), of which each row is corresponding to a value and all of the keys in the same row have the same value.
Suppose we get the following key-value pairs after some increment operations. ("A": 4 means "A" is increased four times so its value is 4, and so on.)
"A": 4, "B": 4, "C": 2, "D": 1
Then one possible matrix may look like this:
row0: val = 4, strs = {"A", "B"}
row1: val = 2, strs = {"C"}
row2: val = 1, strs = {"D"}
If we can guarantee the rows are in descending order in terms of value, then GetMaxKey()/GetMinKey() will be easy to implement in O(1) time complexity. Because the first key in the first row will always has the maximal value, and the first key in the last row will always has the minimal value.
Once a key is increased, we move the key from current row to last row if last_row.val = current_row.val + 1. Otherwise, we insert a new row before current row with vallue current_row.val + 1, and move the key to to the new row. The logic of decrement operation is similar. Obviously, by doing this, the rows will keep its descending order.
For example, after Inc("D"), the matrix will become
row0: val = 4, strs = {"A", "B"}
row1: val = 2, strs = {"C", "D"}
Inc("D") again
row0: val = 4, strs = {"A", "B"}
row1: val = 3, strs = {"D"}
row2: val = 2, strs = {"C"}
Now the key problem is how to maintain the matrix in O(1) runtime when increase/decrease a key by 1.
The answer is hash map. By using a hash map to track the position of a key in the matrix, we can access a key in the matrix in O(1). And since we use linked list to store the matrix, thus insert/move operations will all be O(1).
The psudocode of Inc() is as follows(Dec() is similar).
if the key isn't in the matrix:
if the matrix is empty or the value of the last row isn't 1:
insert a new row with value 1 to the end of the matrix, and put the key in the new row;
else:
put the key in the last row of the matrix;
else:
if the key is at the first row or last_row.value != current_row.value + 1:
insert a new row before current row, with value current_row.value + 1, and move the key to the new row;
else:
move the key from current row to last row;X. TreeMap Not right answer:
https://blog.csdn.net/MebiuW/article/details/53436455
这道题关键在于如何保存数据形式:
1、使用一个Hashmap保存当前存入的key的频次frequency
2、倒序使用一个Treemap保存当前frequency为某个值时的所有key有哪些,Treemap按照key排序
因此在inc和dec时只需要正常的更新两个map就可以,在取最大最小的时候,直接用有序的treemap的第一个key和最后一个key就可以(分别对应最小的frequency和最大的frequency),然后再将数据取出来就好。
当然其实Treemap的排序开销才开始并不是O(1),但如果数据量大,其实也近似O(1)了。。数据量小又不影响~~~
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/65354/ac-java-solution-using-hashmap-and-two-heaps/3
http://blog.csdn.net/mebiuw/article/details/53436455
TreeMap O(logn) not O(1)
TreeMap<Integer,HashSet<String>> reversedIndex; HashMap<String,Integer> index; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ public AllOne() { this.reversedIndex = new TreeMap<>(); this.index = new HashMap<>(); } /** Inserts a new key <Key> with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. */ public void inc(String key) { if (this.index.containsKey(key) == false){ this.index.put(key,1); if(this.reversedIndex.containsKey(1) == false) this.reversedIndex.put(1,new HashSet<String>()); this.reversedIndex.get(1).add(key); } else{ int currentCounts = this.index.get(key); this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts).remove(key); // 这里必须要做remove,因为treemap要直接firstkey()或者lastkey,下面dec同理 if(this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts).size() == 0){ this.reversedIndex.remove(currentCounts); } if(this.reversedIndex.containsKey(currentCounts + 1) == false){ this.reversedIndex.put(currentCounts + 1,new HashSet<>()); } this.index.put(key,currentCounts + 1); this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts + 1).add(key); } } /** Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. */ public void dec(String key) { if(this.index.containsKey(key)){ int currentCounts = this.index.get(key); this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts).remove(key); if(this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts).size() == 0){ this.reversedIndex.remove(currentCounts); } if(currentCounts == 1){ this.index.remove(key); } else{ if(this.reversedIndex.containsKey(currentCounts - 1) == false){ this.reversedIndex.put(currentCounts - 1,new HashSet<>()); } this.reversedIndex.get(currentCounts -1).add(key); this.index.put(key,currentCounts - 1); } } } /** Returns one of the keys with maximal value. */ public String getMaxKey() { if (this.index.size() == 0 ) return ""; return this.reversedIndex.get(this.reversedIndex.lastKey()).iterator().next(); } /** Returns one of the keys with Minimal value. */ public String getMinKey() { if (this.index.size() == 0 ) return ""; return this.reversedIndex.get(this.reversedIndex.firstKey()).iterator().next(); }
http://bgmeow.xyz/2017/02/15/LeetCode-432/
X. https://www.cnblogs.com/EdwardLiu/p/6139859.html
PriorityQueue remove is O(n)
Solution 2: 如果不要求O(1)time, 这个用两个heap方法很常规
1 public class AllOne { 2 3 class Node{ 4 String key; 5 int val; 6 public Node(String key, int val) { 7 this.key = key; 8 this.val = val; 9 } 10 } 11 /** Initialize your data structure here. */ 12 HashMap<String, Node> map; 13 PriorityQueue<Node> minQ; 14 PriorityQueue<Node> maxQ; 15 public AllOne() { 16 map = new HashMap<String, Node>(); 17 minQ = new PriorityQueue<Node>(new Comparator<Node>(){ 18 public int compare(Node a, Node b) { 19 return a.val - b.val; 20 } 21 }); 22 maxQ = new PriorityQueue<Node>(new Comparator<Node>(){ 23 public int compare(Node a, Node b) { 24 return b.val - a.val; 25 } 26 }); 27 } 28 29 /** Inserts a new key <Key> with value 1. Or increments an existing key by 1. */ 30 public void inc(String key) { 31 if (!map.containsKey(key)) { 32 map.put(key, new Node(key, 1)); 33 Node node = map.get(key); 34 minQ.add(node); 35 maxQ.add(node); 36 } else { 37 Node node = map.get(key); 38 minQ.remove(node); 39 maxQ.remove(node); 40 node.val++; 41 map.put(key, node); 42 minQ.add(node); 43 maxQ.add(node); 44 } 45 } 46 47 /** Decrements an existing key by 1. If Key's value is 1, remove it from the data structure. */ 48 public void dec(String key) { 49 if (map.containsKey(key)) { 50 Node node = map.get(key); 51 if (node.val == 1) { 52 map.remove(key); 53 minQ.remove(node); 54 maxQ.remove(node); 55 } else { 56 minQ.remove(node); 57 maxQ.remove(node); 58 node.val--; 59 map.put(key, node); 60 minQ.add(node); 61 maxQ.add(node); 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 66 /** Returns one of the keys with maximal value. */ 67 public String getMaxKey() { 68 return maxQ.isEmpty() ? "" : maxQ.peek().key; 69 } 70 71 /** Returns one of the keys with Minimal value. */ 72 public String getMinKey() { 73 return minQ.isEmpty() ? "" : minQ.peek().key; 74 } 75 }
http://hellokenlee.tk/2017/03/12/leetcode-432/