https://ophaxor.com/leetcode-1766-tree-of-coprimes
There is a tree (i.e., a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 and exactly n - 1 edges. Each node has a value associated with it, and the root of the tree is node 0.
To represent this tree, you are given an integer array nums and a 2D array edges. Each nums[i] represents the ith node’s value, and each edges[j] = [uj, vj] represents an edge between nodes uj and vj in the tree.
Two values x and y are coprime if gcd(x, y) == 1 where gcd(x, y) is the greatest common divisor of x and y.
An ancestor of a node i is any other node on the shortest path from node i to the root. A node is not considered an ancestor of itself.
Return an array ans of size n, where ans[i] is the closest ancestor to node i such that nums[i] and nums[ans[i]] are coprime, or -1 if there is no such ancestor.
Example 1:
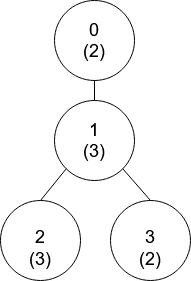
Input: nums = [2,3,3,2], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3]] Output: [-1,0,0,1] Explanation: In the above figure, each node's value is in parentheses. - Node 0 has no coprime ancestors. - Node 1 has only one ancestor, node 0. Their values are coprime (gcd(2,3) == 1). - Node 2 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. Node 1's value is not coprime (gcd(3,3) == 3), but node 0's value is (gcd(2,3) == 1), so node 0 is the closest valid ancestor. - Node 3 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. It is coprime with node 1 (gcd(3,2) == 1), so node 1 is its closest valid ancestor.
Example 2:
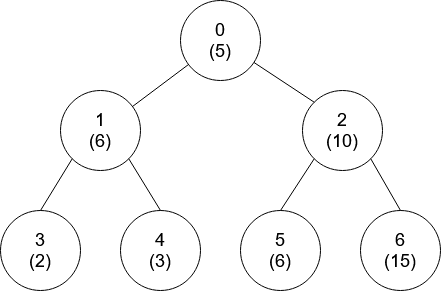
Input: nums = [5,6,10,2,3,6,15], edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]] Output: [-1,0,-1,0,0,0,-1]
Constraints:
nums.length == n1 <= nums[i] <= 501 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[j].length == 20 <= uj, vj < nuj != vj
题意: 对于树上的每个节点,找出与它的值互质的最近的祖先节点。
题解: 由于节点上的值在1-50之间,所以算互质很好算,事先算法。然后就是深度优先遍历树的时候维护路径上的节点的位置,利用1-50这个小范围,快速找到与当前节点值互质的值出现在哪些位置上
https://leetcode.com/problems/tree-of-coprimes/discuss/1074581/Java-or-DFS-or-O(n)
public int gcd(int n1, int n2) {
if (n2 == 0) {
return n1;
}
return gcd(n2, n1 % n2);
}
public void dfs(int[] nums, LinkedList<Integer>[] tree, int depth, int node, boolean[] visited, int[] ans, Map<Integer,int[]> map, boolean[][] poss) {
if(visited[node]) return;
visited[node] = true;
int ancestor = -1;
int d = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 1; i < 51; i++) {
if(poss[nums[node]][i] && map.containsKey(i)) {
if(depth - map.get(i)[0] <= d) {
d = depth - map.get(i)[0];
ancestor = map.get(i)[1];
}
}
}
ans[node] = ancestor;
int[] exist = (map.containsKey(nums[node])) ? map.get(nums[node]) : new int[]{-1,-1};
map.put(nums[node],new int[]{depth,node});
for(int child : tree[node]) {
if(visited[child]) continue;
dfs(nums, tree, depth+1, child, visited, ans, map, poss);
}
if(exist[0] != -1) map.put(nums[node], exist);
else map.remove(nums[node]);
return;
}
public int[] getCoprimes(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
boolean[][] poss = new boolean[51][51];
for(int i = 1; i < 51; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < 51; j++) {
if(gcd(i,j) == 1) {
poss[i][j] = true;
poss[j][i] = true;
}
}
}
int n = nums.length;
LinkedList<Integer>[] tree = new LinkedList[n];
for(int i =0 ; i < tree.length; i++) tree[i] = new LinkedList<>();
for(int edge[] : edges) {
tree[edge[0]].add(edge[1]);
tree[edge[1]].add(edge[0]);
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, -1);
ans[0] = -1;
Map<Integer,int[]> map = new HashMap<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
dfs(nums, tree, 0, 0, visited, ans, map, poss);
return ans;
} https://leetcode.com/problems/tree-of-coprimes/discuss/1074737/Python-3-DFS-Clean-and-Concise
- Time:
O(50 * N) - Space:
O(N)
- Please notice in the constraints that all node values is in range
1..50. - We create an array of 51 elements
path[51]wherepath[x]contains list of nodes fromrootto currentnodewhich their node's value are equal tox. - While traversing nodes using DFS, for current
nodewe can check all pathspath[x](up to 50) wherexand currentnodeare co-prime then we try to pick the node which is close to currentnodeas our ancestor. - A node is close to current
nodeif its depth is largest.
def getCoprimes(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
ans = [-1] * len(nums)
path = [[] for _ in range(51)]
graph = defaultdict(list)
seen = set()
for u, v in edges:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
def dfs(node, depth):
if node in seen: return
seen.add(node)
largestDepth = -1
for x in range(1, 51):
if gcd(nums[node], x) == 1: # co-prime
if len(path[x]) > 0:
topNode, topDepth = path[x][-1]
if largestDepth < topDepth: # Pick node which has largestDepth and co-prime with current node as our ancestor node
largestDepth = topDepth
ans[node] = topNode
path[nums[node]].append((node, depth))
for nei in graph[node]:
dfs(nei, depth + 1)
path[nums[node]].pop()
dfs(0, 0)
return ans
https://easyforces.com/solutions/1766/
Like many other problems, let's figure out the input, limitation and output from the description.
- The input of this problem is a tree where each node has a value. It is given by an array nums representing values of each node. And edges representing the edge between the edge[i][0] and edge[i][1].
- The limitation is given by the definition Coprime, where the greatest common divisor(GCD) of 2 node values is 1.
- The required output is the closest coprime anacestor for each node. The result should be returned by an array where result[i] is the index of node i's closest coprime anacestor.
Data Structure
Even if the input is a tree, since we are only given edges, we can use adjacent list to represent the tree, where adj[i] is a list of nodes who is node i's neighbors.
Basic Idea
The basic idea of this problem is to traverse the tree. And during the traversal, for each node, calculate the closest coprime anacestor. Now let's consider the time complexity of this basic solution.
- To traverse a tree, we can use Depth-first Search (DFS). The basic time complexity of DFS is O(nodes.length + edges.length).
- For each node, we need to go through all it's ancestors from bottom to top to check if they are coprime. The worst case would be there are no coprime in it's ancestors, and the time complexity of this step would be O(tree.depth). Since the tree is not a balanced tree, for it's depth, we need to consider it's the same as node number, which is O(nodes.length).
- To check if 2 numbers are coprime, we would need to check all number which is less than or equal to the minimum number between the 2 numbers, to see if it's a common divisor of them. Time complexity of this step is O(num).
The overall time complexity would be:
O((nodes.length + edges.length) * nodes.length * max(nums))
The input range is given in the problem description.
- nums.length == n
- 1 <= nums[i] <= 50
- 1 <= n <= 100,000
- edges.length == n - 1
- edges[j].length == 2
- 0 <= uj, vj < n
- uj != vj
And the number of operations is:
O( (n + n) * n * len(nums) ) = O( n ** 2 * len(nums) ) = O( (10 ** 10) * 50 ) = O( 10 ** 11 )
This is high above standard which is 1,000,000.
Improvement
The basic solution spend too much time because there are too many operations. In this case, we can consider to pre-calculate something. So the time complexity would be O(pre) + O(solution).
- One key point of this problem is that the range of each number is between 1 and 50. So
we could calculate isCoprime for all integer pairs in time O(max(nums) ** 2) = O(2,500).
- Then, for each node, instead of calculate through all it's ancestors, we maintain a array storing
the closest anacestor for each number. And update this array for each node. This would only take O(max(nums)).
So now, the time complexity is:
O(max(nums) ** 2) + O(n + n) * O(max(nums)) = O(max(nums) ** 2) + O( n * max(nums) ) = O( max(nums) * (max(nums) + n) ) = O( 50 * (50 + 100,000) ) ~= O( 5 * (10 ** 6) ) = O( 5,000,000 )
This would be a just fine time time complexity (around 1,000,000).
About Code
- The method isCoprime is for calculating whether 2 numbers are coprime.
- The method _dfs is the main part of the solution, which traverses the tree and calculate the closest coprime ancestor.
- Variable candidates stores the cloeset coprime ancestor for each possible number, it's maximum length is 50.
X. Videos